 Guadalupe Island or Isla Guadalupe is a volcanic island located off the west coast of Mexico's Baja California Peninsula in the Pacific Ocean. According to Seacology's website, Guadalupe Island is a biosphere reserve.
Guadalupe Island or Isla Guadalupe is a volcanic island located off the west coast of Mexico's Baja California Peninsula in the Pacific Ocean. According to Seacology's website, Guadalupe Island is a biosphere reserve.
Guadalupe is part of Ensenada, a subdivision of the state of Baja California. In 2010, the island had a population of 213 people.
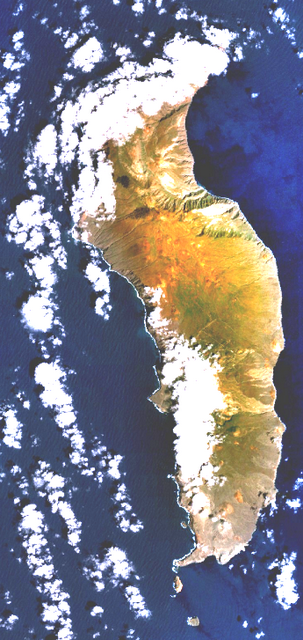
Guadalupe has a rugged landscape with numerous shield volcanoes. The island measures north-south and up to east-west, with a total area of .
The southern part of the island is barren, but there are fertile plateaus and trees in the northern part. The coast generally consists of rocky bluffs with detached rocks fronting some of them.
There are also some islets off the coast of Guadalupe Island, such as Islote Afuera and Islote Adentro.
Guadalupe Island was a major destination for Russian and American fur hunters seeking the Guadalupe fur seal in the 18th and 19th centuries, until they were nearly extinct by 1844. The northern elephant seal was also hunted for the oil in its blubber, but managed to survive and the seals remain today.
Goats were brought to the island in the 19th century by European whalers and sealers for provisions when stopping over. Their numbers have fluctuated over the years, peaking at 100,000 and in more recent times being about 20,000.
The island has been a nature conservancy area since 1928, making it one of the oldest reserves in Mexico.
The island has two major climate zones: a very arid, semi-hot climate between elevation, with mean annual temperature between and a very arid, temperate climate above elevation with temperatures over in the hottest month of the year.
The weather station is at a low elevation, and temperatures may be more than ten degrees Fahrenheit colder at the higher elevations of the island.
Most precipitation occurs over the winter months with strong influence of northwestern winds and cyclones.
Rainfall averages near sea level at the south end but appears to be much more at the higher northern end.
With about 200 people in 50 buildings, Campo Oeste ("West Camp") is by far the largest settlement on the island. It is a fishing community which is connected by a dirt road to the rest of the island. Additional temporary fishing camps are Campo Norte ("North Camp", four buildings), Campo Lima (Campo Corrals) (one building) and Arroyitos (four buildings). An abandoned fishing community, Campo Este ("East Camp"), sits near a cove on the eastern shore.
At the southern tip, on Melpómene Cove, there is a weather station staffed by a detachment from the Mexican Ministry of the Navy. The site is called Campamento Sur ("South Encampment"). Campo Bosque was established in the cypress forest in the north and houses members of a cooperative farming society which removes goats from the island and sells them in the State of Sonora. Campo Pista is located at the small airport, near the center of the island.
Guadalupe shares the California chaparral and woodlands ecoregion with the Channel Islands of California in the United States, but the island was at one time practically denuded of all plants higher than a few centimeters by up to 100,000 feral goats. The goats have continued to be a problem, and their destruction of vegetation has caused desertification on the island. In more recent years, much of this has been prevented with goat fence installation, and the island is recovering.
The goat population was completely eradicated by 2007 due to the activities of a Group for Ecology and Island Conservation NGO, and the vegetation has started to recover. Measures have also been taken to control the populations of wild cats and dogs, which has been of benefit to the island's birds.
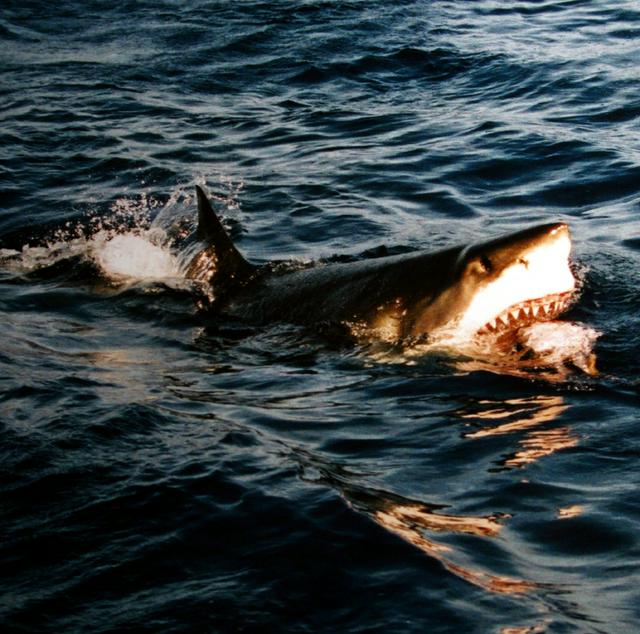
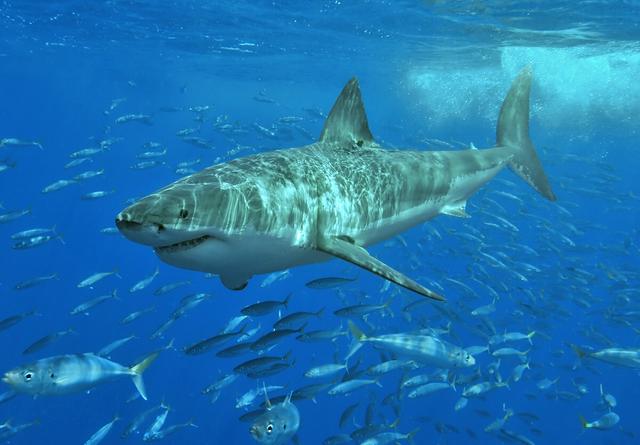
Many island or marine species that reside on or near Guadalupe also frequent the Channel Islands, and vice versa. In stark contrast to the rampant extinction of terrestrial life that happened at the same time, Guadalupe has been the last refuge for the northern elephant seal and the Guadalupe fur seal since the 1890s. The island has been a pinniped sanctuary since 1975, creating a large pinniped population - therefore, Guadalupe is now one of the best spots in the world for sightings of the great white shark.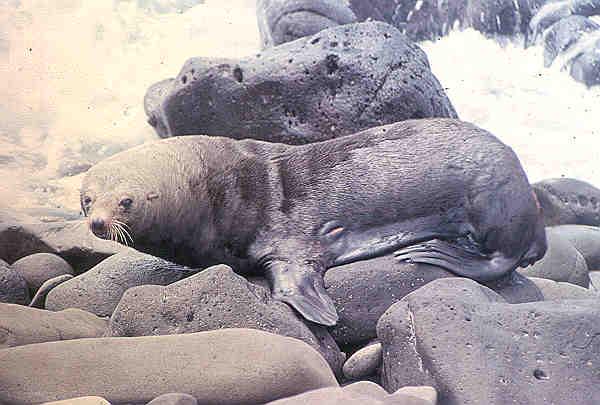
Of course, besides the act of getting there, the main point of all that effort to get to the island is to look around. All of the island is dramatic, and you can really do sightseeing anywhere on Guadalupe Island. The sights on the island consist of some wildlife, particularly on the shorelines and in the upper parts of the island; the great rocky cliffs that go around most of the island; the oceans around the island; and everything on the top of the island.
Guadalupe has some interesting attractions on the island itself, along with some other islets just off the coast.
- Airport. Poorly constructed runway in the center of the island where a plane crashed several years ago.
- Campamento Sur. Small camp on the southern end of the island.
- Campo Bosque. It was established as a temporary camp in 1999 in the cypress forest in the north. The camp houses members of a cooperative farming society which removes goats from the island and sells them in the State of Sonora, with permission of Secretariat of the Environment and Natural Resources and the support of the Secretariat of the Navy.
- Campo Oeste. The main settlement with about 200 people, Oeste is a small community of abalone and lobster fishermen, on the western coast. It is on the north side of West Anchorage, a bay that provides protection from the strong winds and swells that whip the islands during winter. Generators provide electricity, and a desalination plant provides fresh water. Ten months of the year, the 30 families of a fishing cooperative live here.
- Northeast Anchorage. A group of abandoned buildings near a canyon in the north of the island.
Airport. Poorly constructed runway in the center of the island where a plane crashed several years ago.
Campamento Sur. Small camp on the southern end of the island.
Campo Bosque. It was established as a temporary camp in 1999 in the cypress forest in the north. The camp houses members of a cooperative farming society which removes goats from the island and sells them in the State of Sonora, with permission of Secretariat of the Environment and Natural Resources and the support of the Secretariat of the Navy.
Campo Oeste. The main settlement with about 200 people, Oeste is a small community of abalone and lobster fishermen, on the western coast. It is on the north side of West Anchorage, a bay that provides protection from the strong winds and swells that whip the islands during winter. Generators provide electricity, and a desalination plant provides fresh water. Ten months of the year, the 30 families of a fishing cooperative live here.
Northeast Anchorage. A group of abandoned buildings near a canyon in the north of the island.
Two high and prominent islets are within of the southwestern end of the island, separated from one another by a gap called Tuna Alley:
- Islote Adentro. Another barren islet, located near Roca del Skip and Church Rock.
- Islote Afuera. The most distant island, steep with almost vertical walls above and below water
Elsewhere, the other islets are very small and close to the shore, all less than away:
- Islote Bernal. 1.1-ha (2.7-acre) islet about a mile south of a major landslide and a couple miles south of Campo Oeste.
- Islote Negro. 8.8-ha (22-acre) islet off the west coast of Guadalupe Island about a mile north of Camp Sur.
There are five other islets, which are all less than 1ha.
Islote Adentro. Another barren islet, located near Roca del Skip and Church Rock.
Islote Afuera. The most distant island, steep with almost vertical walls above and below water
Islote Bernal. 1.1-ha (2.7-acre) islet about a mile south of a major landslide and a couple miles south of Campo Oeste.
Islote Negro. 8.8-ha (22-acre) islet off the west coast of Guadalupe Island about a mile north of Camp Sur.
Besides the populated places and islets, Guadalupe features a chain of high volcanic mountain ridges. There are some major peaks on these ridges, which are listed below:
- Mount Augusta. This is the highest point on the island. It is not really a large mountain, just a high point on the eastern cliff of Guadalupe. Mount Augusta is 1,298 metres (4,259 ft) above sea level.
- El Picacho. At an elevation of 975 metres (3,199 ft), El Picacho is the highest point on the southern side of the island. It is on a desert ridge which sits above Campo Oeste.
There are also some unattractive volcanoes in the south, which have no vegetation on them and vary from white to gray and red in color. Only one of these are named, which actually in the east of the island:
- Red Cinder Cone. Red-topped volcano on the eastern side of the island.
Mount Augusta. This is the highest point on the island. It is not really a large mountain, just a high point on the eastern cliff of Guadalupe. Mount Augusta is 1,298 metres (4,259 ft) above sea level.
El Picacho. At an elevation of 975 metres (3,199 ft), El Picacho is the highest point on the southern side of the island. It is on a desert ridge which sits above Campo Oeste.
Red Cinder Cone. Red-topped volcano on the eastern side of the island.

On Guadalupe Island, there are no major events, and any exploration is self-guided unless a local is interested in showing you around the island. Hiking is the main thing to do on the island, along with fishing.
For fishing, the best locations are in the towns, where there is a shoreline. Much of the coastline of the island has high cliffs, making any beach or shoreline activity impossible. The best beaches are at Campo Oeste and Northeast Anchorage, with a small beach at Camp Sur; however, all these beaches are a mile or less in practical length.
There are some boat tours which go towards Guadalupe Island, starting from either Alta or Baja California. They will journey for several days looking for sharks around Guadalupe, but will not go on the island itself. This is by far the easiest way to see Guadalupe Island, but you will not get the same experience as one would who was on the island.
(They begin in other places, but go to the Guadalupe Island region)
- Great White Adventures - Guadalupe, +52 510 808-4499. They do 5- or 6-day trips in late summer.
- Great White Sharks of Guadalupe, +52 604 241-1918. They do 5- or 6-day voyages to Guadalupe Island in late-summer.
Great White Adventures - Guadalupe, +52 510 808-4499. They do 5- or 6-day trips in late summer.
Great White Sharks of Guadalupe, +52 604 241-1918. They do 5- or 6-day voyages to Guadalupe Island in late-summer.
Considering how hard it is to get to the island, it is unlikely that the Mexican government will worry about restricting anyone from getting there, although you may want to get in touch with Seacology or another environmental group first before going to Guadalupe Island to make sure they're all right with tourists going there.
There is no entry system at Guadalupe for those who go straight to the island from other countries, so it would be best to go into Baja California (Ensenada) first, and then go to Guadalupe, rather than starting the expedition to Guadalupe from San Diego or Los Angeles in the United States.
There are no restaurants on Guadalupe Island. Most of the locals live not far above subsistence level, and food is obtained through fishing at Campo Oeste. There used to be a lobster camp on the east of the island.
When you go to the island, bring enough food with you to last the trip.
 For water, a desalinization plant has been bought for Guadalupe. The desalinization plant can supply thousands of gallons of water a day. The deal is that a marine reserve will be created as well as this plant, and no fishing can be done in the reserve. The location of this reserve is unknown.
For water, a desalinization plant has been bought for Guadalupe. The desalinization plant can supply thousands of gallons of water a day. The deal is that a marine reserve will be created as well as this plant, and no fishing can be done in the reserve. The location of this reserve is unknown.
Also, a lake is located near the runway, a few hundred feet from the westbound road. The lake is about a hundred feet long and nearly a hundred feet wide.
You should also bring a supply of water, in case there is not enough water at the desalinization plant or the spring.
There are no stores on Guadalupe Island — at least, no stores with connection to the rest of the world. In a place that lives primarily at subsistence level, operating a proper store would be extremely difficult, if not entirely impossible.
Do not go to the island with the intention of buying material; instead, bring any necessary items to the island with you.
 Be extremely careful about exploring the top of the island; cliffs are scattered around the peaks of the island, and it would not be challenging for a tourist to start exploring a woodland or rocky outcrop, and not realize how close they are to a 2,000-foot cliff. The immediate dangers of this situation need not be explained.
Be extremely careful about exploring the top of the island; cliffs are scattered around the peaks of the island, and it would not be challenging for a tourist to start exploring a woodland or rocky outcrop, and not realize how close they are to a 2,000-foot cliff. The immediate dangers of this situation need not be explained.
Also be careful about going in small boats, swimming, or diving in the Pacific Ocean. Great white sharks are known for being numerous here - videos and pictures on the Great White Shark Tour website show someone in an underwater cage, surrounded by sharks. This is a good reason not to swim in the area, even though the locals go diving in the area.
It's extremely hard to get in touch with anyone on Guadalupe Island, at least from outside.
Once on the island, there are no newspapers or radios or even official websites. Since nearly all the islanders live in the same community, there is really little need for such communication.
- Ensenada – the base point for tourist expeditions to the Guadalupe area, it is the third-largest city in Baja California
- Guerrero Negro – town of 13,000 people in Baja California Sur, located near a large lagoon with a lighthouse and numerous whales
- Isla de Cedros – a desert island much like Guadalupe, except that it is near the coast of Baja California Sur
- El Rosario – town on the Baja California coast northeast of Guadalupe Island
[[Ensenada]] – the base point for tourist expeditions to the Guadalupe area, it is the third-largest city in Baja California
Isla de Cedros – a desert island much like Guadalupe, except that it is near the coast of Baja California Sur
[[El Rosario]] – town on the Baja California coast northeast of Guadalupe Island
