 Germany (German: Deutschland), officially the Federal Republic of Germany (Bundesrepublik Deutschland) is the largest country in Central Europe and the most populous EU state.
Germany (German: Deutschland), officially the Federal Republic of Germany (Bundesrepublik Deutschland) is the largest country in Central Europe and the most populous EU state.
Germany has historically been and still is politically, economically and culturally influential and the largest EU member state by population and economic output. Known around the world for "German engineering" as well as world leading banking and insurance companies, it is equally admired by visitors for its old-world charm and Gemütlichkeit (cosiness). Discard any perceptions of Germany as simply homogeneous, and a country of surprising regional diversity awaits.
Germany is a federal republic consisting of 16 politically powerful states (called Bundesländer - shortened to Länder) that sometimes correspond to historic regions predating a unified German state, while they sometimes randomly throw vastly different peoples into the same state while separating them from their more similar kin across state lines. Three of these Bundesländer are actually city-states: Berlin, Bremen and Hamburg. The states can be roughly grouped by geography as listed below, although there are other groupings. For a long time, the cultural division between north and south was the most notable but, because of the legacy of the Cold War, nowadays the division between east and west is more noticeable.

 Germany has numerous cities of interest to visitors; here are just nine of the most famous travel destinations. They are mostly the larger cities of Germany. Some, such as Berlin and Hamburg, stand like urban islands in more rural landscapes, others, like Düsseldorf and Frankfurt, are part of metropolitan areas together with other cities.
Germany has numerous cities of interest to visitors; here are just nine of the most famous travel destinations. They are mostly the larger cities of Germany. Some, such as Berlin and Hamburg, stand like urban islands in more rural landscapes, others, like Düsseldorf and Frankfurt, are part of metropolitan areas together with other cities.
- Berlin. – The reunified and reinvigorated capital of Germany; known for its being divided during the Cold War by the Berlin Wall. Today a metropolis of diversity with some of the world's best clubs, shops, galleries and restaurants. Due to its long status as a divided city, Berlin also boasts more operas and museums per capita than most other places in the world. The suburb of Potsdam with its Royal-Prussian palaces and gardens shouldn't be missed when in Berlin.
- Bremen. – its old market, the Schnoor, the Böttcherstrasse, the Viertel and the maritime flair of Bremen and its harbor Bremerhaven (which together form the Bundesland of Bremen, the smallest Land in both size and population) are a great urban experience.
- Cologne. (Köln) – founded by the Romans 2000 years ago and known for its huge cathedral (second largest in the world), Romanesque churches, archaeological sites and the lively old town quarter. The Cologne Carnival is a major draw around February.
- Dresden. – Once called Elbflorenz ('Florence on the Elbe'), the Frauenkirche (the finest baroque Cathedral outside Italy, destroyed during the war and rebuilt from 1994 to 2005) and its rebuilt historic Altstadt that was also destroyed during the war. The Zwinger and Residenzschloss museums are unmatched in the world.
- Düsseldorf. – Germany's capital of shopping that also has a wide variety of fascinating new architecture. The "Altstadt" quarter and the Rhine embankments have a vibrant nightlife.
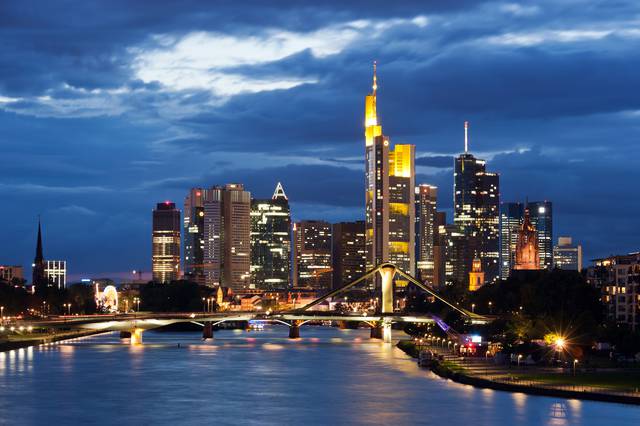
- Frankfurt. – magnificent skyline, financial and transportation hub of Europe, headquarters of the European Central Bank (ECB) and an important trade fair. Small reconstructed centre with half-timbered houses, important museums and galleries around the Museumsufer like the Schirn Art Hall, the Städel and the Senckenberg Natural Museum.
- Hamburg. – Germany's second-largest city, with a metropolitan character second only to that of Berlin, famous for its harbour as well as its liberal culture. Don't miss the bustling nightlife around St. Pauli with the Reeperbahn and its night clubs and entertainment venues. Historically one of the cities of the Hanseatic League and a leading trade center after that, it remains one of three German "city states" i.e. a city that is its own Bundesland.
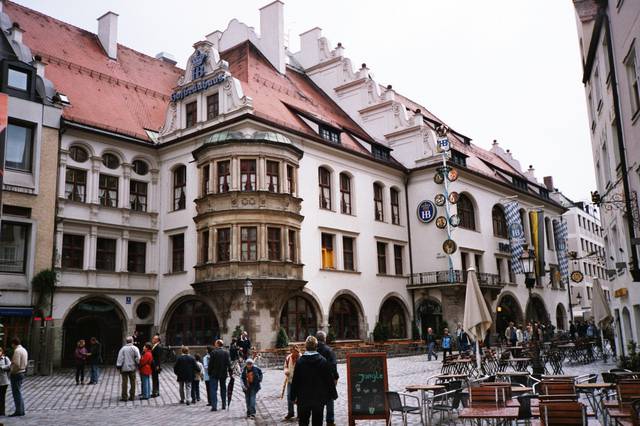
- Munich. (München) – Germany's third-largest city and booming capital of Bavaria is known for the Oktoberfest, the Hofbräuhaus, its manifold cultural offerings including operas, theaters and museums, a vibrant nightlife, many music festivals, its beer gardens and river surfing, and is the gateway to the Alps.
- Nuremberg. (Nürnberg) – a former Reichsstadt with a medieval touch, its old town was partly reconstructed after severe bombing in World War II, including the Gothic Kaiserburg and the major churches, and you can also visit the Nazi party rally grounds, the Documentation Center and Courtroom 600 (the venue of the Nuremberg war crime trials).
Berlin. – The reunified and reinvigorated capital of Germany; known for its being divided during the Cold War by the Berlin Wall. Today a metropolis of diversity with some of the world's best clubs, shops, galleries and restaurants. Due to its long status as a divided city, Berlin also boasts more operas and museums per capita than most other places in the world. The suburb of [[Potsdam]] with its Royal-Prussian palaces and gardens shouldn't be missed when in Berlin.
Bremen. – its old market, the Schnoor, the Böttcherstrasse, the Viertel and the maritime flair of Bremen and its harbor Bremerhaven (which together form the Bundesland of Bremen, the smallest Land in both size and population) are a great urban experience.
Cologne. (Köln) – founded by the Romans 2000 years ago and known for its huge cathedral (second largest in the world), Romanesque churches, archaeological sites and the lively old town quarter. The Cologne Carnival is a major draw around February.
Dresden. – Once called Elbflorenz ('Florence on the Elbe'), the Frauenkirche (the finest baroque Cathedral outside Italy, destroyed during the war and rebuilt from 1994 to 2005) and its rebuilt historic Altstadt that was also destroyed during the war. The Zwinger and Residenzschloss museums are unmatched in the world.
Düsseldorf. – Germany's capital of shopping that also has a wide variety of fascinating new architecture. The "Altstadt" quarter and the Rhine embankments have a vibrant nightlife.
Frankfurt. – magnificent skyline, financial and transportation hub of Europe, headquarters of the European Central Bank (ECB) and an important trade fair. Small reconstructed centre with half-timbered houses, important museums and galleries around the Museumsufer like the Schirn Art Hall, the Städel and the Senckenberg Natural Museum.
Hamburg. – Germany's second-largest city, with a metropolitan character second only to that of Berlin, famous for its harbour as well as its liberal culture. Don't miss the bustling nightlife around St. Pauli with the Reeperbahn and its night clubs and entertainment venues. Historically one of the cities of the Hanseatic League and a leading trade center after that, it remains one of three German "city states" i.e. a city that is its own Bundesland.
Munich. (München) – Germany's third-largest city and booming capital of Bavaria is known for the Oktoberfest, the Hofbräuhaus, its manifold cultural offerings including operas, theaters and museums, a vibrant nightlife, many music festivals, its beer gardens and river surfing, and is the gateway to the Alps.
Nuremberg. (Nürnberg) – a former Reichsstadt with a medieval touch, its old town was partly reconstructed after severe bombing in World War II, including the Gothic Kaiserburg and the major churches, and you can also visit the Nazi party rally grounds, the Documentation Center and Courtroom 600 (the venue of the Nuremberg war crime trials).
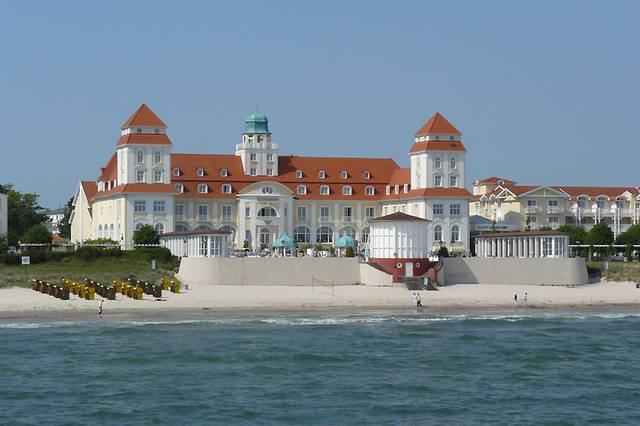

- Baltic Sea Coast. (Ostseeküste) – once the playground for crowned heads, this region is coming into its own again after the Cold War shut much of it off from the wider world. Site of the famous Strandkorb picture of the 2007 G8 summit.
- Bavarian Alps. (Bayerische Alpen) – Germany perhaps at its most clichéd, but also its most beautiful; nice skiing in winter, hiking in summer and Schloss Neuschwanstein are just the most obvious attractions
- Black Forest. (Schwarzwald) – You are likely to think "cuckoo clock" or cherry pie, and you'd be forgiven, but there is much more to this region than that
- East Frisian Islands. (Ostfriesische Inseln) – among Germany's most popular summer holiday spots, those largely car free islands in the Wadden Sea still see less international visitors than they deserve
- Franconian Switzerland. (Fränkische Schweiz) – a favorite with early 19th century poets who gave a name that stuck, this karst region is world renowned for its climbing and has some beautiful caves
- Harz. – long forgotten due to German partition running right through it, the Harz is today attracting tourists with superb hiking and the mystic romanticism of the Brocken mountain that is reputed to attract witches (as mentioned in Goethe's Faust)
- Lake Constance. (Bodensee) – Germany's largest lake, the "Swabian Ocean" (as it is jokingly) offers alpine panorama and water activities at the same time
- Middle Rhine Valley. (Mittelrheintal) – part of the Rhine River is a UNESCO Heritage Site between Bingen/Rüdesheim and Koblenz; the valley is famous for its wines
- North Frisian Islands. (Nordfriesische Inseln) - calm islands with resorts at the North Sea coast, especially Sylt is known for its posh celebrity guests and the pristine landscape
Baltic Sea Coast. (Ostseeküste) – once the playground for crowned heads, this region is coming into its own again after the Cold War shut much of it off from the wider world. Site of the famous Strandkorb picture of the 2007 G8 summit.
Bavarian Alps. (Bayerische Alpen) – Germany perhaps at its most clichéd, but also its most beautiful; nice skiing in winter, hiking in summer and Schloss Neuschwanstein are just the most obvious attractions
Black Forest. (Schwarzwald) – You are likely to think "cuckoo clock" or cherry pie, and you'd be forgiven, but there is much more to this region than that
East Frisian Islands. (Ostfriesische Inseln) – among Germany's most popular summer holiday spots, those largely car free islands in the Wadden Sea still see less international visitors than they deserve
Franconian Switzerland. (Fränkische Schweiz) – a favorite with early 19th century poets who gave a name that stuck, this karst region is world renowned for its climbing and has some beautiful [[caves]]
Harz. – long forgotten due to German partition running right through it, the Harz is today attracting tourists with superb hiking and the mystic romanticism of the Brocken mountain that is reputed to attract witches (as mentioned in Goethe's Faust)
Lake Constance. (Bodensee) – Germany's largest lake, the "Swabian Ocean" (as it is jokingly) offers alpine panorama and water activities at the same time
Middle Rhine Valley. (Mittelrheintal) – part of the Rhine River is a UNESCO Heritage Site between Bingen/Rüdesheim and Koblenz; the valley is famous for its wines
North Frisian Islands. (Nordfriesische Inseln) - calm islands with resorts at the North Sea coast, especially Sylt is known for its posh celebrity guests and the pristine landscape
In the first century AD, after a series of military campaigns, the Romans were able to conquer what is now most of western and southern Germany from the Germanic and Celtic tribes living there. The limits of the Roman empire were marked by the "Limes". The section separating the empire from the Germanic tribes (Limes Germanicus) was 568 km in length stretching from the mouth of the Rhine to the Danube near Regensburg. Sections of the raised bank can still be seen and walked along. However, in Roman times the Limes were anything but a rigid border and trade and occasional Roman military expeditions influenced most of what is now Germany up to at least the fourth century AD.
Several cities that are still important in Germany today were founded by the Romans as military bases and later, settlements, including Mainz, Wiesbaden, Cologne and Bonn. Baden-Baden's springs were also much appreciated by the Romans, who built baths whose remains can be visited under the aptly-named Römerplatz (Roman Square). The most impressive Roman remains in Germany can be found in Trier, the oldest German city. These include the Porta Nigra, the largest Roman city gate north of the Alps, and the Trier Amphitheatre.
Charlemagne, King of the Franks, was crowned first Emperor of the Holy Roman Empire on Christmas Day 800 A.D. by Pope Leo III. Charlemagne is often associated with France, but his realm was vast; his capital was in Aix la Chapelle, known today in German as Aachen. Remains of Charlemagne's winter imperial palace (the Kaiserpfalz) can be seen in the town of Ingelheim. The roots of modern German history and culture date back to the post-Carolingian Holy Roman Empire.
Starting in the early Middle Ages, Germany started to split into hundreds of small states, with strong regional differences that endure to this day, for example in Bavaria. During this period the power of local princes and bishops increased, their legacy being the many spectacular castles and palaces like the Castle Wartburg in Eisenach, Thuringia. From the 1200s, trade with the Baltic area gave rise to the Hanseatic League and rich city states such as Lübeck and Hamburg. Other cities also came to prominence from inland trade routes, such as Leipzig, Nuremberg and Cologne.
As German society gradually changed from having a feudal structure to a mercantilist system, guilds or Zünfte of craftsman were established and became a major factor in German economics and society. Some Medieval guild halls are still standing and can be visited today. This period also saw the rise of banking families such as the Fugger, whose debtors included popes and emperors, and influenced the growth of cities such as Augsburg.
In the Middle Ages and early modern times the Holy Roman Empire (most of which is today Germany, Austria, the Czech Republic and parts of surrounding countries) consisted of some 2,000 semi-independent territories that were all in more or less technical subordination to the emperor. The Holy Roman Empire was - as Voltaire famously quipped - neither Roman nor holy nor an empire. While some petty dukedoms were not much more than a couple of hamlets, important cities gained the status of Reichsstadt (or Reichsstädte in plural) that made them basically city-states subject only to the emperor himself. Their former wealth can still be seen in places like Rothenburg ob der Tauber and Nördlingen. While there were some earnest efforts at modernisation from the 15th to early 17th century, ultimately the Holy Roman Empire lost all but the most nominal central political power. And in the waning years, it wasn't even able to keep the peace between its two most powerful constituents at the time, Austria and Prussia, whose rivalry would dominate the fate of German-speaking areas for most of the 19th century.
A period of religious reform and scientific discovery was marked by the 1517 publication of Martin Luther's 95 Theses in Wittenberg, which started the Protestant Reformation. Luther would go on to translate the Bible into a Central German vernacular at the Wartburg, doing much to standardize German and ultimately exclude northern dialects as "Low German" or "Dutch". The Holy Empire became split between Catholics and several branches of Protestants, while regional powers emerged from the more unified territories of Catholic Bavaria and Protestant Saxony and Brandenburg (later known as Prussia). The Protestant-Catholic conflict reached a climax in the Thirty Years War, which devastated many German territories. It took 100 years until Germany's population had grown back to prewar levels. The rulers of Saxony (but not its population) converted to Catholicism during the rule of Augustus the Strong, who did so as a precondition for becoming King of Poland, thus losing the preeminent position among German Protestants to Prussia.
The rulers of the more affluent duchies and kingdoms of the German Empire supported the development of arts and sciences, like the works of Johann Sebastian Bach, employed by the Elector of Saxony, or the works of Goethe and Schiller who both had high paying sinecures in Weimar during their most productive years as writers. Richard Wagner (who was born in Saxony) found a willing patron in Ludwig II of Bavaria, who also had many palaces built that are now beloved by tourists but bankrupted his personal finances. Notable scientists included Daniel Fahrenheit, Alexander von Humboldt, Carl Wilhelm "hard luck" Scheele and, in mathematics, Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz made major advancements in both Leipzig and Hannover.
During the baroque period in arts and architecture, many of the German rulers created stately royal residences and rebuilt their capital cities to reflect their might and taste. Splendid creations of that period include Dresden and Potsdam.
The Napoleonic Wars ended the last semblance of a German state when Roman-German Emperor Franz II decided to step down in 1806. The various German states were later bound together by a confederation that was essentially a military alliance with fewer "federal" powers than today's EU. This confederation was overshadowed by the conflict between a liberal bourgeoisie and a reactionary aristocracy on the one hand and between Prussia and Austria on the other. In 1848 one of those tensions erupted, when the liberal nationalist opposition and some elements to the left of it called for a more centralized German state, assembling a parliament and constituent assembly in the Paulskirche in Frankfurt. Ultimately the revolution failed because the revolutionaries spent a lot of time arguing whether Austria should be a part of the new Germany ("großdeutsch") or not ("kleindeutsch"). Ultimately, the title of German Emperor was offered to Prussian King Friedrich Wilhelm IV, but he rejected the offer as it was "tainted" by being offered by the bourgeoisie, not his "equals" in rank. More radical elements fought on until 1849 and some revolutionaries lost their lives, but ultimately, the more moderate elements made their peace with the authorities and would later support the Prussian-dominated Empire, while the more radicalized elements increasingly gravitated towards socialism and radical opposition to all things monarchical. Not too small a minority also chose exile, mostly in the United States where "forty-eighters" like Franz Siegel and Carl Schurz were among the most enthusiastic supporters of the North in the American Civil War and among the first to push for emancipation.
In 1866-1871 (after decisive wars with Austria and France), Prussia led by Bismarck united Germany as a nation state called the German Empire (Deutsches Reich, or Kaiserreich). It was a federally organised state that kept the single states with their kings, dukes and princes. Some states, like Bavaria or Württemberg, even kept their own armies, railways and postal services. The states and their residences were still important cultural centres. The Empire combined traditional institutions such as the monarchy with elements of a modern democracy such as a democratically elected parliament (Reichstag) and political parties. There was universal adult male suffrage at the Reich level, but individual states could tie suffrage - or the weight of votes - to property requirements, which Prussia did for all state elections. Furthermore, gerrymandering and legal prosecutions hampered the activities of political parties which were in conflict with Bismarck and/or the Kaiser. First the wrath of the regime fell on political Catholicism with explicit laws banning political sermons against the government, but later social democrats and socialists were singled out. Bismarck followed a shrewd "carrot and stick" with regards to the working class. On the one hand worker's clubs suspected of left wing leanings - even if they were outwardly "just" social clubs dedicated to athletics, singing or soccer - were outlawed or harassed by police while at the same time Bismarck forced through the most advanced and for its time generous social security legislation. State guaranteed pensions, health insurance and payments in case of illness, injury or death all date from this time and while their primary purpose was to nip insurrection in the bud, they greatly improved the situation of the growing urban proletariat. Nonetheless, the social democratic party could increase its share of the vote and ultimately Wilhelm II fired Bismarck and ratcheted down persecution. Consequently, the social democrats changed from being a radical and revolutionary party to increasingly being a "loyal opposition", ultimately voting in favor of loans to finance World War I in 1914 to prove their patriotism. Wilhelm's jubilant "Ich kenne keine Parteien mehr, ich kenne nur noch Deutsche" (I know no parties anymore, I only know Germans) upon hearing that news is still famous in Germany.
As trade barriers gradually fell, Germany found itself a hub of the later period of Industrial Revolution and established itself as a major industrial power. During this period, major companies were founded, including some that survive to this day, and technological innovation took place in various fields, highlighted by the creation of the automobile by Karl Benz and Gottlieb Daimler in Baden-Württemberg. From the founding of the 'Bismarck Empire' to the first World War German manufacturing underwent a development from cheap low quality mass goods (for which the British developed the "warning sign" Made in Germany) to some of the best goods in its respective fields, a reputation many industrial products of Germany enjoy to this day. Germany also began to climb to the top spot in the natural sciences and medicine, with the Nobel Prize until World War II going to Germans almost as frequently as it goes to Americans today. Names like Paul Ehrlich (medicine), Max Planck (quantum physics), Robert Koch (germ theory) or Albert Einstein (who however lived in Switzerland by the time of his annus mirabilis 1905) are still known the world over and several research institutes of good reputation are named after them.
Millions of Germans emigrated overseas, especially to the United States, where they became the dominant ethnic group, especially in the Old West. While the German-American identity faded away during the World Wars, it remains visible in American cuisine with dishes such as the hamburger and Wiener sausage (also known as Frankfurter). Canada had a city named Berlin in an area of heavy German immigration; it was renamed Kitchener, after a British general, in 1916.
At the end of the First World War (1914-18), Emperor (Kaiser) Wilhelm II was forced to abdicate. A revolutionary committee prepared elections for a national assembly in Weimar which gave the Reich a new, republican constitution (1919). The transitional period is called the 'November revolution', and the republic was later usually called 'Weimar republic'. However, Germany remained the "German Reich" until 1945, the first article of the Weimar constitution bringing the debate over whether to call the new constitutional order "German Reich" or "German Republic" onto the compromise formula "The German Reich is a Republic". During the revolution, it briefly appeared as if Germany was to become a socialist/communist state like Russia had two years prior, but the social democrats ultimately made common cause with conservatives and reactionaries of the Kaiserreich era to squash anything to their left, murdering prominent socialists Rosa Luxemburg and Karl Liebknecht in the process. This perceived betrayal embittered many communists and unlike in France or Spain, forces to the left of the social democrats never made common cause with democratic parties to stop the rise of fascism. Instead, KPD (the communist party) and NSDAP (the Nazi party) often voted in concert on motions of no confidence and populist but unrealistic bills.
The young republic was plagued with massive economic problems stemming from the war (such as the 1923 hyperinflation), in particular due to the reparations that Germany had to pay to the Allies as a result of the Treaty of Versailles, as well as disgrace for a humiliating defeat in the First World War. Another problem was that many elites (judges, civil servants and even politicians) were openly monarchist and at best took a "wait and see" approach towards the new system, which led to a justice system that was famously lenient on right wing political violence and draconian when it came to communist insurrection. As the leftist writer Kurt Tucholsky put it: "The Republic was blind in her right eye". To give just one example, the year 1923 saw a right wing coup attempt led by Adolf Hitler and World War I general Erich Ludendorff and a communist insurrection in Hamburg. While Hitler was sentenced to a short prison term, Ludendorff was acquitted. The communist insurrectionists had no such luck - harsh prison sentences or even death sentences were handed down. Individual political assassinations were no different and several famous figures in government and economy - many of them centrist or even center-right and a disproportionate number of them of Jewish ancestry - were murdered by right wing Freikorps and Organisation Consul with virtual impunity. Famous victims include minister of finance Matthias Erzberger (Center Party, politically Catholic), industrialist and foreign minister Walter Rathenau (German Democratic Party, liberal), who had been instrumental in organizing the war industry in World War I and several politicians of the moderate to far left.
Inflation and political turmoil led to the growth of radical parties, on the left most notably the KPD (the communist party) and on the right the NSDAP (the Nazi party). While the coup attempt of 1923 had seemingly discredited the Nazis - at least outside of Bavaria - and the KPD lost support during the economic good times between the end of the hyperinflation and the Great Depression, the 1930 elections saw the return of both radical parties in full force and a virtual collapse of the political center-right (The Social Democrats, while losing some votes to the communists managed to hold relatively steady) as well as pickup of votes from former non-voters led to increasing gains for NSDAP and KPD until there was no possibility to form a majority in the Reichstag without the votes of Communists or Nazis. 1930 also marks the last time the Weimar Republic had a government that could rely on a positive majority in the Reichstag before the rise of Hitler. All cabinets between then and 1933 relied on the extensive "emergency" powers of the Reichspräsident (who could appoint or fire chancellors on his own say-so without consulting the Reichstag) and the parliament increasingly became a place for the enemies of democracy to stage their theatrics rather than the center of political debate and power. The Reichstag never lost its right to a vote of no confidence and indeed, Hindenburg had to dissolve the Reichstag and declare new elections (which again, he could do on his own say-so) to prevent a motion of no confidence against the chancellor from passing.
In the relatively good economic climate of the mid-1920s many banks and business had taken out relatively cheap short term loans to finance long term investments which exposed the economy greatly in the Wall Street crash of 1929. Although the 1920s had seen the recovery of the German economy due to American investment, the Great Depression led to the withdrawal of this investment. As a result, Germany's economy was crippled and the government's deflationary policy as well as a global tendency towards protectionism only worsened the situation. This allowed strong anti-democratic forces (such as the KPD and NSDAP) to take advantage of the inherent organisational problems of the Weimar Constitution. And from the 1930 election onwards there was never again a pro-democratic majority of any kind in the Reichstag.
The National Socialist party (frequently referred to simply as 'Nazis') seized control by winning a plurality of disillusioned German voters seeking change. In early 1933, then 84-year-old Reich president Paul von Hindenburg - a high ranking general during WWI - installed Nazi chief Adolf Hitler as Chancellor. Hindenburg also used his presidential powers to support Hitler's emerging dictatorship. Historians still argue about Hindenburg's motives. He may have underestimated Hitler or may have sympathized with Hitler's authoritarian style at least partially. When Hindenburg died in 1934, Hitler declared himself simultaneously President, Führer and Chancellor, a clear breach of both the letter and the spirit of the constitution, and from there on governed unchecked and on his own.
The year 1933 witnessed the rise to power of the nationalistic and racist National Socialist German Workers' (Nazi) Party and its Führer, Adolf Hitler. Under the Nazi dictatorship, democratic institutions were dismantled and the police state was enhanced. Jews, Slavs, Gypsies, handicapped people, homosexuals, socialists, communists, unionists and other groups not fitting into the Nazis' vision of a Greater Germany faced persecution, and were ultimately enslaved or murdered in death camps. Europe's Jews and Gypsies were marked for total extermination. The site of the first Nazi concentration camp in Dachau as well as several others are now memorials.
Hitler's militaristic ambitions to create a new (third) German Empire in Central and Eastern Europe led to the Second World War, which Nazi Germany lost and which left a solemn mark on the continent and Germany in particular. Due to the two previous "German empires" the Nazi-era is often referred to in German as "drittes Reich" (third empire) among other designations.
Hitler's foreign policy became increasingly militaristic and aggressive. However, the leaders of France and in particular, Britain were wary of another European war and as Germany had gained a lot of concessions through diplomacy between 1919 and 1933, some did not even see the problem in letting Hitler getting away with defying or breaking the Treaty of Versailles. Historians still debate whether Hitler had a grand master plan or whether he just gambled each time to see how far he could go, being encouraged by never being stopped, but the end result remains the same. Germany left the League of Nations (1933) annexed the Saar Area after a plebiscite agreed to before Hitler's rise to power (1935) remilitarized the Rhineland (1936), aided the nationalist (Franco's) side in the Spanish Civil War despite a League of Nations agreement to stay out of the war (1936-1939) including a German Air Force unit bombing Guernica (1937). Germany also annexed and invaded Austria (1938) and assumed an aggressive posture against Czechoslovakia resulting in the now infamous Munich Agreement (1938) in which Czechoslovakia was forced to give up the Sudetenland without being consulted in the matter. When Germany attacked Poland on September 1, 1939, giving a blatantly faked Polish attack as their justification, France and Great Britain finally felt bound by their alliance commitment and declared war on Germany on September 3. However, little offensive action took place in the west until the 1940 offensive by the Nazis which led to the Fall of France and the withdrawal of British troops via Dunkirk. When Hitler betrayed his erstwhile ally Stalin and invaded the Soviet Union, the "Blitzkrieg" failed as neither Moscow nor Leningrad were captured, and ultimately the Soviets managed to turn the tide with horrendous losses on both sides, including gruesome human rights violations and massacres, especially perpetrated by SS and Wehrmacht on civilians in the invaded area. In 1944, the Allies (notably America, Britain and Canada) landed in Normandy while Hitler continued to believe that landing to be a feint with the main thrust coming via Calais, and the Soviets advanced steadily, ultimately culminating with the capture of Berlin in April 1945, the surrender of May 1945 (variously celebrated as May 8 or May 9) and the capture of the last Nazi holdouts in Schleswig Holstein later that month. Nazi war criminals were put on trial in Nuremberg although many escaped judgment and ended up in the Arab world, Latin America or even Germany itself, sometimes in high government, academic or industrial positions.
In the later phase of the war, Allied bomber raids brought destruction to nearly every larger German city (as the German air force had done to Rotterdam, Warsaw, London, Coventry and other cities in the earlier stages of the war). After the war was lost the occupied country lost most of its eastern territories and was faced with a major refugee crisis, with millions of Germans flooding westward into what remained of Germany, and from other countries where significant German minorities were escaping the military and political influence of the victorious Soviet Union.
After the devastating defeat in World War II (1939–45), Germany was divided into four sectors, controlled by British, French, Soviet and US forces. The UK and the US decided to merge their sectors, followed by the French. With the beginning of the Cold War, Germany became increasingly divided into an eastern part under Soviet control and a western part which was controlled by the Western Allies. The western part was transformed into the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG or BRD for its German name), a capitalist, democratic country with Bonn as the de facto capital, which was often referred to as West Germany.
The Soviet-controlled zone became the communist/authoritarian Soviet-style German Democratic Republic (GDR), commonly called East Germany. This encompassed the present-day Länder of Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, Brandenburg and Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania. Berlin, which was geographically left in East Germany, had a special status as it was divided among the Soviets and the West, with the eastern part serving as the capital of the GDR and the western sectors of Berlin (West Berlin) being a de facto exclave of the Federal Republic.
The fates of East and West Germany differed markedly, in political and economic development. The East saw heavy demontage - for example very close to every rail line lost its second track and electrification in the immediate postwar era, some having never regained them - and only a gradual switch to economic aid by the occupying power. Thanks to Western aid, the economy and industrial base in West Germany was quickly rebuilt, resulting in the Wirtschaftswunder (economic miracle). The East became a socialist, centrally-planned economy with almost all of its economy nationalized, and increasingly lagged behind the West as this system proved much less efficient or conducive to growth. The limitations of personal freedoms, ever-present censorship and secret police led many of the East's citizens to attempt to flee to the West. However, compared to the other Soviet Bloc countries like Czechoslovakia, Poland, Hungary, or even the Soviet Union itself, the East Germans were (on average) wealthier.
In 1961, the Berlin Wall was erected around West Berlin as part of a heavily guarded frontier system of border fortifications to deter inhabitants from East Berlin from defecting to the more prosperous West. Today some remnants of the era are now museums, such as the former prisons in Berlin-Hohenschönhausen or Bautzen. While many pieces of the Berlin Wall were destroyed outright or sold to enthusiasts around the world, parts have been preserved in their original location as monuments or art installations. The most widely known such installations is the eastside gallery in central Berlin. If you want to avoid the tacky Checkpoint Charlie in Berlin, Bernauer Straße (the street which had windows walled shut, as the houses were in the East and the street in the West) is more accurate — if chilling — with its museum and monument.
Germany was reunited peacefully in 1990, a year after the fall and collapse of the GDR's communist regime and the opening of the iron curtain that separated German families by the barrel of a gun for decades. The re-established eastern states joined the Federal Republic on 3 October 1990, a day since celebrated as a national holiday (Tag der Deutschen Einheit, day of "German national unity", or "Reunification Day"). The united Berlin became the capital of the unified Germany again, and with all federal government branches gradually moving there in the 1990s, the city saw a continued construction and economic boom, putting the city among the European hotspots.
Reunification meant that the affluent West helped the East rebuild its economy, while also accepting the willing migrants freely. This has not been without social and political tensions, but ultimately reunification is regarded as a success, with many cities of the East regaining their former glory (e.g. Dresden) and industrial might (e.g. Leipzig). The legacy of the GDR is still palpable in a slightly higher unemployment, a slightly lower standard of living and a more even distribution of wealth in some areas of the East, and with numerous mementos to socialism like the huge statue of Karl Marx in the city of Chemnitz, which was called Karl-Marx-Stadt during the period of communist rule. The DDR museum in Berlin offers a way to experience the peculiar, and sometimes absurd, life in the erstwhile East Germany.
While the major cities of the East are once again growing, rural areas and minor towns have been hit hard, and some appear to be on a terminal decline, having lost half their inhabitants to the big cities since 1990, with only elderly people remaining. However, even some places in the West are beginning to encounter problems once characteristic of the post-reunification East, such as dilapidated public infrastructure, empty municipal coffers and shrinking population figures. The overall downward trend was reversed - at least for the short term - due to the influx of refugees in 2015 and there seems to be a trend of re-urbanisation driving up housing costs in major cities, but the decline of rural areas seems to be only getting worse.
In the years after reunification Germany faces challenges such as the climbing average age of its population and partially the integration of inhabitants who immigrated recently. Germany enjoys the benefits of European cooperation and the digital revolution. A very visible modern development are the wind turbines, praised for providing sustainable energy and criticized for their impact on the landscape.
 As one of the 10 biggest economies in the world by total GDP Germany is regarded as an economic powerhouse not only within Europe, but also globally. Much of Germany's economic reputation stems from the export orientation of many of their companies, both those who grew to be large multinationals, but also mid-sized enterprises. Germany is known as an exporter of various kinds of machinery and technology, be it consumer goods like automobiles, and all kinds of machinery for all branches of industry, mining and agriculture. Creative industries, high-tech start-ups and the service sector also play an increasing role for Germany's economical output.
As one of the 10 biggest economies in the world by total GDP Germany is regarded as an economic powerhouse not only within Europe, but also globally. Much of Germany's economic reputation stems from the export orientation of many of their companies, both those who grew to be large multinationals, but also mid-sized enterprises. Germany is known as an exporter of various kinds of machinery and technology, be it consumer goods like automobiles, and all kinds of machinery for all branches of industry, mining and agriculture. Creative industries, high-tech start-ups and the service sector also play an increasing role for Germany's economical output.
A pretty unique feature of Germany's economy is the relative decentralization: you will find large companies headquartered in many different German cities and Länder, not only in or around the capital as in many other European centres. The result of that is not only the widespread relative wealth and high living standards, as well as elegant and tidy appearance of both large cities and small towns, but also the additional tourist opportunities. You can visit the factories and company museums of BMW in Munich or Mercedes and Porsche in Stuttgart. More and more factories are also built to be more than manufacturing plants, but also experience centres, like the BMW and Porsche plants in Leipzig or the gläserne Manufaktur of VW in Dresden, the latter of which has ceased production after the Phaeton was phased out but still welcomes visitors.
The global importance of the German economy and its geographically distributed nature has its reflection in the transportation network of the country. Frankfurt Airport is an important air traffic hub for Europe and the main one for Germany's flag carrier Lufthansa. That said, many other airports have numerous intercontinental connections, as well as busy intra-European and domestic traffic, including those in Berlin, Munich, Düsseldorf, Cologne and Hamburg. The somewhat unsatisfactory airport situation in the capital - in part a legacy of partition - is planned to be remedied by a new "Berlin Brandenburg International Airport", which has however become a laughing stock due to numerous delays and problems with planned openings in the early 2010s now come and gone and still no date for opening in sight. There is also a dense network of railway lines within Germany and to neighbouring countries, many of which have been upgraded to high-speed standards (served by Germany's state operator Deutsche Bahn's Inter-City-Express trains). The Autobahn (motorway) network is world-famous for its quality and comprehensiveness, as well as the lack of speed limits on certain stretches. Unlike most of its neighbors, Germany does not have any tolls (for cars, that is) for the vast majorities of its highways yet. The Autobahnen are also used by many bus companies, which offer a low-cost alternative to airlines and railways.
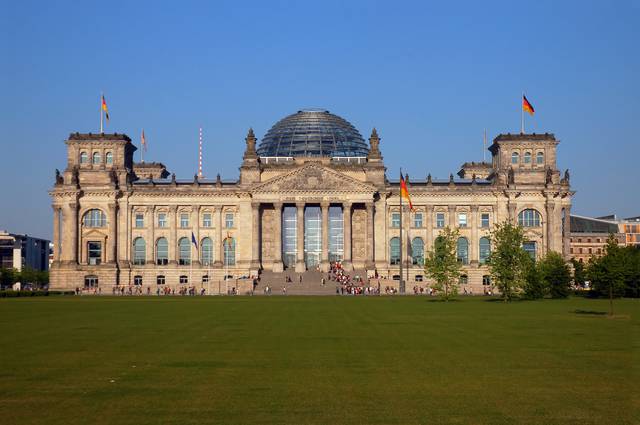 Germany is a federal republic, consisting of 16 federal states (Bundesländer). The federal parliament (Bundestag) is elected every four years in a fairly complicated system, involving both direct and proportional representation. The parliament elects the Federal Chancellor (Bundeskanzler), who serves as the head of the government. The Bundesländer are represented at the federal level through the Federal Council (Bundesrat). Many federal laws have to be approved by this council and this can lead to situations where council and parliament block each other if they are dominated by different parties. The Federal Constitutional Court (Bundesverfassungsgericht) has the right to pass judgement on the constitutionality of laws.
Germany is a federal republic, consisting of 16 federal states (Bundesländer). The federal parliament (Bundestag) is elected every four years in a fairly complicated system, involving both direct and proportional representation. The parliament elects the Federal Chancellor (Bundeskanzler), who serves as the head of the government. The Bundesländer are represented at the federal level through the Federal Council (Bundesrat). Many federal laws have to be approved by this council and this can lead to situations where council and parliament block each other if they are dominated by different parties. The Federal Constitutional Court (Bundesverfassungsgericht) has the right to pass judgement on the constitutionality of laws.
The head of state is the Federal President (Bundespräsident). He or she is not involved in day-to-day politics and has mainly ceremonial and representative duties.
The two largest parties are the centre-right CDU (Christlich Demokratische Union, Christian Democratic Union) and the centre-left SPD (Sozialdemokratische Partei Deutschlands, Social Democratic Party of Germany). Due to the proportional voting system, smaller parties are also represented in parliament. They cover a full spectrum of political views from free market economy, environmentalism to far left socialism. Still, the number of different parties is relatively low because a party is only represented if it gained at least 5 % at the elections. While Germany for a long time did not have a far-right populist party at the federal level - unlike most of the rest of Europe - the "Alternative für Deutschland" (AfD) now fulfills this role to much controversy.
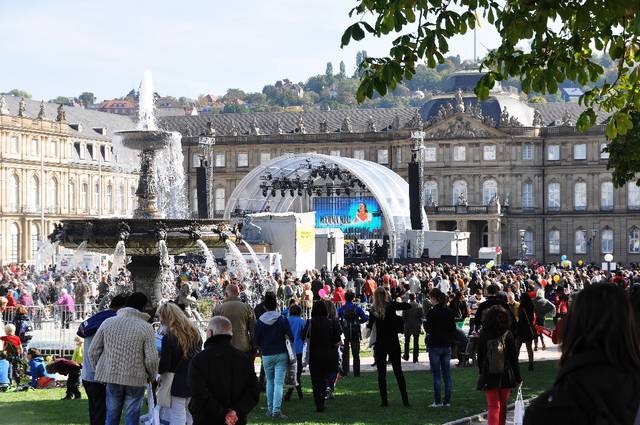

Being a federal republic, Germany is very much a decentralised country, which does justice to the cultural differences between the regions. Some travellers will perhaps only think of beer, Lederhosen and Oktoberfest when Germany comes to mind, but Germany's famous alpine and beer culture is mostly in Bavaria and Munich. The annual Oktoberfest is Europe's most visited festival and the world's largest fair. Germany's south-western regions, however, are well known for their wine growing areas (e.g. Rheinhessen and Palatinate) and Bad Dürkheim on the "German wine route" (Deutsche Weinstraße) organises the biggest wine festival worldwide with over 600,000 visitors annually.
Immigration has also played a large part in Germany over the past 50 years, with approximately 20% of the total population being either foreign or of a 'migrant background' (Germans and non Germans who moved to Germany after 1949 or have at least one parent that did). Many cities have large communities of Turks, Poles, Italians as well as people from Southern and Eastern Europe or the Middle East. Immigration of various types also played a role before that, but in most cases descendants of e.g. refugees from the former German territories east of Oder and Neisse or descendants of French Huguenots are distinguished from other Germans by little more than their last name if that. Although the Jewish community was virtually wiped out by the Nazis, high levels of immigration from the former Soviet Union since its collapse in 1991 have resulted in a large number of Soviet Jews settling in Germany, and Germany now once again has one of the world's largest Jewish communities, and the fourth largest in Europe after France, the United Kingdom and Russia.
Many cities have a vibrant LGBT scene, especially Berlin and Cologne. Berlin's tourism agency and other tourism organisations actively attract gay and lesbian travellers to their cities. Laws legalising gay marriage were passed in June 2017 and were implemented in October 2017. Homosexuality is widely accepted in society. Open homosexuals have attained high political office, including the mayorships of Berlin and Hamburg, vice-chancellor and foreign minister and even some rural and conservative places have elected openly gay mayors. Views on homosexuality have traditionally been more negative in rural areas and among blue collar workers, but even here acceptance is increasing, as is visibility. Some people of Middle Eastern descent - including urban youth - also have more negative views of homosexuals and homosexuality as do people on the extreme political right.
Electricity is supplied at 230 V and 50 Hz and power failures are very rare. Almost all outlets use the Schuko socket, and most appliances have a thinner but compatible Europlug. Travel adapters of all kinds are widely available in electronics stores, but they are often rather expensive.
 The official language of Germany is German (Deutsch). The standard form of German is called "Hochdeutsch" (High German). It's understood by all and spoken by almost all Germans. However, every region has its own dialects, which might pose a challenge even to those who speak German well, even native speakers. This is usually noticeable only in the south and rural areas of the north and east. Dialect remains a strong part of the local identity in Bavaria, Saxony, southern Rhineland and Hesse, Württemberg and Baden. The general rule is that the Main River divides north Germany from the south in both language dialects and local culture.
The official language of Germany is German (Deutsch). The standard form of German is called "Hochdeutsch" (High German). It's understood by all and spoken by almost all Germans. However, every region has its own dialects, which might pose a challenge even to those who speak German well, even native speakers. This is usually noticeable only in the south and rural areas of the north and east. Dialect remains a strong part of the local identity in Bavaria, Saxony, southern Rhineland and Hesse, Württemberg and Baden. The general rule is that the Main River divides north Germany from the south in both language dialects and local culture.
Many Germans have learned some English at school (a compulsory subject since the 80's), so you should be able to get by. However, while many Germans claim to speak it fairly well, actual proficiency varies tremendously across most social, generational, and even geographic dimensions; some Germans have near-native fluency on par with the Netherlands and the Nordic countries, while others maybe barely utter a few sentences. Generally speaking, people in large and affluent urban areas such as Berlin, Hamburg, Munich, and Stuttgart speak very good English, whereas people from more industrial regions, such as much of Rhine-Ruhr, smaller urban areas, rural areas, and most of east Germany may not possess as much fluency. Furthermore, younger people will usually be able to converse in English, whereas older generations tend to not speak any English at all. Germans who were born in other countries or the children of immigrants tend to be more fluent in English than ethnic Germans. Many immigrants who moved to Germany as adults may speak good German but not speak any English at all.
Other languages are spoken in Germany as well. A surprising number of Germans speak French, often with really good proficiency. In parts of Eastern Germany, a small Slavic community of 50,000 also speaks Sorbian. Many people who grew up in the formerly communist East Germany were taught to speak Russian. It is becoming more common to find other foreign languages such as Spanish and Italian. Education is a strongly local issue with the 16 states all having jurisdiction over their school curricula and only broad common standards agreed to among the 16 states (not dictated by the federal government) as such, states which have historical or geographic ties may prefer to teach French (Rhineland Palatinate, Saarland, Baden Württemberg) sometimes even ahead of English whereas states like Brandenburg may teach Russian and some schools near the immediate border may even offer Dutch, Czech or Polish. Due to the economic crisis in most of Southern Europe, university towns have a relatively large number of recent immigrants from these countries.
Germany has experienced a great deal of immigration since the end of World War II starting with millions of ethnically German refugees fleeing the war, and many towns and cities have large communities of Turkish, Italian, ex-Yugoslav and Polish people (among many others) who speak the mother tongue of their ancestors along with German. Germany today is the second most popular immigration destination in the world, after the USA.
Germans tend to be direct, and will often answer in English with short responses. Since it's polite to reply "Bitte" if someone thanks you, Germans may literally translate this with "please" instead of "here you are" or "you're welcome".
Since language ability is a measure of social standing it may be difficult to persuade many Germans to speak German to you if they know you are a native English speaker. Saying that you are (even if pretending to be) a non-native English speaker can get around this situation. That said, Germans who are actually truly fluent and confident in English usually have no issue speaking German with you.
Virtually all movies, in addition to foreign shows broadcast on German TV and cable channel are dubbed into German. If you wish to watch the newest movies in English, they may be shown without dubbing at select theaters at the biggest cities for a little premium fee. Look for the symbol OmU or OmengU (Original with subtitles). An even rarer treat is the cinema showing movies in their original version without subtitles - those usually only exist in cities of half a million or more. Niche films and shows shown on high-brow channels like arte (a French-German channel) or 3sat (a German-Swiss-Austrian channel) may sometimes be shown with their original audio and subtitles due to the cost of dubbing niche media, but those are rare even on these niche channels.
When thinking of Germany, beer, lederhosen and Alpine hats quickly come to mind, but these stereotypes mostly relate to Bavarian culture and do not represent Germany as a whole. Germany is a vast and diverse country with 16 culturally unique states that only form a political union since 1871. Even within states there is often considerable cultural diversity. The government of Bavaria for instance likes to talk of the three "tribes" living in the state; "old Bavarians", Franconians and Swabians. Especially the former two like being lumped together about as much as English and Scots.
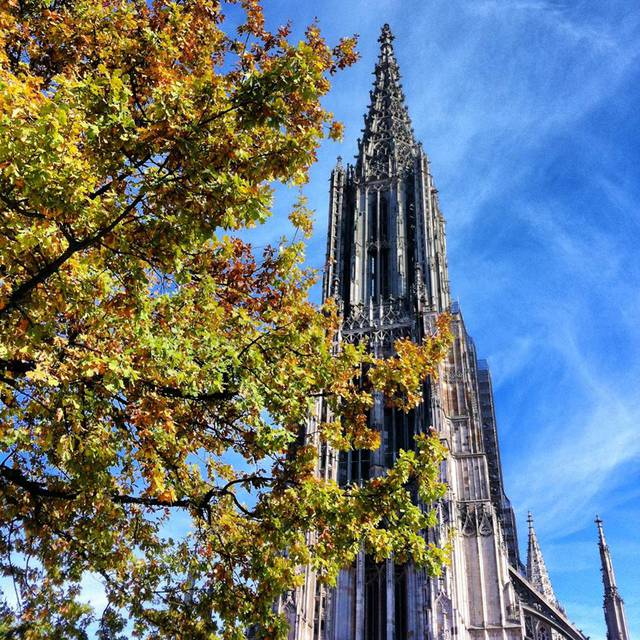

If you're still looking for the cliches, the Romantic Road is a famous scenic route along romantic castles and picturesque villages. With its fairy tale appearance, the Neuschwanstein Castle could be considered the most iconic of German castles. The walled city of Rothenburg ob der Tauber has a beautiful mediaeval centre that seems untouched by the passage of time. Some similar typical German towns can be found elsewhere in the country, like Augsburg, Bamberg, Celle, Heidelberg, Lübeck, and Quedlinburg. Your picture postcard visit to Germany will be complete with a visit to the beer halls of Munich and a peek of the Alps at Garmisch-Partenkirchen. In Ulm you can visit the highest church spire in the world - the Ulmer Münster. You can also go to the lovely yet seldom visited medieval city of Schwäbisch Hall. For those who are fans of the Grimm's Fairy Tales, which include many famous ones such as Rapunzel, Rumpelstiltskin, Snow White and The Pied Piper, the German tourism board has a recommended Fairy Tale Route which takes you to places where the Brothers Grimm lived, as well as towns that were featured in the Grimm's Fairy Tales.
Germany is a modern industrial nation, and the Wirtschaftswunder is best represented by the industrial heritage of the Ruhr. Hamburg is another economic powerhouse with the second busiest port of the continent. Frankfurt is the financial centre of Germany, and of Europe as a whole, as it is the base of the European Central Bank. Its skyline comes close to those found at the other side of the Atlantic. The fashion city of Düsseldorf, media industry of Cologne, and car companies in Stuttgart each represent a flourishing sector of the German economic miracle.
A completely different experience can be found in Berlin, a city unlikely to be found anywhere else on the planet. While architecturally an odd mismatch of sterilised apartment blocks, post-modernist glass and steel structures, and some historic left-overs, it has a laid-back atmosphere and a culture of internationalism. Its turbulent history gave rise to an enormous wealth of historical attractions, among them the Berlin Wall, Brandenburger Tor, Bundestag, Checkpoint Charlie, Fernsehturm, Holocaust Memorial and Rotes Rathaus. But do not miss out the Prenzlauer Berg neighbourhood if you want to feel like a true Berliner. Kreuzberg (once famous for punks, now largely gentrified) and the delightfully named Wedding aren't far behind either.
The dark memories of the Nazi era have also made traces in Germany; see World War II in Europe and Holocaust remembrance. While the subject is a touchy one and "jokes" about the subject are a bad idea unless you know your hosts well, Germany has gone to great lengths to conserve monuments of the era as a warning and the detailed educational exhibits at places like former concentration camps, the former Nazi party rallying grounds in Nuremberg or the former seats of Nazi ministries and offices in Berlin are well worth a visit, if a chilling and depressing one.
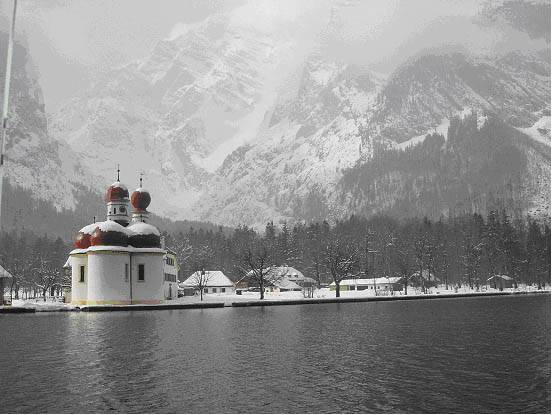
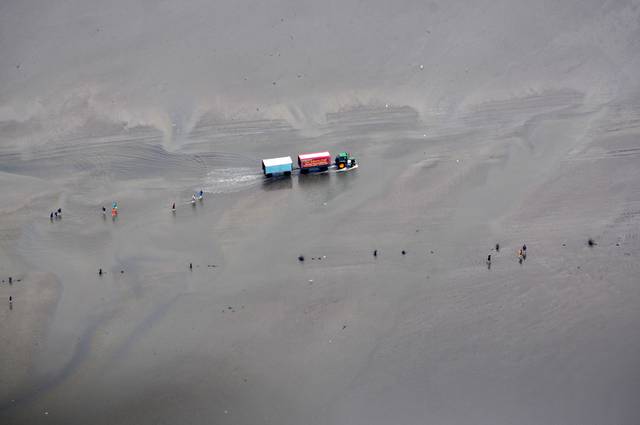 Due to its size and location in Central Europe, Germany boasts a large variety of different landscapes. In the north, Germany has an extensive coastline along the North Sea and the Baltic Seas in a vast area known as the North German Plain. The landscape is very flat and the climate is rough with strong winds and mild, chilly temperatures. Due to the south-easterly winds that press water into the German Bight, tidal variations are exceptionally high, creating the Wadden Sea. Vast areas of the seabed are uncovered twice a day, allowing one to walk from one of the numerous islands to another. (This should only be done with a guide.) The East Frisian Islands just off the coast are very picturesque, although mostly visited by the Germans themselves. Favourite white sand resorts along the Baltic Sea include Rügen and Usedom.
Due to its size and location in Central Europe, Germany boasts a large variety of different landscapes. In the north, Germany has an extensive coastline along the North Sea and the Baltic Seas in a vast area known as the North German Plain. The landscape is very flat and the climate is rough with strong winds and mild, chilly temperatures. Due to the south-easterly winds that press water into the German Bight, tidal variations are exceptionally high, creating the Wadden Sea. Vast areas of the seabed are uncovered twice a day, allowing one to walk from one of the numerous islands to another. (This should only be done with a guide.) The East Frisian Islands just off the coast are very picturesque, although mostly visited by the Germans themselves. Favourite white sand resorts along the Baltic Sea include Rügen and Usedom.
The central half of Germany is a patchwork of the Central Uplands, hilly rural areas where fields and forests intermix with larger cities. Many of these hill ranges are tourist destinations, like the Bavarian Forest, the Black Forest, the Harz, the Ore Mountains, North Hesse and Saxon Switzerland. The Rhine Valley has a very mild, amenable climate and fertile grounds, making it the country's most important area for wine and fruit growing.
In the extreme south, bordering Austria, Germany contains a portion of the Alps, Central Europe's highest elevation, rising as high as 4,000 m (12,000 ft) above sea level, with the highest summit in Germany being the Zugspitze at 2962 m (9717 ft). While only a small part of the Alps lie in Germany, they are famous for their beauty and the unique Bavarian culture. Along the country's southwestern border with Switzerland and Austria lies Lake Constance, Germany's largest fresh-water lake.
- Bertha Benz Memorial Route – follows the world's first long-distance journey by car
- Romantic Road – the most famous scenic route in Germany that starts in Würzburg and ends in Füssen
- Rheinsteig and Rheinburgenweg – Walk the high level path through some of Germany's most beautiful landscapes with spectacular views of castles above the River Rhine between Wiesbaden and Bonn or Bingen and Bonn-Mehlem.
- Elbe Radweg a cycle-route along the Elbe river that passes by Dresden and Magdeburg before it reaches Hamburg. Due to it being close to a river there are few steep ascents, making this route ideal for novice bikers.
[[Bertha Benz Memorial Route]] – follows the world's first long-distance journey by car
[[Romantic Road]] – the most famous scenic route in Germany that starts in Würzburg and ends in Füssen
[[Rheinsteig]] and [[Rheinburgenweg]] – Walk the high level path through some of Germany's most beautiful landscapes with spectacular views of castles above the River Rhine between [[Wiesbaden]] and [[Bonn]] or [[Bingen]] and Bonn-Mehlem.
[[Elbe Radweg]] a cycle-route along the Elbe river that passes by Dresden and Magdeburg before it reaches Hamburg. Due to it being close to a river there are few steep ascents, making this route ideal for novice bikers.

Germany offers a wide variety of activities of both a cultural and sporting nature. Many Germans are members of a sports club.
Germany is crazy about football (soccer) and the German Football Association (DFB) is the biggest football association in the world with 6.35 million members (8% of the German population) in more than 25,000 clubs. Many German football clubs are among the most valuable football brands in Europe, like Borussia Dortmund and FC Bayern Munich. Every village has a club and the games often are the main social event on weekends. Keep in mind that due to the nature of (a small minority of) soccer fans, there is often a heightened police-presence during games and violence is rare but not unheard of. Other popular team sports include (Olympic) handball (especially popular in the north), ice-hockey ("Eishockey"), volleyball and basketball. Motor sports are a popular visitor attraction, with many famous Formula one courses like Hockenheim and Nürburgring ("Green Hell").
Germany - particularly the North - is also one of the best countries when it comes to Handball. Teams like Flensburg, Kiel and others draw sellout crowds to their halls week in week out and produce some of the best Handball in the world.
American football is also played in Germany, enjoying a tradition that goes back to the 1970s. The German national team has won the last two European championships (2010 and 2014). While the crowds are nowhere near those of more popular sports (2000 fans are a number many teams only get for important games) the final draws somewhere between 15 000 and 20 000 spectators and the atmosphere is relaxed with even supporters of the visiting team welcomed and the worst that can happen to you being good natured jabs at your team or its history. On Super Bowl Sunday there are a bunch of "public viewing" (that's the actual German term) events, even though it is in the middle of the night and it is a good opportunity to meet other football enthusiasts as well as the local North American expat population.
During the winter, many people go skiing in the Alps or in mountain ranges like the Harz, Eifel, Bavarian Forest or Black Forest.
One of the more popular individual sports is tennis; although it has declined somewhat since the days of Steffi Graf and Boris Becker, there are still tennis courts in many places and most of them can be rented by the hour.
Almost every middle-sized German city has a spa (often called Therme) with swimming pools, water slides, hot tubs, saunas, steam baths, sun roofs etc.
Several theatres in bigger cities play outstanding classical and contemporary plays. Germany prides itself on the wide variety of cultural events and every city works out a cultural agenda. Most theaters and Opera houses receive generous subsidies to keep tickets affordable and a cheap seat can be had for single digit Euros in many venues if you qualify for certain discounts.
Germany is known for its several world class opera houses (especially Berlin, Bayreuth, and Munich), and the Berlin Philharmonic Orchestra is one of the top three orchestras in the world. Germany is considered to have one of the strongest classical music traditions in Europe, with many famous composers such as Bach, Handel (called Händel before he settled in London in 1712), Beethoven, Schumann, Brahms and Wagner originating from Germany.
While France and Italy may have a longer history with opera, Germany too has developed its own unique operatic tradition. German, along with Italian and French, is considered to be a main operatic language, with many famous German-language operas having been composed by famous composers like Mozart, Beethoven, Wagner, and Strauss.
Germany has more than 130 professional orchestras – more than any other country in the world. This is a legacy of feudal times, when the country's territory was fragmented and each of the local rulers employed a separate court orchestra. Nowadays most orchestras are run by state or local governments or public service broadcasters. The biggest one is the Gewandhausorchester in Leipzig with 185 salaried musicians (however they rarely play all at the same time, parts of the orchestra accompany the opera, ballet, the Thomaner boys' choir and play its own symphonic concerts).
Musicals are popular in Germany. Although there are some touring productions from time to time, most shows stay in a specific city for a few years. The main 'musical cities' are Hamburg, Berlin, Oberhausen, Stuttgart, Bochum and Cologne. German performances include The Lion King, Wicked, Starlight Express and Rocky.
In general, German theatres are plentiful and—compared to most other western countries—dirt cheap, as the government considers them to be "necessary" and subsidizes many of them in order to make visits affordable to everyone. Even some unsubsidized theatres are still pretty affordable compared to e.g. musicals. There are often special discounts for students or elderly people. Most plays are performed in German, but there are occasional events with plays in other languages as well. The best known German language authors can be found both in the names of many streets and in many theatres on a daily basis. Goethe, Schiller and Lessing are all household names but more contemporary authors like Brecht are also frequently interpreted and played. There is really no easy line to be drawn between German theatre and German language theatre outside Germany, so works by Austrian, Swiss, or other German-language writers and directors are also often shown on German stages and vice versa.
Rather interestingly, William Shakespeare is perhaps nowhere more adored than in Germany — the Anglosphere included. For example the - still extant - Deutsche Shakespeare Gesellschaft dates to 1864 and thus predates any English or American Shakespeare society. This can be attributed in large part to Goethe, who fell in love with the Bard's works. If your German is up to it, seeing a performance can be very interesting. According to some Germans, Shakespeare is actually improved in translation, as the language used is arguably somewhat more contemporary. Judge for yourself.
There are some well known and large annual festivals in Germany like the Wacken Open Air (heavy metal music festival), Wave-Gotik-Treffen (festival for "dark" music and arts in Leipzig) and Fusion Festival (electronic music festival in the Mecklenburg Lake District).
Notes larger than €100 while legal tender aren't seen in circulation all that often and will be refused at some stores or for small purchases. Be prepared for larger bills to face more scrutiny with regards to potential counterfeits. Deutschmarks (DM) issued between 1948–2002 can be exchanged free of charge for euro at all Deutsche Bundesbank branches.
Currency exchange has diminished greatly since the introduction of the Euro, though you may still find it at or near major train stations and airports. Foreign currency - even those of neighboring countries - will rarely be accepted and often at pretty bad exchange rates. However, you might have some luck with Swiss Francs in the immediate border area, as Germany is quite a popular shopping destination for Swiss tourists. Similarly some fast food restaurants, especially those near US Army facilities accept US dollars (again, at pretty bad exchange rates) but do not count on it. Normal banks will of course offer currency exchange, but they sometimes charge considerable fees for non-customers and when changing from Euros to foreign cash advance notice may be required. Travelers checks are increasingly rare, but banks still exchange them, though it would likely be less hassle to just take your debit or credit card and withdraw money from regular ATMs.
Cash (Bargeld) is the most preferred way of paying for everyday transactions. Independent vendors, small cafes and stalls on the likes of Christmas Markets by and large do not accept credit cards and there is sometimes a minimum purchase amount. While German domestic debit cards – called EC-Karte or girocard – (and, to a lesser extent, PIN-based Maestro cards and VPay) enjoy almost universal acceptance, credit cards (Visa, MasterCard, American Express) or foreign debit cards (Visa Debit/Electron etc.) are not as widely accepted as in other European countries or the United States. However, they will be accepted in nearly all major retail stores and most fast food chain outlets. Major retailers increasingly accept credit cards (usually Visa and MasterCard only) and the Near Field Communication technology is now widely available (look for the logo) even though many people working in retail may not be familiar with the technology yet.
Most ATMs will accept credit cards and if the ATM charges a fee EU legislation mandates the machine to tell you the fee before the withdrawal. However, your card issuer may levy their own charges regardless of or in addition to the presence of charges levied by the ATM operator; check with your issuer before using.
In common with most other Western European languages, the meanings of points and commas are exactly inverse to the English custom; in German a comma is used to indicate a decimal. For example, "2,99€" is two euros and 99 eurocents. The "€" symbol is not always used and is virtually always placed after the price and some Germans consider the "currency sign first" notation weird. A dot is used to "group" numbers (one dot for three digits), so "1.000.000" would be one million. So "123.456.789,01" in German is the same number as "123,456,789.01" in English-speaking countries.
All goods and services include VAT (Mehrwertsteuer) of 19%. It is always included by law in an item's price tag (only exception is for goods that are commercially exported but then duties might apply). Fuel, sparkling wine, spirits and tobacco are subject to higher taxes. There is a reduced VAT of 7% for hotels (but not for edibles consumed within), edibles (certain items considered luxury goods, e.g. lobster, are exempted from this reduction), print products, public transport (short-distance only) and admission price for opera or theatre.
In Germany tips (Trinkgeld, literally "drink(ing) money") are commonplace in restaurants, bars (not in fast-food restaurants), taxis and hair salons. Whilst not mandatory, it is always appreciated as a thanks for excellent service. Tips rarely exceed 10% of the bill (including tax) and tips are also rather common when the bill is an uneven amount to avoid having to deal with small change (e.g. a bill of €13.80 will commonly be rounded up to €15 to make making change easier). The server will never propose this and even when dealing with one of the annoying €x.99 prices, they will diligently search for the copper coins to make change unless you say otherwise.
Unlike in some other countries, service staff are always paid by the hour and the minimum wage of €9.19 an hour (as of 2019) applies to service staff as well as any other profession. However, service staff is more likely to get only the minimum wage or barely above even in establishments where other jobs get higher wages. A tip is therefore mainly a matter of politeness and shows your appreciation. If you didn't appreciate the service (e.g. slow, snippy or indifferent service) you may not tip at all and it will be accepted by the staff. Americans in particular are known among service staff for being generous tippers pretty much regardless of service, so they may be a lesser priority on busy days in some places.
Tipping in Germany is usually done by mentioning the total while paying. So if e.g. a waiter tells you the bill amounts to "€13.50", just state "15" and s/he will include a tip of €1.50. Alternatively, if you wish to ask them to keep the change, you may say "Stimmt so!" or simply "Danke!".
Tipping in other situations (unless otherwise indicated):
- Taxi driver: 5–10% (at least €1)
- Housekeeping: €1–2 per day
- Carrying luggage: €1 per piece
- Delivery services: 5–10% (at least €1)
Retail prices are reasonable and lower than in northern European countries.
Chains like "Aldi", "Lidl", "Penny" and "Netto" are discount supermarkets (Discounter). Their range of products is limited to the necessities of daily life (like vegetables, pasta, milk, eggs, convenience foods, toiletries etc.), sold in rather simple packaging for tightly calculated prices. While quality is generally surprisingly high, do not expect delicatessen or local specialities when you go to shop there. Don't blame discounter personnel for being somewhat brusque; although they are paid slightly better than usual, they have to cope with a rather grim working atmosphere and a significantly higher workload than colleagues in "standard" supermarkets. Lidl and Aldi have tried to brand themselves as more "upscale" and laying focus on quality since about the mid-2010s but prices have staid the same while new "gimmicks" such as coffee machines (€1 per drink) or freshly baked (from frozen dough) bread, rolls and other baked goods were introduced as part of that strategy.
Examples of standard supermarket chains are Rewe, Edeka, Real, Kaufland, Globus or Famila. Their prices are slightly higher than in discount supermarkets, but they have a much wider range of products (including cheap to high-end quality). Usually there are big cheese, meat and fish counters where fresh products are sold by weight. The personnel in these shops is trained to be especially helpful and friendly.
Plenty of chain supermarkets only exist in certain parts of the country or show a clear geographic focus. Norma is only found in the south, Sky only in the north and Netto "with dog" (there are two separate chains both named "Netto", one of them having a dog as their symbol) only in the north and east.
Beside those major chains, Turkish supermarkets (which can be found in virtually all west German cities) can be a worthwhile alternative since they combine the characteristics of discounters (low price levels but limited assortment) with those of "standard" supermarkets ((Turkish) specialities and usually friendly staff). Fruits and vegetables at Turkish supermarkets tend to be particularly good value for money. Other diaspora groups also own some supermarkets, but they tend to be rarer outside big cities. In Berlin you might find an ethnic enclave of many groups, but they can be harder to find even in Munich or Hamburg and non-existent in smaller cities. The East has a surprisingly large Vietnamese diaspora and "Asia Shops" of varying kinds can be found in many parts of the country. Specialized Asian food items tend to be cheaper, of better quality and more readily available here than at Rewe and co. However, the shop might not look like much from the outside and feel rather cramped on the inside.
If you are looking for organic products, your best bet is to visit a "Bioladen" or "Biosupermarkt". (Bio- generally means organic.) There are also many farmers selling their products directly ("Hofladen"), most of them organized in the "Bioland" cooperative. They offer reasonable food at reasonable prices.
Be prepared to bag your own groceries and goods as well as provide your own shopping bags for doing so. While most stores provide plastic or paper as well as canvas shopping bags at the checkout, you are charged up to 50 cents per bag for them. Buggies/shopping carts usually have to be unlocked with a euro coin which you get back. At most super markets you can spot a canister with lots of cardboard boxes in it, usually after the cash point. You are allowed to take cardboard boxes from there! It's a service the markets offer and also an easy waste disposal for them. Just tell them you are getting yourself a box when the cashier starts to scan your goods, come back and start packing.
Germany has an elaborate beverage container deposit ("Pfand") system. Reusable bottles, glass and plastic, usually cost between 8 and 25 cents Pfand per bottle depending on size and material - the actual value can be found in the packaging. Additional Pfand is due for special carrying baskets matching the bottle measures. The Pfand can be cashed in at any store which sells bottles, often by means of a high-tech bottle reader than spins the bottle, reads the Pfand, and issues a ticket redeemable with the cashier. Plastic bottles and cans usually cost 25 cents Pfand, if not they are marked as pfandfrei. Exempt from Pfand are liquors and plastic boxes usually containing juice. There are also a few other instances where Pfand is due, for example for standardized gas containers. Pfand on glasses, bottles and dishware is also common at discotheques, self-service bars or public events, but usually not at a students' cafeteria.
Outlet Centers as such are a rather new phenomenon, but the similar concept of "Fabrikverkauf" (literally factory sale) where products (including slightly damaged or mislabeled ones) are sold directly at the factory that makes them, often at greatly reduced prices. American style outlets not associated with a factory have become more common and Herzogenaurach for instance has outlets of Adidas and Puma (whose headquarters - but no production - are there) and of other clothing and sports companies.
You can find local food products (not necessarily organic) in most places at the farmer's market ("Wochenmarkt" or simply "Markt"), usually once or twice a week. While your chances on finding English-speaking sellers there may be somewhat reduced, it's nevertheless quite fun to shop there and mostly you will get fresh and good quality food for reasonable prices. Most winemakers sell their products either directly or in "Winzergenossenschaften" (winemaker cooperatives). These wines are almost always superior to the ones produced by German wine brands. Quality signs are "VdP" ("Verband deutscher Prädikatsweingüter", symbolized by an eagle) and "Ecovin" (German organic winemaker cooperative). Wines made of the most typical German wine varieties are usually marked with "Classic".
Some agricultural producers have also started to sell their produce directly to consumers, either via a small stand at the roadside (often along rural Bundesstraßen but sometimes also inside urban areas) or directly from their farm. Dairy farmers sometimes run "Milchtankstellen" (a compound noun from the German word for milk and gas station) where you can get milk from a vending machine similar to a soda fountain. All of those tend to be cash only but prices and value for money tend to be rather good.
German honey is a good souvenir, but only "Echter Deutscher Honig" is a guarantee for reasonable quality. Along the German coasts, smoked eel is quite a common delicacy and a typical souvenir. You can discover an astonishing German cheese variety in cheese stores or in Bioläden.
Some of those products may not be taken into all countries due to agricultural contamination concerns.
Some German brands of high-end goods such as kitchen utensils, stationery, and hiking gear are considerably cheaper than abroad.
Cheap clothing of sufficient quality might be bought at C&A, but don't expect designer clothes. During the end-of-season sales you should also compare prices of conventional stores since they may be even cheaper than the discounters. H&M sells cheap, stylish clothing, but with notoriously awful quality.
Germany is also a good place to shop for consumer electronics such as mobile phones, tablets and digital cameras. Every larger city has at least one "Saturn" or "MediaMarkt" store with a wide selection of these devices, as well as music, movies and video games on CD/DVD. Prices are generally lower than elsewhere in Europe. English-language movies and TV shows are universally dubbed into German, and computer software and keyboards are often German-only.
Opening hours vary from state to state. Some states like Berlin, Hamburg and Schleswig-Holstein have no more strict opening hours from Monday to Saturday (however, you will rarely find 24 hour shops other than at petrol stations), while most stores in Bavaria and Saarland are by law required to close between 20:00 and 06:00. Sundays and national holidays (including some obscure ones) are normally closed for shops nationwide, including pharmacies; single pharmacies remain open for emergencies (every pharmacy will have a sign telling you which pharmacy is open for emergencies or the list can be found here). An exception would be on special occasions called Verkaufsoffener Sonntag, in which shops at selected communes are open from to on selected Sundays, usually coinciding with public holidays or local events. Train stations however are allowed to and frequently have their stores open on Sundays, though usually for limited hours. In some larger cities such as Leipzig and Frankfurt, this can include an entire shopping mall that happens to be attached to the train station. Some shops in touristic areas and towns designated as a Kurort (health resort) are also allowed to have their stores open all week during tourist season.
As a rule of thumb:
- Smaller supermarkets: - give or take an hour
- Big supermarkets - or midnight
- Shopping centres and large department stores: -
- Department stores in small cities: -
- Small and medium shops: or - (in big cities sometimes to ). Small shops are often closed –.
- Spätis (late night shops): - or even longer, some open 24 hours, especially in big cities
- Petrol stations & their attached minimart: in cities and along the "Autobahn" usually 24 hours daily - however during night hours you might have to pay and order through a small window and night cashiers might not always speak English well
- Restaurants: – or midnight, sometimes longer, many closed during the afternoon
If necessary, in many big cities you will find a few (sometimes more expensive) supermarkets with longer opening hours (often near the main station). Bakeries usually offer service on Sunday mornings (business hours vary) as well. Also, most petrol stations have a small shopping area.
In some parts of Germany (like Berlin, Cologne, Düsseldorf and the Ruhr area) there are cornershops called "Späti" oder "Spätkauf" ("latey"), "Kiosk", "Trinkhalle" (drinking hall) or "Büdchen" (little hut) that offer newspapers, drinks and at least basic food supplies. These shops are, depending on the area, open till late night or even 24/7.
In Germany, at sit-down establishments, you usually look for a table that pleases you by yourself. In more expensive restaurants, it is more likely that a waiter attends you at the entrance who will lead you to a table.
When you get a table, it's yours until you leave. There is no need to hurry. That said, if you see that the restaurant is getting really crowded and people find it difficult to get a place, it is polite to leave and continue your after meal chat with your friends elsewhere.
It is also not absolutely unheard of in restaurants in the countryside, and in cities like Munich, to take a seat at a table where other people are already seated, especially if there are no other seats available. While it is uncommon to make conversation, in this case saying a brief hello goes a long way.
You will usually pay your bill directly to your waiter/waitress. Splitting the bill between individuals at the table is common. For tipping practices, see "Tipping" in the "Buy" section.
German food usually sticks to its roots and a typical dish will consist of meat with some form of potatoes and gravy, accompanied by vegetables or salad. Modern German cuisine has been influenced by other European countries such as Italy and France to become lighter. Dishes show a great local diversity which is interesting to discover. Most German Gaststätte and restaurants tend to be children and dog friendly, although both are expected to behave and not be too boisterous.
Putting places to eat into 7 categories gives you a hint about the budget and taste. Starting from the lower end, these are:
Schnellimbiss means 'quick snack', and is what you will see on the sign of German stalls and small shops that sell primarily sausage (Wurst) and fries (Pommes Frites). Sausages will include Bratwurst, which is fried and usually a boiled pork sausage. A very German variant is Currywurst: sausage chopped up and covered in spiced ketchup, dusted with curry powder. Beer and often even spirits are available in most Schnellimbisse.
Döner Kebab is a Turkish dish of veal, chicken or sometimes lamb stuffed into bread, similar to Greek Gyros and Arab Schawarma. Despite being considered Turkish, it's actually a specialty that originated in Germany. According to legend, it was invented by Turkish immigrants in West Berlin during the 1970s. In fact, the Döner is Germany's most loved fast food. The sales numbers of Döner shops exceed those of McDonald's and Burger King products by far.
Nevertheless, fast food giants like McDonald's, Burger King and Pizza Hut can be found in most cities. Nordsee is a German seafood chain, which offers 'Rollmops' (pickled herrings) and many other fish and seafood snacks. However, many independent seafood snack-bars (most common along the German coasts) offer slightly better and slightly cheaper seafood. You can also find independent shops selling pizza by the slice.
In addition to being able to grab a sweet snack at a bakery, during the summer, it seems like ice cream shops are on every block. Try Spaghettieis for a popular sundae that is hard to find elsewhere. They press vanilla ice cream through a potato ricer to form the "noodles". This is topped with strawberry sauce to mimic the "spaghetti sauce" and usually either white chocolate shavings or ground almond nuts for "Parmesan cheese".
Germans do not have a tradition of sandwich shops, but you will find that bakeries and butchers sell quite good take-away food and are serious competition for the fast food chains. Even the smallest bakeries will sell many sorts of bread or rolls, most of them darker (for example, using wholemeal or rye flour) than the white bread popular around the world and definitely worth a try. Even if they don't already have it prepared, almost all butchers will prepare a sandwich for you if you ask. Some butchers even prepare meals for you.
This butcher 'imbiss' is mainly popular in southern Germany, and the quality and freshness of food is usually high. Butcher shops that sell a lot of meals will often have a narrow, stand-up counter along one edge, so that you have a place to put your food while you stand up and eat it. Other bakeries and butcher shops even have tables and chairs and serve you more or less like a Café, as they also sell coffee and other hot beverages.
Although rarely a tourist attraction in themselves, if you are wanting to sit down to eat but have little time or a limited budget, canteens and cafeterias are a good alternative to fast food restaurants. Many companies allow non-employees to eat at their canteens although most of these require some local knowledge about location and access, as do the university and college cafeterias. Another option popular with pensioners and office workers are self-service restaurants in the larger furniture stores such as XXXL.
In a beer garden, you can get the obvious drink. In traditional beer gardens in Bavaria, it is possible to bring your own food if you buy their drinks. Most places will offer simple meals. Some Biergärten are also known as Bierkeller (literally beer cellar), especially in Franconia. Historically, Bierkeller originate from the need to store beer in a cool place prior to artificial refrigeration. Thus underground structures were dug and soon beer would be sold directly out of storage in the summer months, giving rise to the Bierkeller tradition as we know it today. Many are set in quite beautiful natural surroundings, but probably the best known ensemble of Bierkeller can be found in Erlangen where they gave rise to the Bergkirchweih, one of the biggest beer festivals in the area. They were dug through a mountain just out of town and gave the city an edge in beer storage and consequently higher production capabilities, which led to beer from Erlangen becoming a household name once the railway connection enabled export. The invention of artificial cooling ended that advantage, however. The cellars still exist and besides their role in Bergkirchweih one of them operates as a normal Keller (as it is often shortened to) year round.
As the name implies, a beer garden is in a garden. It may be entirely outdoors, or you may be able to choose between an indoor (almost always non-smoking) area and an outdoor area. They range in size from small, cozy corners to some of the largest eating establishments in the world, capable of seating thousands. Munich's Oktoberfest, which happens at the end of September each year, creates some of the most famous temporary beer gardens in the world.
Smaller breweries sell their products straight to the customer and sometimes you will find food there as well. Haxe or Schweinshaxe (the ham hock, or the lower part of the pig's leg) will usually be among the offerings. It is a distinctively German specialty and probably the best dish in almost every establishment of that sort.
Probably 50% of all eating places fall into this group. They are mainly family-run businesses that have been owned for generations, comparable to pubs in the UK. You can go there simply for a drink, or to try German food (often with a local flavour). Food quality differs significantly from place to place but the staff will usually give you an indication of the standard; regulations require restaurant owners to indicate certain possibly harmful ingredients (e.g. glutamates/MSG) in footnotes – a menu containing lots of such footnotes usually indicates low quality; if a cheap "Gasthaus" / restaurant is overcrowded with Germans or Asians, this indicates at least sufficient quality (unless the crowd is thanks to an organized coach excursion).
Germany has a wide range of flavors (e.g. German, Chinese, Japanese, Thai, Polish, Indian, Italian, French, Spanish, Greek, Turkish, Vietnamese) and almost all styles of the world are represented.
Turkish cuisine in Germany ranges from simple "Döner" shops to mostly family-run restaurants offering a wide variation of usually very cheap (in relation to German price levels) Turkish home cooking.
You will rarely find restaurants catering for special needs within Germany (e.g. kosher restaurants are common only in cities with a notable Jewish population like Berlin), although most restaurants will prepare special meals or variants for you if they are neither relying on convenience foods only nor too fancy. Most restaurants have at least some vegetarian meals. Muslims may want to stick to Turkish or Arabic restaurants. At some Turkish or Arab food stalls vegetarians might find falafel and baba ganoush to suit their tastes. For not-so-strict Jews the halal (sometimes spelled helal for the Turkish word for it) Turkish food stalls are also the best option for meat dishes.
In most restaurants in Germany you can choose your own table. You can make reservations (recommended for larger groups and haute cuisine on Saturday nights) and these are marked by reservation cards ("Reserviert"). In expensive restaurants in larger cities you will be expected to make reservations and will be seated by the staff (who will not allow you to choose your table).
Restaurants in commercial areas often offer weekday lunch specials. These are cheap (starting at €5, sometimes including a beverage) options and a good way to sample local food. Specials tend to rotate on a daily or weekly basis, especially when fresh ingredients like fish are involved.
Some restaurants offer all-you-can-eat-buffets where you pay around 10 euros and can eat as much as you want. Drinks are not included in this price.
"XXL-Restaurants" are rising in popularity. These offer mostly standard meat dishes like Schnitzel or Bratwurst in big to inhumane sizes. There is often a dish that is virtually impossible to eat alone (usually bordering 2 kg!) but if you manage to eat everything (and keep it inside), the meal will be free and you'll get a reward. Unlike in other restaurants it is common and encouraged to take leftover food home.
At very formal events and in high-end restaurants, a few German customs may differ from what some visitors may be used to:
- It's considered bad manners to eat with your elbows resting on the table. Keep only your wrists on the table. Most Germans will keep up these manners in everyday life since this is one of the most basic rules parents will teach their children. If you go to a restaurant with your German friends, you may want to pay attention too.
- When moving the fork to your mouth, the tines should point upwards (not downwards as in Britain)
- When eating soup or other food from your spoon, hold it with the tip towards your mouth (not parallel to your lips as in, again, Britain). Spoons used to stir beverages, e.g. coffee, should not be put in the mouth at all.
- If you have to temporarily leave the table, it's fine to put your napkin (which should have rested, folded once along the centre, on your lap until then) on the table, to the left of your plate, in an elegant little pile—unless it looks really dirty, in which case you might want to leave it on your chair.
- If you want the dishes to be cleared away put you knife and fork parallel to each other with the tips at roughly the half past eleven mark of your plate. Otherwise the waitstaff will assume you are still eating.

Rinderroulade mit Rotkraut und Knödeln: this dish is quite unique to Germany. Very thin sliced beef rolled around a piece of bacon and pickled cucumber until it looks like a mini barrel (5 cm diameter) flavoured with tiny pieces of onion, German mustard, ground black pepper and salt. The meat is quick-fried and is then left to cook slowly for an hour, meanwhile red cabbage and potato dumplings are prepared and then the meat is removed from the frying pan and gravy is prepared in the frying pan. Knödel, Rotkraut and Rouladen are served together with the gravy in one dish.
 Schnitzel mit Pommes Frites: there are probably as many different variations of Schnitzel as there are restaurants in Germany, most of them have in common a thin slice of pork that is usually breaded, and fried for a short period of time and it is often served with fries (usually called Pommes Frites or often just Pommes). Variations of this are usually served with different types of gravy: such as Zigeunerschnitzel, Zwiebelschnitzel, Holzfäller Schnitzel and Wiener Schnitzel (as the name suggests, an Austrian dish – the genuine article must be veal instead of pork, which is why most restaurants offer a Schnitzel Wiener Art, or Viennese-style schnitzel which is allowed to be pork). In the south you can often get Spätzle (pasta that Swabia is famous for) instead of fries with it. Spätzle are egg noodles typical of south Germany – most restaurants make them fresh. Due to the ease of its preparation ordering it might be perceived as an insult to any business with a decent reputation (with the exception of Wiener Schnitzel perhaps), admittedly it is almost unavoidable to spot it on the menu of any sleazy German drinking hole (and there are many...), if nothing else therefore it might even be the most common dish in German restaurants (yes, at least German government officials do call their taverns as well as the common fast food stalls restaurants!).
Schnitzel mit Pommes Frites: there are probably as many different variations of Schnitzel as there are restaurants in Germany, most of them have in common a thin slice of pork that is usually breaded, and fried for a short period of time and it is often served with fries (usually called Pommes Frites or often just Pommes). Variations of this are usually served with different types of gravy: such as Zigeunerschnitzel, Zwiebelschnitzel, Holzfäller Schnitzel and Wiener Schnitzel (as the name suggests, an Austrian dish – the genuine article must be veal instead of pork, which is why most restaurants offer a Schnitzel Wiener Art, or Viennese-style schnitzel which is allowed to be pork). In the south you can often get Spätzle (pasta that Swabia is famous for) instead of fries with it. Spätzle are egg noodles typical of south Germany – most restaurants make them fresh. Due to the ease of its preparation ordering it might be perceived as an insult to any business with a decent reputation (with the exception of Wiener Schnitzel perhaps), admittedly it is almost unavoidable to spot it on the menu of any sleazy German drinking hole (and there are many...), if nothing else therefore it might even be the most common dish in German restaurants (yes, at least German government officials do call their taverns as well as the common fast food stalls restaurants!).
Rehrücken mit Spätzle: Germany has maintained huge forests such as the famous Black Forest, Bayrischer Wald and Odenwald. In and around these areas you can enjoy the best game in Germany. Rehrücken means venison tenderloin and it is often served with freshly made noodles such as Spätzle and a very nice gravy based on a dry red wine.
 Wurst "sausage": there is no country in the world with a greater variety of sausages than Germany and it would take a while to mention them all. "Bratwurst" is fried, other varieties such as the Bavarian "Weißwurst" are boiled. Here is the shortlist version: "Rote" beef sausage, "Frankfurter Wurst" boiled pork sausage made in the Frankfurt style, "Pfälzer Bratwurst" sausage made in Palatine style, "Nürnberger Bratwurst" Nuremberg sausage – the smallest of all of them, but a serious contender for the best tasting German sausage, "grobe Bratwurst", Landjäger, Thüringer Bratwurst, Currywurst, Weißwurst ... this could go on till tomorrow. If you spot a sausage on a menu this is often a good (and sometimes the only) choice. Often served with mashed potato, fries or potato salad. The most popular type of sausage probably is the Currywurst (Bratwurst cut into slices and served with ketchup and curry powder) and can be bought almost everywhere.
Wurst "sausage": there is no country in the world with a greater variety of sausages than Germany and it would take a while to mention them all. "Bratwurst" is fried, other varieties such as the Bavarian "Weißwurst" are boiled. Here is the shortlist version: "Rote" beef sausage, "Frankfurter Wurst" boiled pork sausage made in the Frankfurt style, "Pfälzer Bratwurst" sausage made in Palatine style, "Nürnberger Bratwurst" Nuremberg sausage – the smallest of all of them, but a serious contender for the best tasting German sausage, "grobe Bratwurst", Landjäger, Thüringer Bratwurst, Currywurst, Weißwurst ... this could go on till tomorrow. If you spot a sausage on a menu this is often a good (and sometimes the only) choice. Often served with mashed potato, fries or potato salad. The most popular type of sausage probably is the Currywurst (Bratwurst cut into slices and served with ketchup and curry powder) and can be bought almost everywhere.
Königsberger Klopse: Literally "meatballs from Königsberg", this is a typical dish in and around Berlin. The meatballs are made out of minced pork and anchovies and are cooked and served in a white sauce with capers and rice or potatoes.
Matjesbrötchen: Soussed herring or "roll mops" in a bread roll, typical street snack.
 Starting from the north of Germany going south you will find a tremendous variety of food and each region sticks to its origins.
The coastal regions are fond of seafood and famous dishes include "Finkenwerder Scholle".
Starting from the north of Germany going south you will find a tremendous variety of food and each region sticks to its origins.
The coastal regions are fond of seafood and famous dishes include "Finkenwerder Scholle".
In the region of Cologne you will find Sauerbraten, which is a roast marinated in vinegar. Traditionally made from the tough meat of the horses who worked their lives pulling river barges up the Rhine, these days the dish is usually made from beef.
Labskaus (although strictly speaking not a German invention) is a dish from the north and the opinions about this dish are divided, some love it, others hate it. It is a mash of potato, beetroot juice and cured meat decorated with rollmops and/or young herring and/or a fried egg and/or sour cucumber and/or beetroot slices on top. The north is also famous for its lamb dishes, the best type of lamb probably being "Rudenlamm" (lamb from Ruden, a small island in the Baltic Sea; only a few restaurants in Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania serve this), the second best type being "Salzwiesenlamm" (salt meadow lamb). The Lueneburger Heide (Lueneburg Heath) is famous not only for its heath but also for its Heidschnucken, a special breed of sheep. Be aware that a lot of restaurants import their lamb from New Zealand though because it is cheaper. Crabs and mussels are also quite common along the German coasts, especially in North Frisia.
A specialty of Hamburg is "Aalsuppe" which – despite the name (in this case "Aal" means "everything", not "eel") – originally contained almost everything – except eel (today many restaurants include eel within this soup, because the name confused tourists). At the coast there's a variety of fish dishes. Beware: if a restaurant offers "Edelfischplatte" or any dish of similar name, the fish may not be fresh and even (this is quite ironic) of poor quality. Therefore, it is strongly recommended that, for eating fish, you visit specialised (or quality) restaurants only. A fast-food style restaurant chain serving standardized quality fish and other seafood at low prices all over Germany is "Nordsee", though you will rarely find authentic specialties there.
 Pfälzer Saumagen: Long a well-known dish in Palatinate, but difficult to find outside of this area. Literally this is pig stomach filled with a mash of potato and meat, cooked for 2–3 hours and then cut into thick slices. It is often served with sauerkraut. It gained some notoriety as Helmut Kohl was fond of serving it to official state guests such as Gorbachev and Reagan when he was Chancellor.
Pfälzer Saumagen: Long a well-known dish in Palatinate, but difficult to find outside of this area. Literally this is pig stomach filled with a mash of potato and meat, cooked for 2–3 hours and then cut into thick slices. It is often served with sauerkraut. It gained some notoriety as Helmut Kohl was fond of serving it to official state guests such as Gorbachev and Reagan when he was Chancellor.
Swabia is famous for Spätzle (a kind of noodle, often served with cheese as Kässpätzle) and "Maultaschen" (noodles stuffed with spinach and mince meat, but lots of variations, even veggie ones, exist).
In Bavaria this may be Schweinshaxe mit Knödeln (pork's leg with knödel, a form of potato dumplings), "Leberkäs/Fleischkäse mit Kartoffelsalat" (a type of meat pie and potato salad), "Nürnberger Bratwurst" (probably the smallest sausage in Germany), Weißwurst (white sausages) and "Obatzda" (a spicy mix of several milk products).
The south is also famous for its nice tarts such as the "Schwarzwälder Kirschtorte" (tart with lots of cream and spirits made from cherries).
A delicacy in Saxony is Eierschecke, a cake made of eggs and cream similar to cheese cake.
A specialty of the East is "Soljanka" (originally from Ukraine, but probably the most common dish in the GDR), a sour soup containing vegetables and usually some kind of meat or sausages.
 White asparagus (Spargel) floods the restaurants from April to June all over Germany, especially in and around Baden-Baden and the small town of Schwetzingen ("The Asparagus Capital"), near Heidelberg, in an area north and north-east of Hannover ("Lower Saxony's Asparagus Route"), as well as in the area southwest of Berlin, especially in the town of Beelitz and along the Lower Rhine ("Walbecker Spargel"). Franconia, particularly the Knoblauchsland around Nuremberg also produces quite good asparagus. Many vegetables can be found all year round and are often imported from far away, whereas asparagus can be found for only 2 months and is best enjoyed fresh after harvest, it stays nice for a couple of hours or until the next day. The asparagus is treated very carefully and it is harvested before it is ever exposed to daylight, so that it remains white. When exposed to daylight it changes its colour to green and might taste bitter. Therefore, white asparagus is considered to be better by most Germans. Especially in areas with a Spargel growing tradition the devotion to this white vegetable can seem near-religious and even rural mom and pop restaurants will have a page or more of Spargel recipes in addition to their normal menu.
White asparagus (Spargel) floods the restaurants from April to June all over Germany, especially in and around Baden-Baden and the small town of Schwetzingen ("The Asparagus Capital"), near Heidelberg, in an area north and north-east of Hannover ("Lower Saxony's Asparagus Route"), as well as in the area southwest of Berlin, especially in the town of Beelitz and along the Lower Rhine ("Walbecker Spargel"). Franconia, particularly the Knoblauchsland around Nuremberg also produces quite good asparagus. Many vegetables can be found all year round and are often imported from far away, whereas asparagus can be found for only 2 months and is best enjoyed fresh after harvest, it stays nice for a couple of hours or until the next day. The asparagus is treated very carefully and it is harvested before it is ever exposed to daylight, so that it remains white. When exposed to daylight it changes its colour to green and might taste bitter. Therefore, white asparagus is considered to be better by most Germans. Especially in areas with a Spargel growing tradition the devotion to this white vegetable can seem near-religious and even rural mom and pop restaurants will have a page or more of Spargel recipes in addition to their normal menu.
The standard asparagus meal is the asparagus stalks, hollandaise sauce, boiled potatoes, and some form of meat. The most common meat is ham, preferably smoked; however, you will also find it teamed with schnitzel (fried breaded pork), turkey, beef, or whatever is available in the kitchen.
White asparagus soup is one of the hundreds of different recipes that can be found with white asparagus. Often it is made with cream and contains some of the thinner asparagus pieces.
 Another example of a seasonal specialty is kale (Grünkohl). You can find that mainly in Lower Saxony, particularly the southern and south-western parts such as the "Emsland" or around the "Wiehengebirge" and the "Teutoburger Wald", but also everywhere else there and in the eastern parts of North-Rhine-Westphalia. It is usually served with a boiled rough sort of sausage (called "Pinkel") and roasted potatoes. If you are travelling in Lower-Saxony in fall, you should get it in every "Gasthaus".
Another example of a seasonal specialty is kale (Grünkohl). You can find that mainly in Lower Saxony, particularly the southern and south-western parts such as the "Emsland" or around the "Wiehengebirge" and the "Teutoburger Wald", but also everywhere else there and in the eastern parts of North-Rhine-Westphalia. It is usually served with a boiled rough sort of sausage (called "Pinkel") and roasted potatoes. If you are travelling in Lower-Saxony in fall, you should get it in every "Gasthaus".
Lebkuchen are some of Germany's many nice Christmas biscuits and gingerbread. The best known are produced in and around Nuremberg.
Stollen is a kind of cake eaten during the Advent season and yuletide. Original Stollen is produced only in Dresden, Saxony; however, you can buy Stollen everywhere in Germany (although Dresdner Stollen is reputed to be the best and comparatively cheap).
Around St. Martin's day and Christmas, roasted geese ("Martinsgans" / "Weihnachtsgans") are quite common in German restaurants, accompanied by "Rotkraut" (red cabbage, in southern Germany it is often called Blaukraut) and "Knödeln" (potato dumplings), preferably served as set menu, with the liver, accompanied by some kind of salad, as starter, goose soup, and a dessert.
 Germans are very fond of their bread (Brot), which they make in many variations. This is the food that Germans tend to miss most when away from home. Most people like their bread relatively dark and dense and scorn the soft loaves sold in other countries. Bakeries will rarely provide less than twenty different sorts of bread and it's worth trying a few of them. In fact, many Germans buy their lunch or small snacks in bakeries instead of takeaways or the like. Prices for a loaf of bread will range from to, depending on the size (real specialties might cost more).
Germans are very fond of their bread (Brot), which they make in many variations. This is the food that Germans tend to miss most when away from home. Most people like their bread relatively dark and dense and scorn the soft loaves sold in other countries. Bakeries will rarely provide less than twenty different sorts of bread and it's worth trying a few of them. In fact, many Germans buy their lunch or small snacks in bakeries instead of takeaways or the like. Prices for a loaf of bread will range from to, depending on the size (real specialties might cost more).
Because German bread tends to be excellent, sandwiches (belegtes Brot) are also usually to a high standard, including in train stations and airports. However, if you want to save money do as most locals and make the sandwich yourself as belegtes Brot can be quite expensive when bought ready made.
Outside of big cities like Berlin, there aren't many places which are particularly aimed at vegetarian or vegan customers. Most restaurants have one or two vegetarian dishes. If the menu doesn't contain vegetarian dishes, don't hesitate to ask.
Be careful when ordering to ask whether the dish is suitable for vegetarians, as chicken stock and bacon cubes are a commonly "undeclared" ingredient on German menus.
However, there are usually organic food shops ("Bioladen", "Naturkostladen" or "Reformhaus") in every city, providing veg(etari)an bread, spreads, cheese, ice cream, vegan milk substitutes, tofu and seitan. The diversity and quality of the products is great and you will find shop assistants that can answer special nutritional questions in great depth.
Veganism and vegetarianism is on the rise in Germany so that many supermarkets (such as Edeka and Rewe) have a small selection of vegan products as well in their "Feinkost"-section such as seitan-sausages, tofu or soy milk at a reasonable price.
When shopping for foods, the package labelling in Germany is generally reliable. All food products must be properly labelled including additives and preservatives. Be on the look out for Weizen (wheat), Mehl (flour) or Malz (malt) and Stärke (starch). Be extra cautious for foods with Geschmacksverstärker (flavour enhancers) that may have gluten as an ingredient.
- Reformhaus. 3,000 strong network of health food stores in Germany and Austria that has dedicated gluten-free sections stocked with pasta, breads and treats. Reformhaus stores are usually found in the lower level of shopping centres (eg: PotsdamerArkaden, etc.)
- DM Stores. The CWS/Shopper's Drug Mart equivalent in Germany has dedicated wheat and gluten free sections
- Alnatura. – natural foods store with a large dedicated gluten-free section
Reformhaus. 3,000 strong network of health food stores in Germany and Austria that has dedicated gluten-free sections stocked with pasta, breads and treats. Reformhaus stores are usually found in the lower level of shopping centres (eg: PotsdamerArkaden, etc.)
DM Stores. The CWS/Shopper's Drug Mart equivalent in Germany has dedicated wheat and gluten free sections
Alnatura. – natural foods store with a large dedicated gluten-free section
The legal drinking ages are:
- 14 - minors are allowed to buy undistilled (fermented) alcoholic beverages in a restaurant, such as beer and wine, as long as they are in the company of their parents or a legal guardian.
- 16 - minors are allowed to buy undistilled (fermented) alcoholic beverages, such as beer and wine without their parents or a legal guardian. Any drink that contains distilled alcohol (even if the overall alcohol content is lower than for a typical beer) is not allowed
- 18 - having become adults, people are allowed unrestricted access to alcohol.
For centuries, beer-making in Bavaria has been governed by the Reinheitsgebot (purity law) that was made national policy with the unification of Germany in 1871, which states that German beer may be made only from hops, malt and water (yeast was still not known back then). The Reinheitsgebot has been watered down with imports due to European integration, but German breweries still have to stick to it since for them, national law applies. The national law has however also been watered down and now states that a variety of additives and auxiliary substances may be used during the production process, as long as they aren't found in the end product.
The domestic beer market is not dominated by one or only a few big breweries. Even though there are some big players, the regional diversity is enormous, and there are over 1,200 breweries with most of them serving only local markets. Usually bars and restaurants serve the local varieties that differ from town to town. However the North has less variety than the south and especially in localities that aren't specialized in beer you are more likely to get mass-produced watered down Pils from the big breweries than not. If you truly want to experience German beer, try sticking with smaller brands, as they don't have to appeal to a mass market and are thus more "individual" in taste. When sitting in a German Kneipe, a local beer is always an option, and often the only option.
Specialties include Weizenbier (or Weißbier in Bavaria), a refreshing top-fermented beer which is popular in the south, Alt, a kind of dark ale that is especially popular in and around Düsseldorf, and Kölsch, a special beer brewed in Cologne. "Pils", the German name for pilsner, is a light-gold beer that is extremely popular in Germany. There are also seasonal beers, which are made only at particular times of the year (such as Bockbier in winter and Maibock in May, both containing a greater quantity of alcohol, sometimes double that of a normal Vollbier).
Beer is usually served in 200 or 300mL glasses (in the northern part) or 500mL in the South. In Biergartens in Bavaria, 500mL is a small beer ("Halbe") and a litre is normal ("Maß" pronounced "Mahss"). Except in "Irish pubs", pints or pitchers are uncommon.
For Germans, a lot of foam is both a sign of freshness and quality; thus, beer is always served with a lot of head. (All glasses have volume marks for the critical souls.)
Additionally, Germans are not afraid to mix beer with other drinks (though the older generation may disagree). Beer is commonly mixed with carbonated lemonade (usually at 1:1 ratio) and called a "Radler" (or cyclist so named because it is commonly associated with a refreshing drink a cyclist might enjoy in spring or summer during a cycling excursion) (or "Alsterwasser"/"Alster" (after the river in Hamburg) in the north); "Cocktails" of Pilsener/Altbier and soft drinks like Fanta, a "Krefelder"/"Colaweizen" cola and dark wheat beer is another combination that can be found. Pils mixed with Cola is very popular especially among younger Germans and goes by different names – depending on your area – such as "Diesel", "Schmutziges" (dirty) or "Schweinebier" (pigs beer). Another famous local delicacy is "Berliner Weiße", a cloudy, sour wheat beer of around 3% abv. that is mixed with syrups (traditionally raspberry) and is very refreshing in summer. These beer-based mixed drinks are widespread and popular and can be bought as pre-mixed bottles (typically in six packs) wherever regular beer is sold.
Pubs are open in Germany until 02:00 or later. Food is generally available until midnight. Germans typically go out after 20:00 (popular places are already full by 18:00).
 Undisputed capital of "Apfelwein" (or Äbblwoi as it is locally called) cider in Germany is Frankfurt. Frankfurters love their cider. There are even special bars ("Apfelweinkneipe") that will serve only Apfelwein and some gastronomic specialities. Cider is often served in a special jug called "Bembel". The taste is slightly different from ciders in other countries and tends to be quite refreshing. In autumn when apples are turned into cider you might find "Frischer Most" or "Süßer" signposted at some places. That is the first product in the chain of "Apfelwein" production; one glass of it is nice, but after two or three glasses you will have a problem unless you enjoy spending lots of time on the toilet. In the Saarland and surrounding regions "Apfelwein" is called "Viez". It varies here from "Suesser Viez" (sweet), to "Viez Fein-Herb" (medium sweet) to "Alter Saerkower" (sour). The Viez capital of that region is Merzig. During winter it is also quite common to drink hot cider (along with some cloves and sugar). It is
considered an efficient measure against an oncoming cold.
Undisputed capital of "Apfelwein" (or Äbblwoi as it is locally called) cider in Germany is Frankfurt. Frankfurters love their cider. There are even special bars ("Apfelweinkneipe") that will serve only Apfelwein and some gastronomic specialities. Cider is often served in a special jug called "Bembel". The taste is slightly different from ciders in other countries and tends to be quite refreshing. In autumn when apples are turned into cider you might find "Frischer Most" or "Süßer" signposted at some places. That is the first product in the chain of "Apfelwein" production; one glass of it is nice, but after two or three glasses you will have a problem unless you enjoy spending lots of time on the toilet. In the Saarland and surrounding regions "Apfelwein" is called "Viez". It varies here from "Suesser Viez" (sweet), to "Viez Fein-Herb" (medium sweet) to "Alter Saerkower" (sour). The Viez capital of that region is Merzig. During winter it is also quite common to drink hot cider (along with some cloves and sugar). It is
considered an efficient measure against an oncoming cold.
Germans drink lots of coffee. The port of Hamburg is the world's busiest place for coffee trading. Coffee is always freshly made from ground coffee or beans – no instant. However, persons coming from countries with a great coffee tradition (like Italy, Portugal, Turkey, Greece or Austria) might find the coffee that is served in normal restaurants a bit boring. A German specialty, originating from North Frisia but nowadays also common in East Frisia, is "Pharisäer", a mixture of coffee and a spirit, usually rum, with a thick cream top. A variation of this is "Tote Tante" (dead aunt, with coffee replaced by hot chocolate).
Over the past few years, American coffee house chain Starbucks or clones have expanded into Germany, but mostly you will encounter "Cafés" which usually offer a large selection of cakes to go along with the coffee.
Visiting Germany in December? Then go and see one of the famous Christmas Markets (the most famous taking place in Nuremberg, Dresden, Leipzig, Münster, Bremen, Augsburg and Aachen) and this is the place where you find Glühwein (mulled wine), a spiced wine served very hot to comfort you in the cold of winter.
A generic word for spirits made from fruit is Obstler, and each area has its specialities.
Bavarians like their beer as well their Enzian, a spirit high in alcohol that is best as a digestive after a hefty meal.
Kirschwasser literally means cherry water; it certainly tastes of cherry but on the other hand it is not regular drinking water. There is a long lasting tradition in making spirits in Baden, and "Kirschwasser" is probably the flagship product and it might encourage you to taste other specialties such as Himbeergeist (from raspberry), Schlehenfeuer (flavored with sloe berries), Williamchrist (pear) and Apfelkorn (apple juice and Korn).
Korn, made of grain, is probably the most common spirit in Germany. Korn is more popular in the North, where it exceeds beer in popularity. In the South the situation is reversed. Its main production center (Berentzen) lies in Haselünne, where tours and tastings can be arranged in the distilleries. The town is near the river Ems in northwest Germany; for rail service to Haselünne (very sparse) see Eisenbahnfreunde Hasetal. A common mixture is Korn with apple juice ("Apfelkorn") which usually works out to about 20% abv. and is usually consumed by younger people. Another town famous for its Doppelkorn (with over five hundred years of tradition to boot) is Nordhausen in Thuringia, where tours and tastings are also easily arranged.
In Lower Saxony, especially in areas surrounding the Lüneburg Heath, different specialised liquors and schnaps are prominent. Ratzeputz holds 58% alcohol and contains extracts and distillates of root ginger. Heidegeist is a herbal liquer that contains 31 heather ingredients with an alcohol content of 50%. It is clear in colour and has a strong, minty taste.
In North Frisia, Köm (caraway spirit), either pure or mixed with tea ("Teepunsch", tea punch), is very popular.
Eiergrog is a hot mixture of egg liquor and rum.
Tea, Tee, is also very popular, and a large choice is readily available. The region of East Frisia in particular has a long tea tradition, and is probably the only place in Germany where tea is more popular than coffee. The East Frisian tea ceremony consists of black tea served in a flat porcelain cup with special rock sugar (Kluntje) that is put in the cup before pouring the tea. Cream is added afterwards, but is not stirred into the tea. The East-Frisian fondness for tea was made fun of in a rather infamous commercial for a certain sweet that supposedly goes well with coffee, only for the claim to be interrupted by a noisy East-Frisian who would say "Und was is mit Tee?" (And what about tea?) in a stereotypical Northern German accent. Most Germans still know this sentence, if not necessarily its origin.
Especially in winter, Germans love their hot chocolate (heiße Schokolade), which is widely available. Hot chocolate in Germany tends to be more or less Zartbitter — that is, bittersweet — and in the more gourmet establishments, it can be quite dark and bitter and only a little sweet. It is commonly served with Schlag (fresh whipped cream, also called Schlagsahne). Although usually served pre-prepared some cafes will serve a block of chocolate that you mix and melt into the hot milk yourself. Milk chocolate is called Kinderschokolade ("children's chocolate") in Germany and not taken seriously at all, so don't expect to be able to order hot milk chocolate if you are an adult.
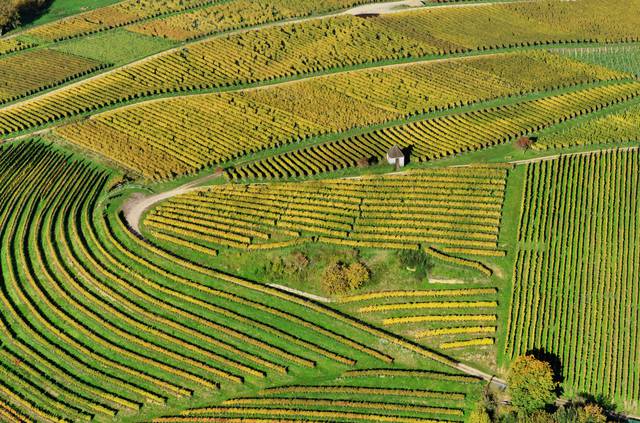 Some Germans are just as passionate about their wines (Wein) as others are about their beer. The similarities don't stop here; both products are often produced by small companies, and the best wines are consumed locally. The production of wine has a 2,000-year-old history in Germany as may be learned from the Rheinisches Landesmuseum in Trier but, of course, this was a Roman settlement at that time. Sunshine is the limiting factor for the production of wines in Germany and, therefore, wine production is limited to the south. White wine plays a main role in the wine production, but some areas produce red wines (Ahr, Baden Württemberg). White wines are produced from Riesling, Kerner and Müller-Thurgau grapes (there are many more), and produce generally fresh and fruity wines. German wines can be rich in acid and are quite refreshing. It is generally accepted that Riesling grapes produce the best German wines, but they demand a lot of sunshine and they grow best in very exposed areas such as the Mosel, Rheingau, Bergstraße, Kaiserstuhl and Pfalz.
Some Germans are just as passionate about their wines (Wein) as others are about their beer. The similarities don't stop here; both products are often produced by small companies, and the best wines are consumed locally. The production of wine has a 2,000-year-old history in Germany as may be learned from the Rheinisches Landesmuseum in Trier but, of course, this was a Roman settlement at that time. Sunshine is the limiting factor for the production of wines in Germany and, therefore, wine production is limited to the south. White wine plays a main role in the wine production, but some areas produce red wines (Ahr, Baden Württemberg). White wines are produced from Riesling, Kerner and Müller-Thurgau grapes (there are many more), and produce generally fresh and fruity wines. German wines can be rich in acid and are quite refreshing. It is generally accepted that Riesling grapes produce the best German wines, but they demand a lot of sunshine and they grow best in very exposed areas such as the Mosel, Rheingau, Bergstraße, Kaiserstuhl and Pfalz.
The best way to learn about wines is go to the place where they are grown and taste them on the spot. This is called "Weinprobe" and is generally free of charge - though in touristed areas you have to pay a small fee.
Good wines usually go together with good food so you might like to visit when you are hungry as well as thirsty. The so-called Straußenwirtschaft, Besenwirtschaft or Heckenwirtschaft are little "pubs" or gardens where a wine-producer sells his own wine, normally with little meals such as sandwiches or cheese and ham. Normally, they are open only in summer and autumn, and not longer than 4 months a year (due to legal regulations). As they are sometime in the vineyards or in some back streets, they are not always easy to find, so you best ask a local for the next (or best) Straußenwirtschaft he knows.
During the fall you can buy "Federweisser" in south-western Germany. This is a partially fermented white wine and contains some alcohol (depending on age), but tastes very sweet. It is also available from red grapes, being called "Roter Sauser" or "Roter Rauscher".
 Wine producing areas are:
Wine producing areas are:
- Ahr is the paradise of German red wines. Half of the production is dedicated to red wines and it is densely populated with "Gaststätten" and "Strausswirten". A saying goes: Whoever visited the Ahr and remembers that he was there, hasn't actually been there.
- Baden with c. 15,500 hectares of wine yards and a production of 1 million hectolitres, Baden is Germany's third biggest wine growing area. It's the most southerly German wine growing area and is Germany's only member of the European Wine Category B together with the famous French areas Alsace, Champagne and Loire. Baden is more than 400 km long and is split into nine regional groups: Tauberfranken, Badische Bergstraße, Kraichgau, Ortenau, Breisgau, Kaiserstuhl, Tuniberg, Markgräflerland and Bodensee. The Kaiserstuhl and the Markgräflerland are the most famous areas for wine from Baden. One of the largest wine cooperatives is the Badischer Winzerkeller in Breisach.
- Franken: Franconia is in the northern part of Bavaria and you can find there very nice wines, most commonly the dry white wine. Some wines produced in Franconia are sold in a special bottle called "Bocksbeutel".
- Hessische Bergstraße: on the slopes of the Rhine valley it is a quiet small wine producing area and wines are usually consumed within the area in and around Heppenheim.
- Mosel-Saar-Ruwer: the steepest vineyards in Germany can be seen when driving in the Mosel valley from Koblenz to Trier.
- Pfalz: biggest wine producing area in Germany. Has some excellent wines to taste and a lot of nice villages embedded in vineyards. Tasting wine in Deidesheim is a good idea and several prime producers of German wine are on the main road. Want to see the biggest wine barrel in the world? Then go to Bad Dürkheim.
- Rheingau: is the smallest wine producing area, but it produces the highest -rated Riesling wines in Germany. Visit Wiesbaden and make a trip on the Rhine to Eltville and Rüdesheim.
- Rheinhessen too is especially famous for its Riesling. Visit Mainz and make a trip on the Rhine to Worms, Oppenheim, Ingelheim or Bingen.
- Saale-Unstrut: in the state of Saxonia-Anhalt on the banks of the rivers Saale and Unstrut is the most northern wine producing area in Europe.
- Sachsen: One of the smallest wine regions in Germany, nestled along the Elbe River near Dresden and Meissen.
- Württemberg: As was mentioned before, here the rule that the best wine is consumed by locals, strictly applies; wine consumption per head is twice as high as in the rest of Germany, regardless of whether it's red or the white wine. The speciality of the region is the red wine called Trollinger and it can be quite nice by German standards.
Ahr is the paradise of German red wines. Half of the production is dedicated to red wines and it is densely populated with "Gaststätten" and "Strausswirten". A saying goes: Whoever visited the Ahr and remembers that he was there, hasn't actually been there.
Baden with c. 15,500 hectares of wine yards and a production of 1 million hectolitres, Baden is Germany's third biggest wine growing area. It's the most southerly German wine growing area and is Germany's only member of the European Wine Category B together with the famous French areas Alsace, Champagne and Loire. Baden is more than 400 km long and is split into nine regional groups: Tauberfranken, Badische Bergstraße, Kraichgau, Ortenau, Breisgau, Kaiserstuhl, Tuniberg, Markgräflerland and Bodensee. The Kaiserstuhl and the Markgräflerland are the most famous areas for wine from Baden. One of the largest wine cooperatives is the Badischer Winzerkeller in [[Breisach]].
[[Franconia|Franken]]: Franconia is in the northern part of [[Bavaria]] and you can find there very nice wines, most commonly the dry white wine. Some wines produced in Franconia are sold in a special bottle called "Bocksbeutel".
[[Hessische Bergstraße]]: on the slopes of the Rhine valley it is a quiet small wine producing area and wines are usually consumed within the area in and around [[Heppenheim]].
Mosel-Saar-Ruwer: the steepest vineyards in Germany can be seen when driving in the Mosel valley from [[Koblenz]] to [[Trier]].
[[Pfalz]]: biggest wine producing area in Germany. Has some excellent wines to taste and a lot of nice villages embedded in vineyards. Tasting wine in [[Deidesheim]] is a good idea and several prime producers of German wine are on the main road. Want to see the biggest wine barrel in the world? Then go to [[Bad Dürkheim]].
[[Rheingau]]: is the smallest wine producing area, but it produces the highest -rated Riesling wines in Germany. Visit [[Wiesbaden]] and make a trip on the Rhine to [[Eltville]] and [[Rüdesheim]].
[[Rheinhessen]] too is especially famous for its Riesling. Visit [[Mainz]] and make a trip on the Rhine to [[Worms]], [[Oppenheim]], [[Ingelheim]] or [[Bingen]].
Saale-Unstrut: in the state of Saxonia-Anhalt on the banks of the rivers Saale and Unstrut is the most northern wine producing area in Europe.
Sachsen: One of the smallest wine regions in Germany, nestled along the Elbe River near [[Dresden]] and [[Meissen]].
Württemberg: As was mentioned before, here the rule that the best wine is consumed by locals, strictly applies; wine consumption per head is twice as high as in the rest of Germany, regardless of whether it's red or the white wine. The speciality of the region is the red wine called Trollinger and it can be quite nice by German standards.
Germany is a very safe country. Crime rates are low and the rule of law is strictly enforced.
Violent crimes (murders, robberies, rapes, assaults) are very rare compared to most countries. For instance, 2010 murder rates were 0.86 cases per 100,000 inhabitants — significantly lower than in the UK (1.17), Australia (1.20), France (1.31), Canada (1.81) and the US (5.0) – and they continue to decline. Pickpockets may sometimes be an issue in large cities or at events with large crowds. Begging is not uncommon in some larger cities, but to no greater extent than in most other major cities and you will rarely encounter aggressive beggars.
If you're staying in certain parts of Berlin or Hamburg (Schanzenviertel) around 1 May (Tag der Arbeit) expect demonstrations that frequently degenerate into clashes between the police and a minority of the demonstrators.
Take the usual precautions and you will most likely not encounter any crime at all while staying in Germany.
The nationwide emergency number for the police, fire and rescue services is 112 (same as in all EU countries) or 110 for police only. These numbers can be dialed toll-free from any phone, including phone booths and mobile phones (SIM-card required). If you are reporting an emergency, the usual guidelines apply: stay calm and state your exact location, the type of emergency and the number of persons involved. Do not hang up until the operator has received all required information and ends the call.
There are orange emergency telephones interspersed along the main motorways. You can find the closest SOS-phone by following arrows on the reflection posts at the side of the road.
Ambulances (Rettungswagen) can be summoned via the national toll-free emergency number 112 and will help you regardless of insurance issues. All hospitals (Krankenhäuser) except for the smallest private ones have 24-hour emergency rooms able to cope with all kinds of medical problems.
The overwhelming majority of foreign visitors will never deal with issues of open racial discrimination or racism in Germany. Large cities in Germany are very cosmopolitan and multiethnic with large communities of people from all continents and religions. Germans are also very aware and ashamed of the historical burden of the Nazi era and are usually open-minded and tolerant in contacts with foreigners. Non-white visitors may get an occasional wary look, but not to a greater extent than in other countries with a predominantly white population.
This general situation may be different in some predominantly rural parts of East Germany (including the outskirts of some cities with higher unemployment levels and high rise neighborhoods i.e. "Plattenbau"). Incidences of racist behaviour can occur with a few incidents of violence. Most of these happen at night when groups of drunken "Neo-Nazis" or some migrant groups might look for trouble (and solitary victims) downtown or near public transport. This might also affect foreign visitors, homeless persons, West Germans and people with alternative looks such as Punks, Goths, etc.
Public displays of overt anti-semitism are strictly forbidden by laws that are very much enforced. The Hitler salute and the Nazi Swastika (but not religious Swastikas) are banned, as is the public denial of the Holocaust. Violations of these laws against racism are not taken lightly by the authorities, even when made in jest. You should also avoid displaying a Swastika even for religious reasons.
 German Police (German: Polizei) officers are always helpful, professional and trustworthy, but tend to be rather strict in enforcing the law, which means that one should not expect that exceptions are made for tourists. When dealing with police you should remain calm, courteous and avoid getting into confrontations. Most police officers should understand at least basic English or have colleagues who do.
German Police (German: Polizei) officers are always helpful, professional and trustworthy, but tend to be rather strict in enforcing the law, which means that one should not expect that exceptions are made for tourists. When dealing with police you should remain calm, courteous and avoid getting into confrontations. Most police officers should understand at least basic English or have colleagues who do.
Police uniforms and cars are green or blue. Green used to be the standard, but most states and the federal police have transitioned to blue uniforms and cars to comply with the EU standard.
Police officers are employed by the states except in airports, train stations, border crossings etc. which are controlled by the federal police (Bundespolizei). In mid-sized towns and big cities, local police (called Stadtpolizei, kommunale Polizeibehörde or Ordnungsamt) have some limited law enforcement rights and are in general responsible for traffic issues. States have a pretty big leeway when it comes to police and their tactics and as most police are state police, there is a marked difference between left wing city states like Berlin and conservative Southern states like Bavaria. As a broad generalization, police in the North tend to be more hands-off and tolerant of minor misbehavior while police in the South show more presence and are stricter about the rules, but you may get fined for jaywalking in Berlin just as well. The only major cases of police using violence on citizens (or vice versa) happen during demonstrations and soccer games, but you will notice that by the riot gear and mounted police patrolling in seemingly vastly excessive numbers. Police are armed but will hardly ever use their weapons and never on unarmed people.
If you get arrested, you have the right to have an attorney. Foreign nationals also have the right to contact their respective embassy for assistance. You are never obliged to make a statement that would incriminate yourself (or someone related to you by blood or marriage) and you have the right to remain silent. Wait until your attorney arrives and talk to your attorney first. If you do not have a lawyer then you can call your embassy or else the local justice official will appoint an attorney for you (if the alleged crime is serious enough).
If you are a victim of a crime (for example robbery, assault or theft in public) and wave an oncoming patrol car or officer, it is not uncommon that the officers will (sometimes very harshly: "Einsteigen") command you to enter the back seat of the police cruiser. This is an action to start an instant manhunt to identify and arrest the suspect. In this case remember that you are not under arrest but to help the officers to enforce the law and maybe get back your property.
German police do have ranks but are not that keen about them; many Germans won't know the proper terms. Do not try to determine seniority by counting the stars on the officers shoulders in order to choose the officer you will address, since such behaviour can be considered disrespectful. Talk to any officer and they will answer your questions or redirect you to the officer in charge.
Prostitution is legal and regulated in Germany.
All larger cities have a red light district with licensed bars, go-gos and escort services. Tabloids are full of ads and the internet is the main contact base. Brothels are not necessarily easily spotted from the streets (outside of redlight districts) to avoid legal action by neighbours. Places best known for their redlight activities are Hamburg, Berlin, Frankfurt and Cologne.
Recreational vehicles parked by the roadside in forests along Bundesstraßen (German for "federal highway"), with a red light in the front window and perhaps a lightly dressed woman on the passenger's seat, are most likely prostitutes soliciting customers.
Due to Germany's proximity to Eastern Europe, several cases of human trafficking and illegal immigration have taken place. Police regularly raid brothels to keep this business within its legal boundaries, and check the identity documents of workers and patrons alike.
Alcohol may be purchased by persons 16 years and older. However, distilled beverages and mixed drinks with those (including the popular 'Alcopops') are available only at 18. It is not technically illegal for younger people to drink, but it is illegal to allow them to drink on premises. Youth 14 years and older are allowed to drink fermented beverages in the presence and with the allowance of their legal guardian. If the police notices underage drinking, they may pick the person up, confiscate the drinks and send the person home in the presence of an officer.
Smoking in public is allowed starting at age 18. Vending machines for cigarettes require a valid "proof of age", which in practice means that you need a German bank card or a (European) driving license to use them.
The situation on marijuana can be confusing. The Constitutional Court ruled that possession for "personal use", though still illegal, should not be prosecuted. Germany is a federal state; therefore the interpretation of this ruling is up to the state authorities. In fact charges are sometimes pressed even for tiny amounts, which will cause you a lot of trouble regardless of the outcome. As a general rule the northern states tend to be more liberal while in the south (especially Bavaria), even negligible amounts are considered illegal. The customs officials are also aware of the fact that you can legally buy marijuana in the Netherlands and therefore set up regular border controls (also inside trains), as importation of marijuana is strictly prohibited.
Even if you get off the charges, the authorities may cause different problems, like revoking your drivers license and if you have more than a few grams, you will be prosecuted in any case. Drugs will be confiscated in all cases.
All other recreational drugs (like ecstasy) are illegal and possession will lead to prosecution and at least a police record.
Crimes with date-rape drugs have been committed, so as anywhere else in the world be careful with open drinks.
Some types of knives are illegal in Germany: this concerns mostly some types of spring knives, "butterfly" knives, knuckle knives and the like — possessing such knives is an offense. Knives that are intended as weapons are restricted to persons over 18. Furthermore, nunchakus, even soft-nunchakus, are illegal in Germany.
It is illegal to carry any type of "dangerous knife" on your person in public unless you have a valid reason to do so. For example, if you are out fishing you are still entitled to carry a fishing knife. "Dangerous" knives are generally those with a blade length exceeding 12 cm and locking "one-handed" folding knives.
Carrying any knife beyond a pocket knife (typically Swiss army knives) without any professional reasons (carpenter, etc.) is seen as very rude and unacceptable in Germany. Germans consider any non-professional used knives as signs of aggression and do not accept this behaviour. Flashing a knife (even folded) may cause bystanders to call the police, who will be very serious in handling the upcoming situation.
Firearms are strictly controlled. It is practically impossible to legally carry a gun in public unless you are a law enforcement officer. "Fake" firearms may not be carried in public if they resemble real guns. CO2 and air guns are relatively easy to acquire. If the police find any kind of weapon or firearm on you, you will appear highly suspicious.
Bow and arrow do not legally count as weapons while crossbows do, but you're certain to get stopped by police openly carrying either. Hunting is only legal with firearms or employing birds of prey and requires a license with rather strict requirements for environmental and animal welfare reasons.
Avoid bringing any fireworks into Germany, especially from outside the EU. Even bringing those can be an offence. Fireworks are traditionally used on New Year's Eve. Most "proper" fireworks (marked as "Klasse II") will be available at only the end of the year; they may be used by persons only over 18 on December 31 and January 1. Really small items (marked as "Klasse I") may be used around the year by anyone.
Fishing laws differ a lot from state to state. Obtaining a fishing license for Germans and foreigners has become a highly bureaucratic process due to animal protection laws.
Germany is in general very tolerant of homosexuality. Nevertheless, like in every country some individuals still may disapprove and some areas are more accepting than others, so use common sense and be geared to the behaviour of the locals around you. In small towns and in the countryside, open displays of homosexuality should be limited.
The attitude towards gays and lesbians is rather tolerant, with openly gay politicians and celebrities being considered increasingly normal. While some, especially the elderly, Germans inwardly still don't approve of homosexuality or bisexuality, they usually suppress open utterances of homophobia. Therefore, in most cases, display of homosexuality (holding hands or kissing) will at most provoke stares or sometimes comments by children or elderly people.
Sanitary and medical facilities in Germany are excellent. The phone book lists telephone numbers for various medical services, many hotlines and services exist that are open during "off hours". See the section Medical Emergencies above if you are in an emergency
If you have an non-urgent medical problem, you may choose from any local doctor. The German health system allows specialists to run their own surgery so you will usually be able to find every discipline from Dentistry to Neurology on duty within reasonable reach. In remote regions finding a doctor might require a ride to the next town but the German infrastructure allows fast connections. GPs/family doctors will usually describe themselves as "Allgemeinmediziner" – meaning "general medical doctor".
 Pharmacies are called "Apotheke" and are marked by a big, red "A" symbol. At least one pharmacy in the area will be open at all times (usually a different one every day), and all pharmacies will post the name and address of the pharmacy-on-duty in the window. Some medication that is sometimes freely available in other countries (e.g. antibiotics) needs a prescription in Germany, so you may want to check before your journey. The staff of an Apotheke is well-trained, and it is mandatory to have at least one person with a university degree in pharmaceutics available in every Apotheke during opening hours. A German pharmacist is able to offer advice on medications. The apotheke is also where you go to get common over-the-counter medications such as aspirin, antacids, and cough syrup. Don't be misled by the appearance of "drug" in the name of a drogeriekonzern, such as the large dm-drogerie markt chain: "drug stores" in Germany sell everything except drugs.
Pharmacies are called "Apotheke" and are marked by a big, red "A" symbol. At least one pharmacy in the area will be open at all times (usually a different one every day), and all pharmacies will post the name and address of the pharmacy-on-duty in the window. Some medication that is sometimes freely available in other countries (e.g. antibiotics) needs a prescription in Germany, so you may want to check before your journey. The staff of an Apotheke is well-trained, and it is mandatory to have at least one person with a university degree in pharmaceutics available in every Apotheke during opening hours. A German pharmacist is able to offer advice on medications. The apotheke is also where you go to get common over-the-counter medications such as aspirin, antacids, and cough syrup. Don't be misled by the appearance of "drug" in the name of a drogeriekonzern, such as the large dm-drogerie markt chain: "drug stores" in Germany sell everything except drugs.
In Germany pharmaceuticals tend to be expensive, so it might be wise to ask the pharmacist for "Generika" (generic drugs): A "Generikum" is virtually the same substance and dose, often even produced by the same pharmaceutical trust, just lacking the well-known brand name and being considerably cheaper. As the brand names for even common substances can vary a lot between countries as well as brands try to know the scientific name of the substance you need as they will be printed on the package and trained pharmaceutical professionals will know them.
EU citizens that are members of any public health insurance can get a European Health Insurance Card. The card is issued by your insurance provider and lets you use the public health care system in any EU country, including Germany.
If you're from outside the EU, or if you have a private health insurance, check if your insurance is valid in Germany. If not, get a travel health insurance for the trip – German health care is expensive.
Foreign insurance, even if it covers travel abroad, may not be accepted by local hospitals.
In any somewhat urgent case you will be treated first and asked for insurance or presented a bill later.
Tap water (Leitungswasser) is of excellent quality, and can be consumed with little concern. Exceptions are labeled ("Kein Trinkwasser", no drinking water) and can for example be found on fountains and in trains. In restaurants and cafes you will often have to specifically request 'Leitungswasser' since it is not generally assumed.
Many Germans tend to avoid drinking tap water and prefer bottled water (still or sparkling), in the erroneous belief that tap water is somehow of inferior quality. The term Leitungswasser actually means 'plumbing water' which also doesn't actually sound too enticing. As a matter of fact, tap water is sometimes of even better quality than bottled water and unlike in e.g. the US there is no chlorine taste to it whatsoever. However, on some areas there is a taste difference for particularly sensitive palate due to the different mineral composition. Be aware however that some regions tap water have nitrate content above WHO levels and should not be drunk by women in early stages of pregnancy for any prolonged period.
Many Germans prefer sparkling (carbonated) water. Sparkling water is sold in any store that sells beverages and prices range from inexpensive 19-cent bottles (1.5 L) of "no-name" brands to several euros for fancy "premium" brands.
Most people buy bottled water in crates of 12 glass bottles or packs of 6 plastic bottles. Both the bottles and crates include a returnable deposit (Pfand). While the deposits for reusable plastic (15 cents) or glass bottles (8 cents) are relatively low, the deposit for disposable plastic bottles (marked by a special symbol on the side of the bottle) is relatively high at 25 cents and may be higher than the price of the water itself. Bottled water is usually sold carbonated (sparkling), although regular water (stilles Wasser) is also widely available and slowly gaining popularity among Germans. Sparkling water is usually sold in supermarkets in two degrees of sparkling: one with more CO2 (usually called spritzig or classic) and one with less CO2 (usually called medium).
Most springs and many public restrooms (e.g. on planes or trains) use non-potable water that has to be clearly marked by the words "kein Trinkwasser" or a symbol showing a glass of water with a diagonal line through it. If there is no such sign and the surroundings don't indicate otherwise it is safe to assume that the water is safe for human consumption.
Many lakes and rivers, as well as both the North Sea and Baltic Sea are generally safe for swimming. Nevertheless, while there may be no life-threatening pollutants in most bodies of water, you would do very well to inform yourself about local regulations. If you intend to swim in a large river, at best do so only on official bathing locations. Keep away from structures (power plants might cause streams you don't see from the surface) in the river or reaching from the shore into the river, also keep out of the path of ships. Both structures and ships, even if they look harmless or far away, may create major sucks underwater. Take particular care of children.
If you intend to swim in the North Sea you should inform yourselves about the tide schedules and weather conditions – getting caught in a tide can be fatal, getting lost in the mist, too. Hiking in the Wattenmeer without a local guide is extremely dangerous. In the Baltic Sea, on the other hand, there are virtually no tides.
You should be aware of rabies (Tollwut) which has been a problem in some areas in the past, even though the authorities take it very seriously. If you go hiking or camping then be careful around wild animals such as foxes and bats.
The biggest risks hikers and campers face are two diseases transmitted by ticks. In some parts of Germany there is a (low) risk of contracting tick-borne encephalitis; vaccination is advised if you plan out-door activities in high-risk areas. The risk of Lyme disease is higher and vaccination is not available. Therefore, you should try to prevent tick-bites by wearing long trousers and appropriate shoes. Chemical repellents can also be effective. You should also check for ticks afterwards since the risk of transmission is lower if the tick is removed early. The safest way to remove a tick is by using a credit card sized device called a "Zeckenkarte" (tick card), which you can get at most pharmacies. Other methods (fingers, using glue, etc.) might lead to the tick injecting even more infectious material into the wound. If in any doubt consult a doctor.
Today, wild animals, although they abound, are mostly very shy, so you might not get to see many. When a few wolves in Saxony and Pomerania and a bear in Bavaria have been sighted, their immigration from Eastern Europe caused quite a stir. In the course of events, "Bruno" (the bear) was shot, and while the wolves are under heavy protection, local hunters have been suspected of killing them illegally. The most dangerous animal in Germany's forests is by far the wild boar; in particular, sows leading young are nothing to joke about. Wild boar are used to humans, since they often plunder trash cans in villages and suburbs, and their teeth can rip big wounds. If you see one, slowly walk into the opposite direction while still facing the animal. Also the poisonous crossed viper can pose a threat (
in the Alpine region and natural reserves), though they are rare - don't provoke them.
It can be surprisingly hard to locate a public toilet when needed. They are usually indicated by the letters WC, pictograms or the letter "H" (Herren; gentlemen) or "D" (Damen, ladies). Public toilets are rarely free. Sometimes you have to be a customer at the place they're attached to, sometimes there's an attendant and a "tip plate" to guilt trip you into paying money that may or may not be handed on to cleaning personnel. But one of the more common ways they charge you is the Sanifair system whereby you pay an amount of money and get a voucher for a lower amount of money (75 cents pay, 50 cents value) that you are able to cash in for goods at the adjacent (and other) stores, often subject to a bunch of conditions. Thankfully toilets in trains air-planes and buses are still free, but patrons often leave them in a disgusting state and sadly there isn't always someone around who can clean them. Fast food outlets and hotel receptions are usually a good option, fuel stations will usually provide facilities on request of a key.
Individual Bundesländer started banning smoking in public places and other areas in early 2007, however the laws vary from state to state. Smoking is generally banned in all restaurants and cafes. Some places may provide separate smoking areas but it is best to enquire when booking. Smokers should be prepared to step outside if they want to light up. The only three states with a strict non-smoking law without exceptions are Bavaria, Saarland and North Rhine-Westphalia. Smoking is banned on all forms of public transport including on railway platforms (except in designated smoking areas, which are clearly marked with the word Raucherbereich [smoking area]). The laws are strictly enforced.
In restaurants it is widely accepted for customers to leave their table without paying the bill to go for a smoke and return later. If you are alone, tell the staff that you are going outside to smoke, and if you have a bag or coat, leave it there.
Vaping is also upcoming in Germany, more in the urban areas than the country sides. In nearly every city you can find a Dampfershop [vaping store] where you can get hardware or liquid, with or without Nicotine, €3-6 per 10ml. If you stay longer buy base and aroma separate and mix by yourself, it is much cheaper. Bringing large liquid bottles with Nicotine into Germany, in particular with more than 20 mg/ml and from outside the EU, can be illegal. To be safe carry only your needs for few days. The law say vaping is not smoking and so it is not affected by the non-smoking law, but most people do not know this. So if you like to be kind and safe do it like smoking and accept the common no-smoking rules too. Deutsche Bahn and other state-level public transport companies do not allow vaping on stations (except in the smoking areas), nor on their public transport.
The Germans have earned themselves a reputation for being stiff and strict with rules but also hard working and efficient. If you are caught breaking the rules, this will be readily pointed out to you by someone. The main exception in Germany seems to be speed limits. A quintessentially German action is waiting at a red traffic light at 2 AM with all streets empty.
More importantly, the German sense of "politeness" differs significantly from the Anglo-American concept of courteous remarks, small talk and political correctness. Germans highly value honesty, straight talking, being able to cope with criticism and generally not wasting other people's time. For instance, while the answer to "How is your day?" is a standard pleasantry like "It's going very well." in the Anglosphere, Germans will feel obliged to answer the question honestly when asked. Consequently, business meetings tend to lack the introductory chit-chat.
Titles (such as Dr., Prof. etc.) tend to be more used in the south than in the north. One would not blame you to leave them away. Some colleagues that have worked together for many years still call each by their surname. When a German introduces himself to you, he/she will often simply state their surname, prompting you to call them "Mr/Mrs...". Germans would not expect you to use the German words "Herr" (man) and "Frau" (woman) when speaking in English. The title "Fräulein" for an unmarried woman is considered nowadays to be dated or even sexist, so just stick to "Frau".
Using first names immediately is most likely seen as derogatory, depending on the situation. Of course, there are differences between the young and older people. You should consider the use of the surname and the formal Sie as a sign of friendly respect. If you have a drink together, you may be offered the non-formal Du and to call your colleague by his first name, you can also offer it. However it might be seen as a faux-pas to do so if you are clearly younger or "lower-ranking".
The German word Freund actually means close friend, or "boyfriend". Someone you may have known for a few years may still not refer to you as a Freund but rather Bekannter (an acquaintance).
There is also a strong desire to achieve mutual agreement and compromise. As for the infamous efficiency: Germans are the world's leading recreationists (at an average of 30 days of paid leave per year, not counting public holidays), while maintaining one of the highest productivity rates on earth. A late-running train is considered a sign of the degradation of society.
Despite popular belief, the Germans do have a sense of humour although it is often expressed differently than it is in English-speaking countries. If you are around people, you get to know well that sarcasm and irony are very common kinds of humour. Puns are popular too, just like in anglophone countries. However, humor is not the default approach to the world (unlike in - say - England) and therefore a quip in the wrong situation may draw blank stares or disapproval or simply not be understood as a joke.
In official contexts (when conducting business) punctuality is seen not as a courtesy but as a precondition for future relations. As in most countries, you are expected to arrive on time at a business meeting unless you can give a good reason in your defense (i.e. being stuck in unforeseeable heavy traffic). It is seen as a courtesy to call the other participants if you seem to be running late, even if there is still a chance that you will arrive on time. Regular delays are seen as disrespect for the other participants.
For personal relations, importance attached to punctuality may differ from individual to individual. It is still always safer to be punctual than late, but the subject may be a negotiable matter: if unsure just ask 'is punctuality important to you?'. Punctuality also depends on the milieu, in a collegiate environment, for example, it is taken much less seriously. For private invitations to a home, it may even be considered more polite to be 5–15 minutes late as to not embarrass the host in case not everything has been prepared.
Germany, especially urban Germany, is rather tolerant and your common sense should be sufficient to keep you out of trouble.
Drinking alcohol in public is not forbidden and is even a common sight in the far west (Cologne and the Rhine-Ruhr Area). In some larger cities (such as Cologne), there are local laws that in theory make drinking alcohol in public a misdemeanour punishable with a fine of tens of euros; these laws are rarely enforced against tourists, except in cases when drinking leads to rowdy behaviour. Such laws have also been successfully challenged in court in several places. Behaving aggressively or disturbing the peace will earn you a conversation with German police officers and possibly a fine or an order to leave, regardless of whether you're drunk or stone-cold sober.
Be particularly careful to behave respectfully in places of worship and places that carry the dignity of the state, such as the numerous war and holocaust memorials, parliaments and other historical sites. Some such sites will post Hausordnung (house rules) that prohibit disrespectful or disruptive behaviors. These rules may range from common-sense prohibitions against taking pictures during religious ceremonies to things that may seem strange to you, like prohibiting men from keeping their hands in their pockets. You should keep an eye out for these signs and obey the posted rules. Another very common sight is a sign that says Eltern haften für ihre Kinder (parents are liable for their children). This is a reminder that German people believe both that children should be children, and also that parents should supervise them, so that no one gets hurt and nothing gets broken. If your child is being rowdy and accidentally spills or breaks something in a store, you can generally expect to pay for it.
Insulting other people is prohibited by German law and, if prosecuted, can result in jail time and a heavy fine. It is unusual that charges are brought, but exercise common sense in all cases. Insulting a police officer will always lead to charges though.
On German beaches, it's generally all right for women to bathe topless. Full nudity is tolerated on most beaches, although not a frequent sight outside of the numerous nudist areas (labeled "FKK" or "Freikörperkultur", literally free body culture). These are especially common at the East German Baltic Sea coastline, due to the high popularity of nudism in the former GDR. It's also possible to spot nudists in Berlin's public parks and in Munich's "English Garden". In most saunas, nudity is compulsory and mixed sessions are common practice. One day of the week is usually only for women.
Owing in part to the long era of numerous German petty states being de jure or de facto sovereign, Germany has strong regional identities and local patriotism that may refer to a city, a federal state or a region within a federal state or crossing state lines. While some state boundaries are drawn pretty arbitrarily, states are politically powerful and many have their own unique character. The rule of thumb is that wealth rises towards the south and west: While Baden-Württemberg and Bavaria compete with Switzerland and Austria for quality of life, the economy of the eastern states is still lagging behind. A more liberal atmosphere is dominant as the traveler goes northward: Hamburg and Berlin have had homosexual mayors, bars and clubs are open all night and the density of young artists in Berlin Friedrichshain easily surpasses that of London, Paris or Manhattan. Northern Germany is in the same cultural sphere as the Netherlands and Scandinavia with even the food and architecture more pragmatic, simple and unrefined than in the south, where Catholicism has been predominant. Contrary to the general trend, Hamburg is the richest city in Germany (and one of the ten richest regions in Europe) even outpacing trendy Munich.
In the late 19th Century, Germany was arguably one of the most enlightened societies in the world. As a mental exercise, try to think of five famous physicists, philosophers, composers or poets without mentioning a German name. This dignity and prestige faced a severe setback during the period of National Socialist rule under Hitler (1933-1945). Since then, the Third Reich has been a permanent scar on the German national identity, and is considered a blot on Germany's national honor and will remain so for a very long time. Every German pupil has to deal with it at about 5 different times during his or her schooling and is very likely to visit a concentration camp at least once (most such sites have been transformed into memorials). Not a single day passes without educational programmes on television and radio dealing with this period of time.
Growing up in Germany, whether in the GDR or West Germany, meant and still means growing up with this bitter heritage, and every German has developed her or his own way of dealing with the public guilt. For the traveler, this can mean confusion. You might come across people (especially young ones) eager to talk to you about Germany's troubled history, feeling the urge to convince you Germany has come a long way since then. Choose adequate places to talk about the issue and be polite about it. If you are visiting friends, you might find it hard to keep them from dragging you into a memorial.
Humour, even made innocently, is absolutely the wrong way of approaching the matter and is insulting. All Nazi-era slogans, symbols, and gestures are forbidden (except for educational purposes, and even these are regulated). Displaying them in public or spreading propaganda material is illegal. Foreigners are not exempt from these laws. Do not even think about jokingly giving a stiff arm Nazi (roman) salute! This is a punishable act according to the German Penal Code, §86a: displaying the symbols of anticonstitutional organisations. Usually you will face 'only' a fine, of like €500. If the authorities suspect you of having propagandistic intentions, they can put you in jail for up to three years! (Religious Swastikas are exempted from this rule, though you are still advised to avoid wearing these Hindu or Buddhist symbols so you do not cause any unintentional offence.)
The German national anthem is the third stanza of a traditional song from the 19th century, Lied der Deutschen, written to the melody of Joseph Haydn's Gott erhalte Franz den Kaiser by one August Heinrich Hoffmann von Fallersleben on the island of Heligoland while the latter was under English control. The first stanza starts with Deutschland, Deutschland über Alles (Germany, Germany above everything). While this stanza is not forbidden, and even was officially a part of the national anthem during the Weimar Republic, do not quote or sing this stanza. Many people associate it with hyper-nationalism, and it will disgust them the same way as a Nazi slogan. Similarly, symbols of the 1871-1918 Kaiserreich like the Black-White-Red flag are not officially forbidden, but are these days virtually only used by the far right and will draw very negative reactions.
Probably the best way to deal with the issue is to stay relaxed about it. If the people around you like to talk about German history then use the opportunity for a sincere, maybe even very personal conversation. If you want to steer clear of awkward moments, don't bring up the matter.
Compared to the Nazi era, Germans have a more open attitude to the postwar division of Germany into East and West. Communist symbols, GDR songs and other East-German related regalia are circulated freely (though uncommon in the western parts) and many are somewhat nostalgic about the country, hence the artistic and commercial movement "Ostalgie" (nostalgia for the East). Be careful when discussing the East German secret police (Stasi) since many people in the East were negatively affected by the control of all aspects of life by this organisation, that maintained an extensive network of informants throughout the country during the communist era. While the division is some time in the past now, there are still cultural remnants often referred to as the "mental wall" (Mauer in den Köpfen) and the last couple of years seem to have reinforced stereotypes between East and West if anything.
Many Germans are fiercely attached to their region or even town and it is nothing out of the ordinary to hear people making disparaging remarks about a town a few miles over or even a different neighborhood in large cities like Berlin. While the purported reasons for such rivalries vary, they're almost never as serious as they may appear. Some of those rivalries overlap with sports rivalries (mostly soccer), but even then they only get heated when a game is on or someone is wearing the uniform of a team involved. While saying positive things about the town or region you're in is always appreciated, you should tread more lightly with bashing other places, even if locals seem to be doing it constantly.
Traditionally, regional rivalries also extended to religion, with the north and east being predominantly Lutheran, and the south and west being predominantly Roman Catholic, however cuius regio eius religio and early modern splintering of territories ensured heavily Catholic areas could lie right next to heavily Lutheran or reformed areas. However, this has diminished significantly in modern times as Germany has transformed into a largely secular society, with regular churchgoers now being in the minority. Work migration and the influx of (post-) World War II refugees has also made erstwhile confessionally homogenous villages much more mixed. In general, people from formerly communist East Germany tend to be less religious than people from the West, due to the fact that religion was discouraged by the officially-atheist communist regime.
The international calling code for Germany is 49, and the prefix for international calls is 00; the area code prefix is 0. Some number blocks are reserved for special use: Number starting with 010xx let you choose a different phone provider, 0800 and 00800 are toll-free numbers, 0180 are service numbers (which may or may not be more expensive than a local call). Avoid 0900 prefix numbers. These are for commercial services and usually incredibly expensive.
German phone numbers are of the form +49 351 125-3456 where "49" is the country code for Germany, the next digits are the area code and the remaining digits are the "local" part of the subscriber number that can be called from within that particular area code using abbreviated dialing. Since there are no standard lengths for either geographic area codes or subscribers' numbers, the last part may be as short as two digits! The 5000-odd German area codes vary in length from 2 thru 5 digits. You need to dial "0" in front of the geographic area code from outside that particular area code (but when still within Germany).
Since the liberalisation of Germany's phone market, there are a multitude of phone providers on the market. If you're calling from a private landline phone, you can usually choose from the different providers (and thus from different pricing schemes) by using special prefix numbers (starting with 010xx) with prices of €0.01 or €0.02, sometimes below €0.01 even for international calls. There's a calculator on the net where you can compare the prices for different destinations. Hotels usually have contracts with a particular phone provider and won't let you use a different one. The telephone rates charged by hotels can be staggering, especially at luxury hotels, where a five-minute phone call to make restaurant reservations can cost €50. Be certain that you have checked the tariff card before even picking up the phone.
Mobile numbers in Germany must always be dialed with all digits (10-12 digits, including a "0" prefixing the "1nn" within Germany), no matter where they are being called from. The 1nn is a mobile prefix, not an "area code", as such and the second and third digits (the nn part) denotes the original mobile network assigned before number portability is taken into account, for example +49 151-123-456.
Mobile phone coverage on the three networks (Deutsche Telekom, Vodafone, and O2) is by and large excellent throughout the country. UMTS (3G data and HSDPA), LTE (4G), and EDGE is also available. LTE is still somewhat limited to urban areas. All mobile providers use GSM technology on the 900 and 1800 MHz frequency ranges. This is different to the GSM 1900 standard used in the United States, but modern "multi-band" handsets will usually work in all GSM networks. Non-GSM phones cannot be used in Germany. If you have a GSM mobile telephone from the USA, make sure to call your provider in the USA prior to your trip and have them "unlock" your telephone handset so that you can use it with a German SIM card. The toll for a phone call to a German mobile phone number is paid by the caller.
If you stay for a longer period of time, consider buying a prepaid phone card from one of the mobile phone companies; you won't have trouble finding a Deutsche Telekom (bought at a Telekom Shop), Vodafone, or O2 store in any major shopping area.
Mobile telephony is still comparatively expensive in Germany. Depending on your contract you may be charged about €0.10–0.39 per minute for calls to German mobile and landline phones. Calls from your German mobile phone to non-German telephone numbers (including non-German mobile phones that are physically present in Germany) often cost €1 to €2 per minute, depending upon the country in question and your plan. Generally, for mobile phones, T-Mobile and Vodafone are the preferred choices for people who want high-quality service, especially outside of cities. O2/E-Plus has lower prices. If you expect to need customer support in English, then Vodafone might be one of your better options.
In most supermarket chains (for example Aldi, Lidl, Penny, Netto, Tchibo, Rewe, toom) you can buy prepaid SIM cards from their own virtual providers, although their network are still operated by the big 3 German telecom operators. These are normally quite cheap to buy (€10–20 with 5–15 minutes' airtime) and for national calls (€0.09–0.19/minute), but expensive for international calls (around €1–2/min), but incoming calls are always free and SMS cost around €0.09–0.19. While international calls using the German SIM card can be expensive, there are some prepaid offers with good rates.
Companies like Lyca Mobile, Lebara and others have specialized on providing rather affordable international calling rates (sometimes cheaper than Voice over IP services), mostly aimed at diaspora and immigrant groups.
However, unfortunately, paranoia over mobile phones being used in crime or terrorism have made it increasingly hard to simply buy a phone or a pre paid SIM and start calling. Depending on the provider you may need to provide a credit card number, identify yourself via Post ID or video ID. Even when those are doable, they are not always designed in a way to be easy for foreigners without residency status, although in theory, anyone with a valid identification can purchase these cards and that the German address given does not have to written in the system. That said, it's best to purchase a SIM card from a store that offers SIM card registration services and make sure you bring your ID card with you. Alternatively, if you already have an active mobile phone package from a provider based in another EU country, you will generally be able to use the data (subject to a monthly EU-imposed data cap), SMS and calls to your homecountry included in the package in Germany without the need to register it or incurring extra charges (although calling a German telephone number may cost extra: check with your provider).
The vast majority of Germans own mobile phones (called "Handys" in German, pronounced "hendy"); the disadvantage of this is that the once-common phone booths have started to disappear except at "strategic" locations such as train stations. They usually consist of a silver column with a pink top and the phone attached on the front. At some places there are still older versions consisting of a yellow cabin with a door and the telephone inside.
Alternatively, you can also buy prepaid phone cards you can use by calling a toll-free number; this is especially a good deal if you intend to make international calls. Card quality and prices vary wildly, however, so a good recommendation cannot be made.
In phone shops, which you can find in the major cities, you can make international calls at cheap rates. These call shops are mostly in city areas with a lot of immigrants and are your best option to call internationally. Apart from offering calls abroad, they sell international calling cards for use from any phone in Germany. You can usually spot these shops by the many flags decorating their windows.
Internet access through Wi-Fi (also commonly called WLAN) is common in Germany. Internet cafes are starting to become less common due to widespread offers of free Wi-Fi by shops, restaurants or cafes. Sometimes it requires minimum consumption but usually it's free within the premises. Phone shops will often offer internet access, too. The following shops provide free Wifi access:Galeria Kaufhof, real (supermarket), REWE, IKEA, H&M, dm-Drogerie, Subway, McDonald’s, Starbucks, and Burger King.
Many hotels offer internet access for guests, however speeds are limited and may be inadequate for viewing and using multimedia-rich pages/apps quickly. Premium high-speed internet may be available - often at high rates, so confirm access and rates with your hotel before using. Small private hotels and cheaper chain hotels will often offer Wi-Fi for free (e.g. Motel One) when you book as a package with breakfast, the larger chains will usually charge exorbitant rates. It is recommended to get a membership in their loyalty program, as this will usually give you free internet access.
In several cities, projects exist to provide free "community" hotspots for wireless networking. For example, the "Freifunk" hotspots are provided for free by local communities and don't require any registration. freifunk-karte.de show a map of these hotspots.
Passenger lounges at some airports and central railway stations also provide internet access to their customers.
Public libraries often offer Internet access, though it is not usually free of charge. The libraries are open to the public for free. Taking a book home might require you to get a customer card at a low fee, though. The National Library branches in Leipzig, Frankfurt am Main and Berlin are not free.
Most universities in Germany participate in eduroam. If you are a student or staff member of a participating university, this service may allow you to get guest access to their wireless networks. Check with your own university for details in advance of your trip.
On transport, there is Wi-Fi in a small (but growing) number of local trains (mostly due to pre-smartphone era contracts between the railway and the state subsidizing the service WiFi was not always seen as a huge priority). Intercity trains do not have any kind of WiFi, but virtually all ICE trains do have free WiFi in second and first class. Long distance buses are usually equipped with WiFi but bandwidth is often limited and buses may lack WiFi without prior announcement. Local buses are increasingly equipped with WiFi. All those have in common that connecting to the WiFi will put you on a landing page where you are to either enter some data or an email address or simply confirm that you accept the terms and conditions. Due to those mobile hotspots being provided through the normal mobile internet network, they tend to be less stable in rural areas or when many people at once are using them and if you have a data plan that allows it, your own phone can be faster than the WiFi provided by the mode of transport. WiFi on airplanes is relatively uncommon, even on domestic flights. Flixbus offers free WiFi (and commonly also power sockets) on their coach services.
Several pre-paid SIMs allow Internet access for a monthly flat fee, for example those available at Tchibo coffee stores (o2 network, €10/month limited to 500 MB, €20/month for 5 GB) or Aldi (E-Plus network). A regular O2 SIM card, which can be used for calls and text messages, is €15 and another €15 buys 1GB of data valid for 1 month. Vodafone offers a prepaid SIM card for €25 which includes €22.5 of credit, out of which you can get 300 MB of data for 2 days for €15 and be left with €7.5 of credit.
File sharing and streaming of copyright protected content is illegal in Germany. Specialized lawfirms are continuously tracking violators by their IP-numbers and are charging hefty fines (up to several thousand Euros) as well as requesting the violator to sign legal documents that he/she will refrain from doing so again. Even if you have left the country, bear in mind that the registered owner of the internet connection you used might get in serious trouble. This refers in particular to private connections (friends, family and so on). In your own and your hosts interest be sure that all file sharing applications on your devices are inactive while being in Germany as well as refrain from streaming content from sites that are not doubtlessly legal, or use a VPN service.
 Deutsche Post, the German postal service, runs several international companies including DHL and others. A standard postcard costs €0.45 to send within Germany and €0.90 everywhere else. A standard letter not weighing more than 20 grams costs €0.70 to send within Germany and (again) €0.90 everywhere else. Letters weighing up to 50 grams cost €0.85 (Germany) or €1.50 (international).
Deutsche Post, the German postal service, runs several international companies including DHL and others. A standard postcard costs €0.45 to send within Germany and €0.90 everywhere else. A standard letter not weighing more than 20 grams costs €0.70 to send within Germany and (again) €0.90 everywhere else. Letters weighing up to 50 grams cost €0.85 (Germany) or €1.50 (international).
Stamps are available at post offices and sometimes at newsagents or shops selling postcards, even though you might experience shops that will only sell postage stamps to accompany postcards that you have purchased with them. Also stamp vending machines can be found at a lot of places around the cities. You can purchase every stamp you need from this machines. They are unique as they accept every coin from 1 cent to 2 euro but change is only given in stamps. Because these "change-stamps" may display strange values, you'd better make sure to have enough small coins.
 Letters within Germany are mostly delivered within 1 day, allow a bit longer for Europe. Mail to North America may take up to a week.
Letters within Germany are mostly delivered within 1 day, allow a bit longer for Europe. Mail to North America may take up to a week.
The service has been reduced in the privatization process. Due to a surge in the theft rate (especially by outsourced letter carriers and contractors) any international shipments, especially incoming, should be insured if they are valuable.
Air mail (Luftpost) can be as cheap as the alternative, Landweg. If you want to send packages, there are three options (cheapest to most expensive): Maxibrief (an oversized letter up to 2 kg and L+W+H=900 mm), Päckchen (a small package up to 2 kg, uninsured for international mail), and DHL Paket. If only books are sent, reduced rates apply (Büchersendung), but expect the mail to be opened and looked at, as really only books are allowed in them. Rates for Büchersendungen vary between €1.00 and €1.65, depending on size and weight.
It's possible to drop letters and parcels at FedEx and UPS stations. Expect to queue.
Germany is an excellent starting point for exploring the rest of Western Europe, while Frankfurt airport has direct connections to many major airports around the world. Also from Frankfurt a number of direct high speed rail connections get you to major European capitals within a couple of hours.
- From the east it is easy to reach Prague in the Czech Republic and Warsaw in Poland
- From the south west the French cities of Reims and Paris as well as the country and town of Luxembourg would make good first goals.
- The direct TGV/ICE to Paris stops in Strasbourg, a lovely town at the border with French and German influence alike
- Belgium and Netherlands from the west with Leuven and Maastricht being recommended first stopping points; and Denmark in the north west
- From the south and south west into the mountains of Austria and Switzerland with Salzburg and Lausanne being "must visit" places.
- By sea in the north east try Cruising the Baltic Sea to access the Baltic states and Nordic Countries.
