Train Companies (TOC, Train Operator Companies)
Most of the British Railways are named according to the area where the train routes are distributed, so it is easier to understand. For example, Cross Country covers the whole country. East Midlands Trains are mainly concentrated in the Middle East of England. Scotrail mainly operates in Scotland. The following are the main railway companies:
Cross Country
East Midlands Trains
EuroStar
Virgin Train
ScotRail
Arriva Trains Wales
CrossCountry Trains

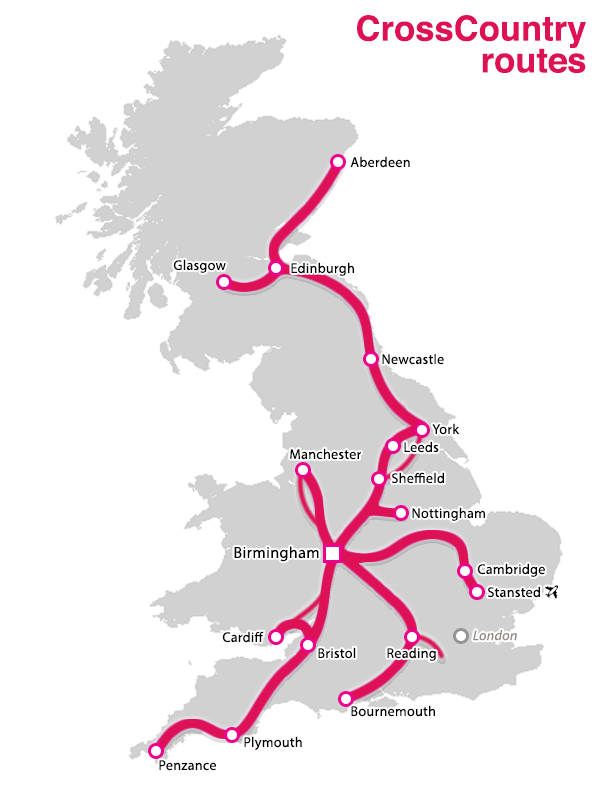
Cross Country Trains is owned by Arriva UK Trains. Cross Country Trains has a wide range of train services. Travelers in the UK often take their trains. It can be seen from the north to Aberdeen, the south to Plymouth, the west to Cardiff, and the east to Cambridge.
East Midlands Trains

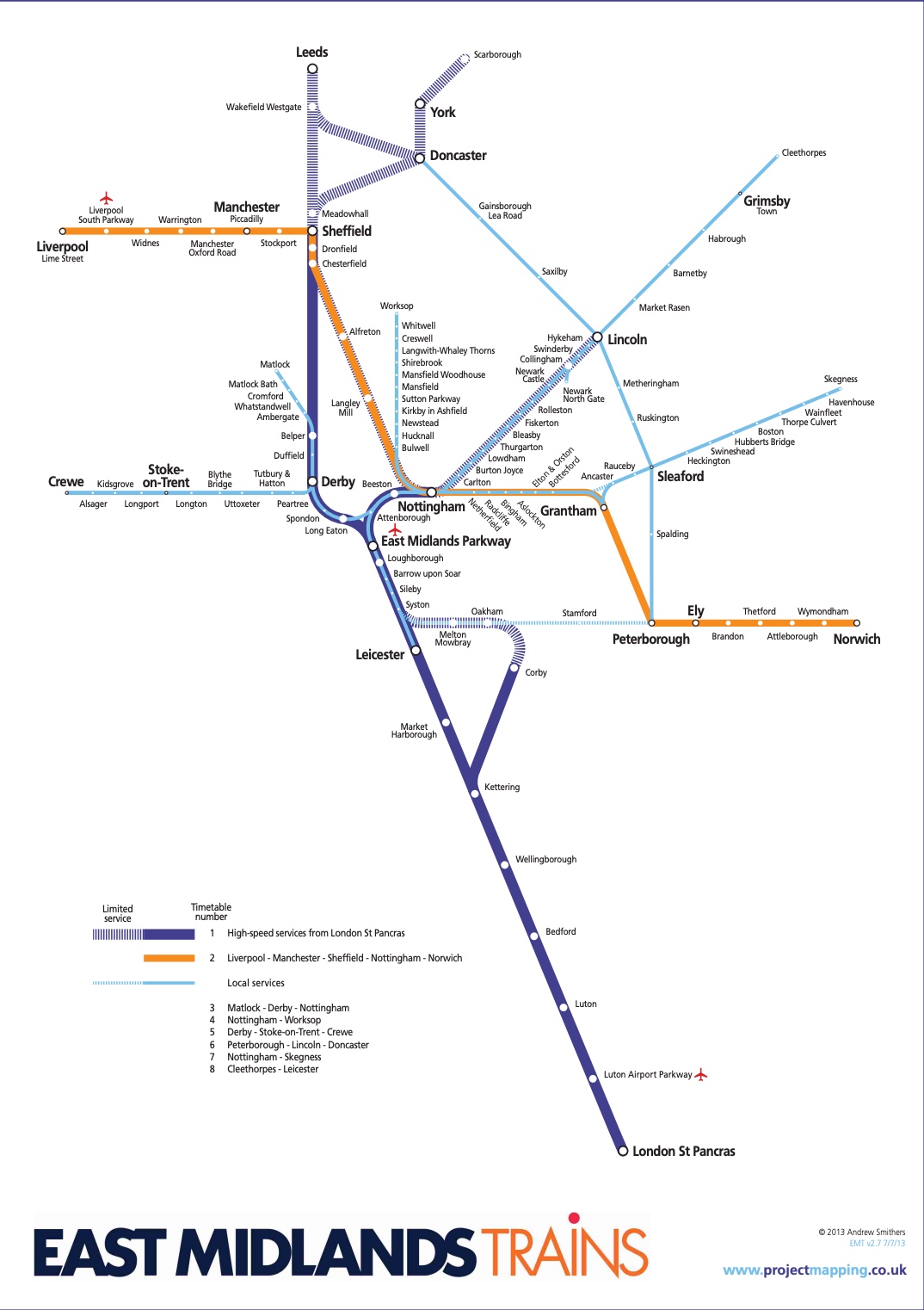
East Midlands Trains (EMT) is a British train operating company owned by Stagecoach Group. The company is headquartered in Derby. The main routes are concentrated in the central and eastern England. Train services are provided in parts of East Midlands and Yorkshire. They are mainly located in Lincolnshire, South Yorkshire, Nottinghamshire, Leicestershire, Derbyshire and Northamptonshire. The average weekly mileage of East Midlands Trains is about 115,000 miles per year. Compared with the existing HST, they are faster and have a maximum speed of 125mph.
The service of the East Midlands is great. They have 24/7 service. If you encounter a delay in the train, you need to get a refund. If you lose your luggage, you can always contact their staff. If the train is delayed for 30-59 minutes, the Single Ticket can get 50% compensation, and the Return Ticket can get 50% compensation for any one of the fares going or returning; if the delay is between 1 hour and 1 hour 59 minutes , Single Ticket can be compensated with a full ticket, and Return Ticket can be compensated with one of the tickets going or returning; if the delay is 2 hours or more, whether it is a Single Ticket or a Return Ticket, you can enjoy full ticket compensation
Virgin Trains

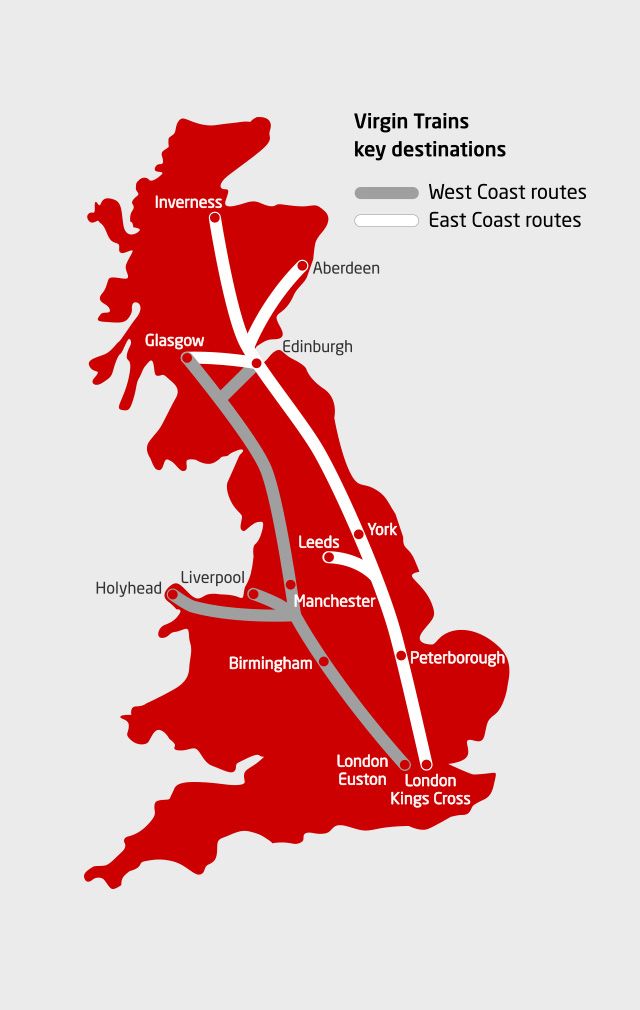
The Virgin Train, part of the Virgin Group, is very large. There are two railway companies, including Virgin Trains West Coast and Virgin Trains East Coast. Virgin trains use high-speed rail, and the main speed of the west coast has reached 125mph per hour. The main stations of its train are: Birmingham, Edinburgh, London (London Euston Station), Glasgow, Leicester, Liverpool (Liverpool Lime Street Station Liverpool Lime Street), Manchester (Manchester Piccadilly Station Manchester Piccadilly) , Sheffield and other major cities. Virgin Trains is the best long-distance train line in the UK. The cumulative mileage of these trains now exceeds 145 million miles (together, they can circle the earth 3 times). Because it is a train line that runs through more than half of the British Empire, high-speed trains are used, and the main speed of the west coast reaches 125mph per hour. The fare is also very reasonable. The first-class pre-order price starts from £7.50, comes with free WIFI, comfortable lounge chairs and high-end catering services. All other cabin passengers can purchase WIFI by themselves.
Although it is a long-distance train, it has extremely frequent trains, even reaching the frequency of 20 minutes on the busiest line. The Virgin Trains West Coast has become the most frequently used and most popular long-distance line in the UK, and is rated as the “all-round and most satisfactory” and “most value for money” long-distance line by passengers.
ScotRail

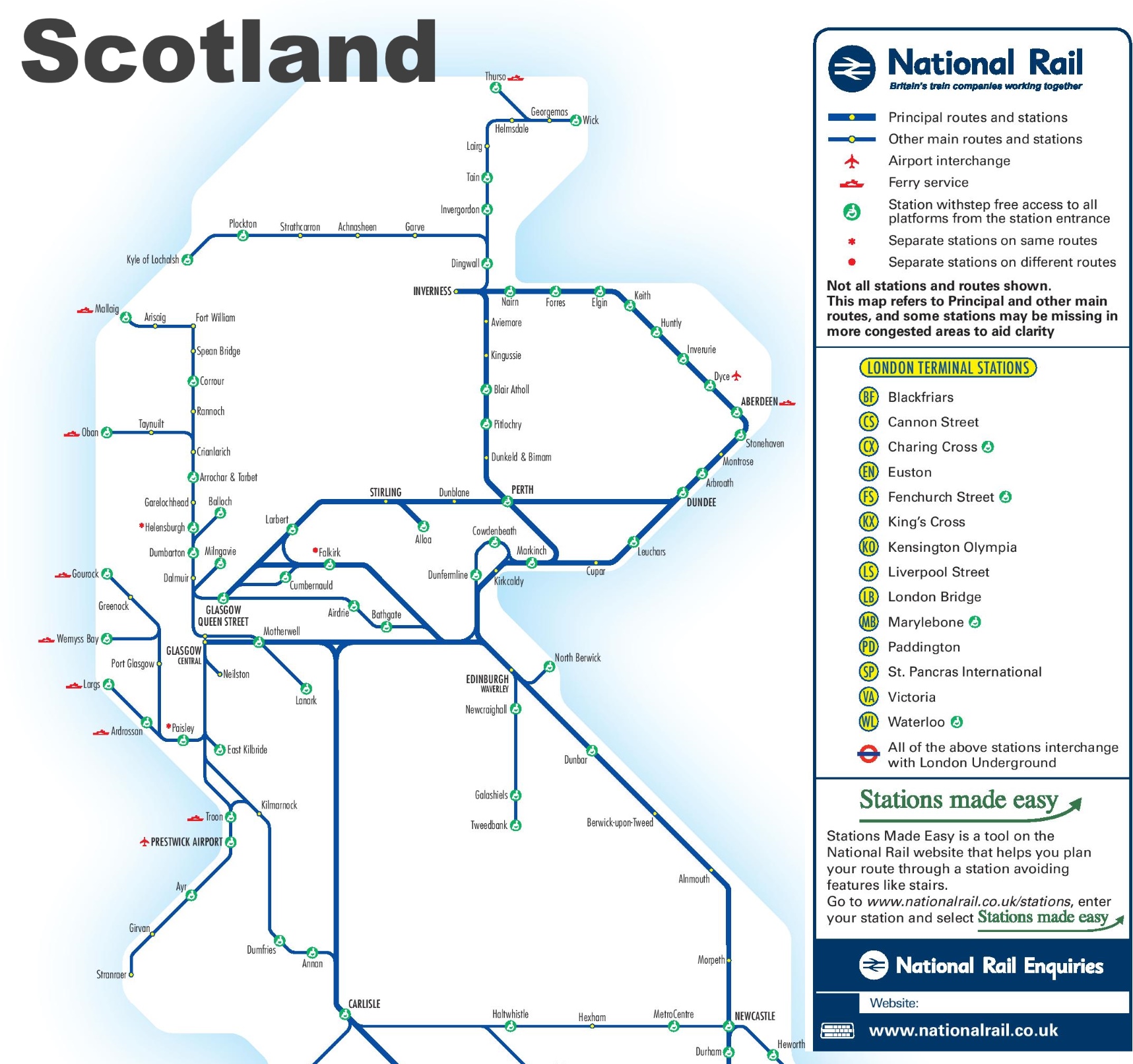
Scottish Railways is affiliated with Abellio Train Company and is mainly engaged in Scotland. The main sites are the big cities of Scotland: Aberdeen, Edinburgh, Glasgow, etc. From October 2004 to March 2015, ScotRail was operated by FirstGroup. Starting in April 2015, ScotRail was in charge of Abellio and changed its name to Abellio ScotRail.
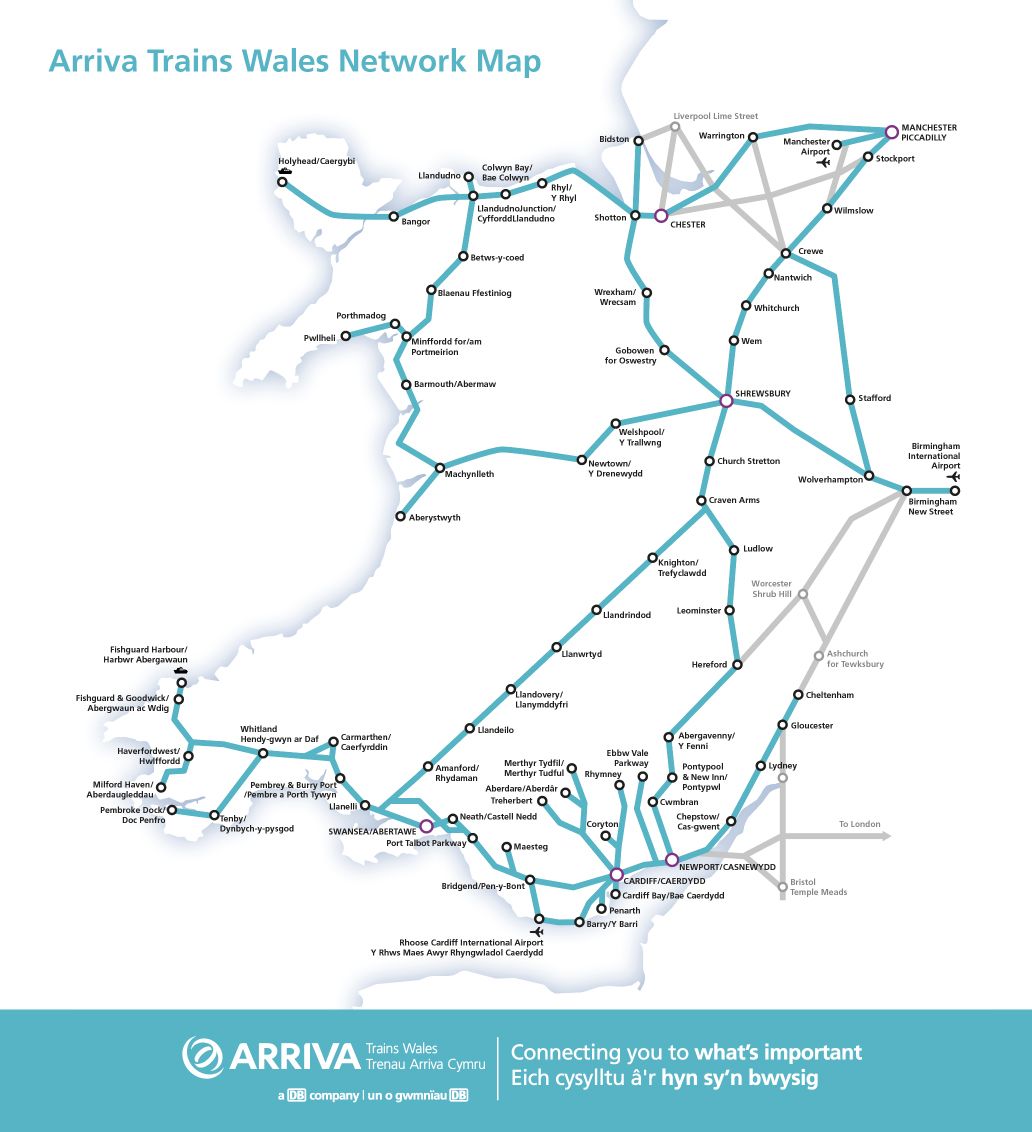
ArrivaTrains Wales

Arriva Trains Wales is a subsidiary of Arriva UK Trains. The main stations are: Birmingham (Birmingham New Street Station), Cardiff, Coventry, Manchester City, Swansea, etc. The biggest feature of Arriva Trains Wales is the beautiful scenery along the way, but if you want to take a photo, you must apply on the official website 14 working days in advance to shoot!
EuroStar

Eurostar is divided into business class, first class and second class. Business Class and First Class include meals during meal times, and there are dedicated lounges at the station. Each column of Eurostar consists of 20 cars, up to 400 meters long, of which 18 are manned, 1 luxury cabin, 5 first-class cabins, 10 second-class cabins and 2 dining cars. The car has a total of 766 seats, including 206 seats in the deluxe cabin and first-class cabin and 560 seats in the second-class cabin. Why is this train so long? That is because there are only two railways in the English Channel, and it is the main artery connecting the British mainland and continental Europe. It is an important transportation hub. If the capacity of each train is sufficient, even if there are only two railways, the entire traffic demand is still Can be satisfied.
Of course, such a high-end train must be equipped with high-end staff. The train crews must all be proficient in English and French, and must be fluent, very fluent. Although most of them will become "Frenglish", most passengers still seem to buy it. Although a Schengen visa is required to go to a European country, customs clearance procedures can often be completed by the destination country after security check at the departure station (ie, one place and two inspections) when taking the Eurostar, so that passengers can easily get off and get out of the station after arriving , Saving a lot of time.
Coach Class
Although all trains provide Second Class (Standard), on some trains also provide First Class seats. This provides a more unique travel environment, in most cases, more spacious and/or comfortable seats than standard.
In order to enjoy first-class service, you need to buy first-class train tickets. On most trains, first-class tickets are required to pass through or even stand in the first-class vestibule, but this requirement is waived on some trains because the layout of the cars makes it difficult to implement.
You can usually upgrade a second-class ticket to a first-class ticket through excess or supplement. The regulations for this are very complex and vary from train company to train company.
Service for first-class passengers
Depending on the train companies and routes, passengers in first-class cabins may receive certain additional benefits (such as free food, drinks and newspapers). This is especially common on long-distance intercity routes.
First-class tickets are also often allowed to enter the dedicated lounge at the main stations.
Eurostar's VIP lounge at St. Pancras Station in London

Routing
A characteristic of the British National Railways network is that for many journeys, most of which are medium- to long-distance travel, passengers can choose the route on which their ticket is valid.
The route guide states "most customers want to travel by train or the shortest route" but in some cases, passengers may want to take the fastest route, while in other cases passengers want to go through a specific place for various reasons, In this case, this section may help determine whether the required route is allowed.
Determining the shortest route or identifying direct trains is not as simple as it seems, and many tickets also allow travel through the “mapped route” allowed in the “National Route Guide”.
Many tickets limit the routes you may or may not use. These are always printed at the bottom of the ticket under "Route".
If the route is ANY PERMITTED, you can take any route allowed by NRCoT or the route guide.
Some tickets DIRECT. This meaning is ambiguous. However, one explanation is that the only allowed route is by train or the route that follows the shortest route rule.
If the route is VIA station, your trip must pass through this station, although the train does not need to stop there. If multiple workstations are separated by hyphens, all workstations must be passed. If they are separated by a slash, you only need to pass one of them. If there are no routes allowed to travel through these sites, please see tickets routed through stations that are not on the allowed routes.
If the route is NOT VIA one or more stations, you can take any train that does not stop or pass.
Train Types
Train ticket
British train tickets are not only expensive but also complicated, which is a headache for many newcomers to the UK. For example, a train journey of 2 to 3 hours will cost tens of pounds, and the price will vary depending on the time of purchase, time of travel, seat class, and ticket type. Similar to other European countries, the British Rail also has a BritRail Pass and Point to Point Ticket. Of course, you can save money by split ticket or early ticket early booking (Advanced Ticket).
BritRail Pass
The British Train Pass (BritRail Pass) is only applicable to foreigners, so it is only sold outside the UK, and it is also divided into several types, including: British Region Pass (BritRail Pass, which can be used throughout the UK), England Train Pass (BritRail Pass (England), only applicable to England), Scotland Free Travel Train Ticket (BritRail Pass (Central Scotland), only applicable to all areas of Scotland, and includes the ferry tickets of the outer islands) and so on.
Map of the British Rail Pass
British Rail Optional Pass

The train pass is divided into a continuous pass (Consecutive Pass) and an optional pass (Flexible Pass). The continuous pass can be used for an unlimited number of times and miles within consecutive valid days; the optional pass is within six months after the purchase of the ticket. Any number of days to ride, users need to write the date of the ride by themselves, and they can ride with unlimited times and mileage on that day.
The choice of days for both types of tickets is 3 days, 4 days, 8 days, and 15 days. Continuous tickets also provide 22 days and one month validity period. In the same number of days, the price of the flexible ticket is higher.
British Rail Pass (National) (Optional Pass)
British Rail Pass (National) (Continuous Pass)
British Rail Pass (England) (optional pass)
British Rail Pass (England) (Continuous Pass)
British Rail Pass (Central Scotland)
UK Heathrow Express
Point-to-point ticket
The British rail ticket system is very complicated. If you buy a point-to-point train ticket separately, pay special attention to the difference between different types of tickets. Different types of tickets and different prices. British point-to-point train tickets will have the following different types of tickets.
According to the number of round trips
Single Ticket (Single Ticket)
One way travel from origin to destination is allowed.
*Return Ticket *
Return and return journeys from departure to destination are allowed, whether on the same day or after a month, depending on the type of train ticket.
The return journey starts without completing (or completing) the Outward Journey, but the outgoing portion of the train ticket subsequently becomes invalid and cannot be used anymore. In other words, the outbound part is only valid if you still have an unused return part.
Other options for single and return tickets include:
Multi-journey Tickets
Even if only one trip is made, train tickets that allow multiple trips usually provide better value. These tickets include Season Tickets, Rangers, Rover and TravelCards.
Integrated Fares
When long-distance travel involving multiple modes of transportation is available, comprehensive fares can be provided, including buses, boat trips, and rail journeys, all fares are on one ticket.
According to time
All round-trip tickets and most one-way tickets (except Early Tickets) are one of two categories
- One-way ticket for unlimited hours (Anytime)
- One-way ticket during off-peak hours (Off-Peak)
Definition of Anytime, Off-Break time for different British railway companies
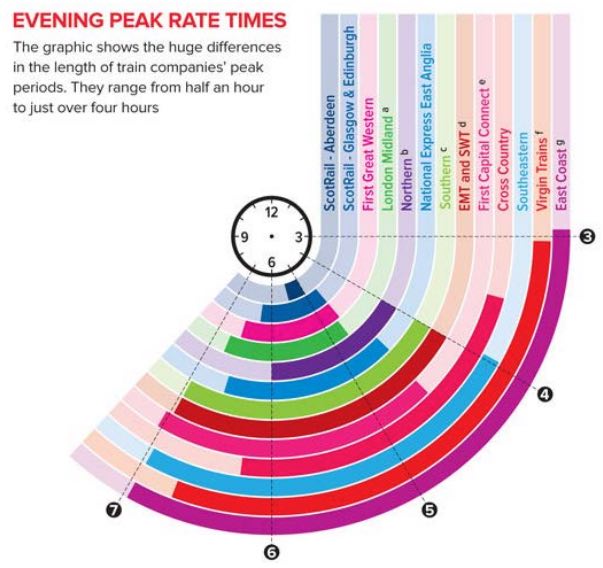
These two types of tickets are also collectively called Walk-Up Fares. Although you must specify the required date at the time of purchase, it can be purchased one year in advance from the day of travel. Depending on the type of ticket, the ticket may only be valid on this date, or it may be valid for a few days thereafter. Anytime and Off-Peak tickets will not restrict you from traveling on a specific train, you can go to a specific itinerary through any permitted route (need to participate in the later route part). You must complete the journey at 04:29 on the last day of the validity period.
Most one-way fares allow trips to be dropped off on the way and re-boarded to continue the route, some of which allow trips to be separated within two days and rest overnight. Most outbound tickets (Outward Journey) and almost all return tickets (Return) return part are allowed to rest halfway. If the validity period exceeds 1 day, if necessary, it can include multiple overnight stays on the way.
The main difference between Anytime and Off-Peak tickets is related to the time they may be used. These time limits will be discussed in detail in the next section. The second difference is that unless there is no ticketing facility at the station where you board the train, it is usually impossible to buy Off-Peak tickets on the train. Anytime tickets can usually be purchased on the train, but in some cases, Anytime tickets cannot be sold on the car, so they can only be fined. Therefore, buying tickets before boarding (when facilities are available) is the best policy to avoid paying more than necessary. Off-Peak's time definition is also related to different train companies (TOC).
Passengers purchasing Anytime and Off-Peak tickets must take the train according to the ticket date. The train frequency and off-peak time that passengers can choose depends on the itinerary, departure date and train operator. Passengers can start a journey at any station on the train route, interrupt the journey, continue the journey, or end the journey. If the passenger wants to get off the bus and stay overnight or the trip cannot be completed within one day, the trip can be interrupted and stay overnight. If you need to continue your trip the next day, you must depart by 12 noon to board the train, subject to the relevant departure time. The trip must not be interrupted again, except for transfers. Some routes may not interrupt the itinerary. For details, please see the ticket terms and restrictions.
Advance (also known as advance ticket) is a completely independent Anytime and Off-Peak ticket category, the ticket validity conditions are much stricter-Anytime and Off-Peak tickets purchased in advance are not early bird tickets ( Advance)! Because early bird tickets are cheap and complicated, we will introduce them in the next section.
Ticket Type
When selling train tickets in the UK, they will be divided into different ticket types according to time, number of trains, cabin class, etc. There are currently more than 1,800 kinds in use. Tickets are usually abbreviated. The following are some of the more commonly used. Abbreviations and corresponding ticket types.
Second Class (Standard)
- SOR/GOR-Standard Open Return -> Anytime Return round-trip ticket for unlimited hours
- SOS-Standard Open Single -> Anytime Single
- SDR/GPR-Standard Day Return -> Anytime Day Return
- SDS-Standard Day Single -> Anytime Day One-way ticket for any period on the specified date
- ADT-Anytime Day Travelcard
- SVR/BVR-Saver Return -> Off Peak Return round trip ticket during non-peak hours
- SVS/BVS-Saver Single -> Off Peak Single Standard One-way ticket during non-peak hours
- CDR/1DR/1DT-Cheap Day Return -> Off Peak Day Return non-peak period round-trip ticket on the specified date
- CDS(Cheap Day Single)/SVH(Saver Half) -> Off Peak Day Single One-way ticket during non-peak hours
- ODT-Off Peak Day Travelcard Travel card for non-peak hours on designated days
- FTC -> Family Travelcard
- SSR/OPR/SOP -> Super Off Peak Return Super non-peak return ticket
- SSS/OPS-Super Off Peak Single One-way ticket
- OPD/GDS/PDS/SWS -> Super Off Peak Day Single One-way ticket for non-peak hours on the designated day
- SCO/PDR/C1R/CBA/GDR/SRR -> Super Off Peak Day Return round-trip ticket for non-peak hours on super designated days
- STO/WRE/WDT -> Super Off Peak Day Travelcard
- 7DS -> 7 Day Season
- 7TS -> 7 Day Travelcard
First Class (First)
- FOR/GFR-First Open Return -> Anytime First Return unlimited return ticket for first class
- FOS/GFS- First Open Single -> Anytime First Single unlimited ticket
- FDS-First Day Single -> Anytime Day First Single unlimited ticket
- FDR-First Day Return -> Anytime Day First Returns
- FDT-First Day Travelcard -> Anytime Day First Travelcard First-class first-class non-peak travel card
- FSR/BFR/SFR -> First Off Peak Return -> Super Off Peak Return Super First Class Round-trip ticket during non-peak hours
- FSS/BFS -> First Off Peak Single non-peak period one-way ticket
- FSO -> First Super Off Peak Day Return round trip ticket for super first class during non-peak hours
- FCD/FCR/GE1-> Firs
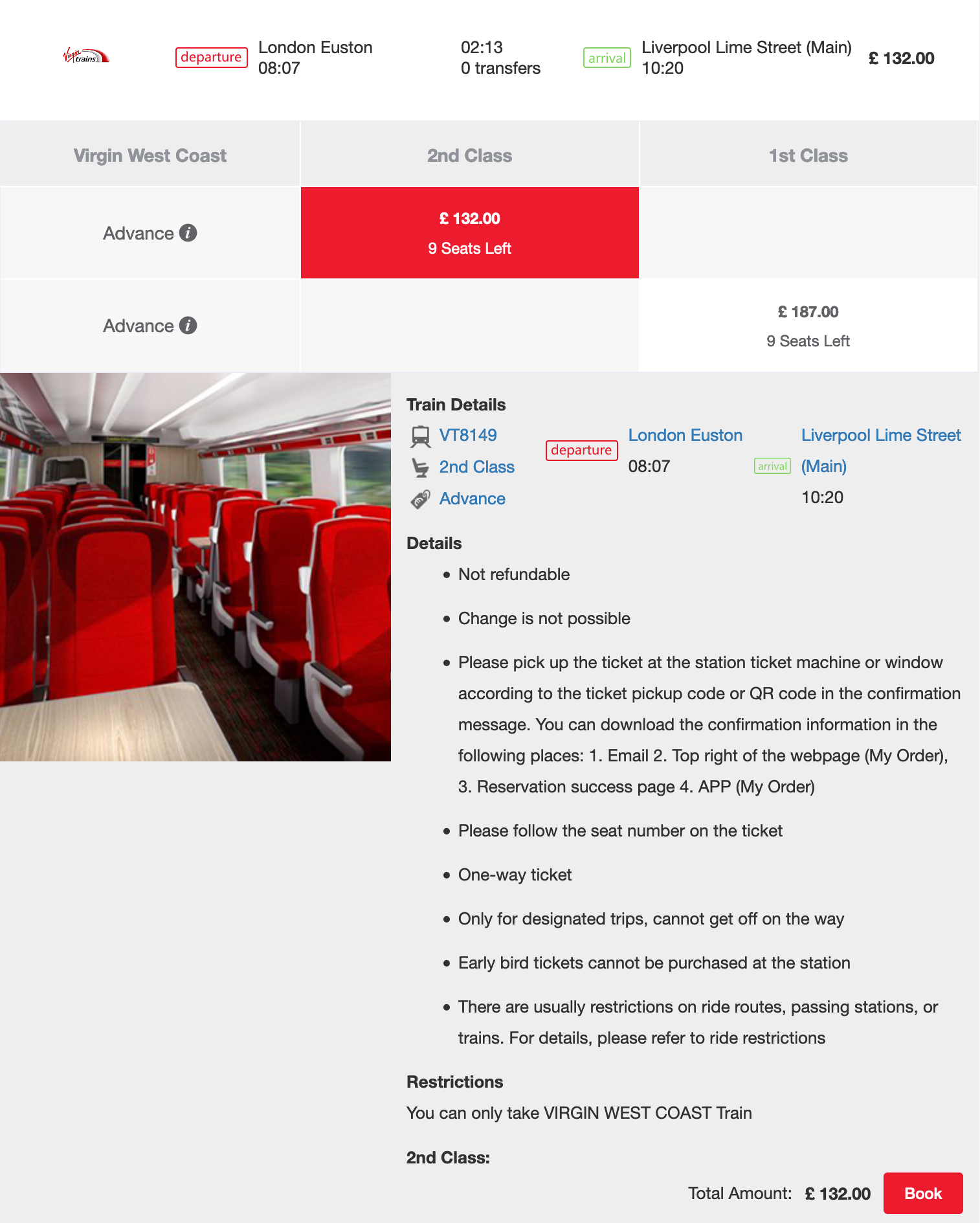
Advance Ticket
Early bird ticket from London Euston to Manchester Piccadilly

Early Bird Ticket Only Single Ticket. Each Advance ticket has a limited number, and not all trains have early bird tickets. Early bird tickets must be purchased before departure. You can book up to 90 days in advance.
Booking deadlines vary; the day before the trip is usually 18:00 or 23:59, although more and more train companies (including Northern, Virgin Trains, TransPennine Express, Greater Anglia, East Midlands Trains and CrossCountry) are also starting now Advance tickets are sold on the day of departure.
You can directly select the station time in G2Rail or xmove App and check the early bird ticket price and remaining ticket amount.
When travelling with Advance tickets, you must take the booked train to travel the entire distance between the origin and destination of the ticket. If you do not comply with this requirement, your Advance fare will no longer have any value and will neither refund the ticket nor upgrade or overtake. Instead, you need to buy a new ticket for the journey. The tickets you can use depend on the specific situation as follows:
If your pre-sale ticket matches the date of travel and you have complied with the train company or route restrictions shown on the ticket:
- You can buy the cheapest Anytime or Off-Peak one-way (or, depending on your choice, return) fares that can be used for your journey, these fares can be found at the station reservation before boarding.
- If your pre-sale tickets have different dates, or you take the wrong train company or route, you may be considered as a ticketless ride. Depending on the train company you are traveling and whether you have the opportunity to pay before boarding, this may be a full Anytime fare.
Ladder of early bird ticket
Early bird fares for specific journeys are usually offered at fixed price levels. As the cheaper grade "Sold Out" (that is, its quota is used up), more expensive grades will be sold. The number of available floors can vary greatly depending on the journey and the train company involved. For example, the standard cabins in Sheffield to London have 17 different advance price levels, while Holyhead to Liverpool have only one floor. When querying the British Railways on the G2Rail website, the type of Advance ticket remaining for each bus and the number of remaining seats will be displayed.
Early Bird Ticket Limit (Advance Quota)
As we all know, early bird fares are subject to quota control according to the reservation system, and it is important to book the cheapest fare as soon as possible after the reservation is opened. Many travelers are not clear about the rules for early bird ticket quotas. It is generally believed that there is a fixed prepayment quota for each price class between each pair of origin and destination stations, but in reality the quota mechanism is more complicated than this.
The itinerary of each train offering early bird fares is divided into sections, corresponding to the train's call point. For example, a train from Edinburgh to London King Cross station may have 4 sections:
- Edinburgh to Newcastle
- Newcastle to York
- York to Peterborough
- Petersburg to London
For Edinburgh to London Early Bird fares for a specific price class available through the train, a quota for that price class must be provided for each part of the journey. Even if only one sub-segment has been used up, the advance payment for the entire journey at this level cannot be provided. Instead, the booking engine will provide the lowest-priced early bird ticket level, and quotas are available for each section.
Therefore, if many people travel between Newcastle and York one day, they may “exhaust” all the cheapest quotas on their journey. This will affect not only passengers traveling between Newcastle and York, but also those who may travel on the journey. E.g. Even the sections from Edinburgh to Newcastle, York to Peterburg, and Peterborough to London can still get the cheapest prepayment from Edinburgh to Kings Crossroads.
The result of this is the "weak link" effect: if there are cheap quotas available for each part of the journey, then cheap prepayments are only applicable for the entire journey-if not, you can only sell the pass High price early bird ticket.
The cheapest quotas for the trips closest to the main population center will usually be exhausted quickly, resulting in only expensive progress available for longer trips, including two "weakest links". A good example is the CrossCountry journey from Cambridge to Birmingham. Early bird tickets between Leicester and Birmingham are very popular, and the cheapest tier quotas will soon be depleted-usually there are still many cheap quotas for journeys east of Leicester. In this case, buy a cheaper prepayment from Cambridge to Leicester and combine it with a higher level forward or off-peak single, for the last journey between Leicester and Birmingham, Prices will be very different. Starting from Cambridge, you can save higher prepaid prices.
Seat reservation and quota
In order to explain some further know-how related to early bird fares, it is necessary to briefly summarize the mechanism for implementing quotas. The reservation system enforces the early bird ticket quota by attempting to reserve seats on the relevant train. This is done in a very direct way:
For each train in the itinerary, the reservation system first asks "Is it possible to reserve a seat on this train?" (This information is stored as part of the schedule)
If it is, the reservation system is then connected to the national reservation system, and for each advance price class (ie, ticket type), starting from the cheapest, it asks "Can I use this ticket class to reserve seats for these journey segments?"
If a given train has a quota available for that ticket type (ie price class) for each journey segment, the seat reservation is successful and the early bird fare has been successfully booked at the cheapest possible level.
The fact that booking early bird fares is intrinsically linked to booking seats can have many complications.
Ticket Restriction (Route Restriction)
Advance ticket for second class with route restrictions (VTEC trains & connections)

Advance ticket is always restricted to the train company or the available route (Route Restriction). This is printed on the ticket under the route-but from the passenger's point of view, under normal circumstances, the information is superfluous, because the early bird ticket is only valid on certain reserved trains!
However, two situations in which train companies or route restrictions are related to passengers are determining the appropriate transfer itinerary for multiple journeys, and determining which trains can be used in the event of delays that cause missed reservations. Therefore need to introduce here:
Early bird ticket routes or train company restrictions usually appear in one of the following three forms:
- TOC ONLY-This ticket can only be used for trains operated by TOC.
- Passing station (AP STATION)-The train used in the journey must pass the indicated station. The train does not need to stop at the station, it can only pass. There may also be two stops, in which case the following cars must pass through the two stops.
- TOC & CONNECTIONS-This ticket can be used on the train operated by the TOC shown, or on the appropriate transfer train shown on the valid travel route.
Route Restrictions
Many tickets limit the routes you may or may not use. These are always printed at the bottom of the ticket under "Route". If it is ANY PERMITTED, you can take any route allowed by NRCoT or the route guide (see below-route). Some ticket restrictions are DIRECT. This meaning is ambiguous. However, one explanation is that the only allowed route is by train or the route that follows the shortest route rule.
If the route is VIA one or more stations, your trip must pass through these stations, although the train does not need to stop there.
If the route does not pass through one or more stations (NOT VIA), you can take a train that does not pass through that station, and you must follow the allowed route.
If you wish to travel on a permitted route that is not permitted by your ticket, you need to be authorized to travel on your preferred route.
Train Operating Company (TOC) Restrictions
Some tickets restrict the trains you can travel through the TOC. In this case, the name of the TOC you may or may not use must be printed on the ticket, although sometimes the abbreviation is printed on the ticket. If you have any questions, please contact our customer service.
For example, "WM TRAINS ONLY" train tickets can be used only on trains operated by West Midlands Trains (regardless of the route brand). If you try to use it on another operator's train, you will be charged Anytime single fare as if you were traveling without a ticket, or you may receive a fine.
Including the multi-segment transfers
As mentioned above, early bird tickets are only valid on the reserved train. When there is only one journey in the journey, that is, the whole journey is on a train, the meaning of booking a train is clear and clear. However, sometimes the journey on the early bird ticket also involves one or more connecting trains.
A common problem is:
I have a TOC & Connections ticket. Are there any rules about trains that can be used for my transfer?
The general rule is that if reservations have been issued for transfer trains, they are also counted as reserved trains. They must be used. If any other train is used, the early bird ticket is invalid.
On the other hand, if there is no reservation for the connected train (because it does not provide reservations), you can use other connected trains freely as long as the following conditions are met:
- When transferring between trains, you still allow the shortest connection time at the relevant station. (The shortest connection time for all stations can be viewed on brtimes.com-enter it in the desired radio station, select "Radio Information Only" and click search. When making a journey across London via the subway, the minimum connection time is the sum of arrivals and The time to leave the station plus the transfer time across London.)
- Reservations are not available for alternative connecting trains. (This can be checked by checking the relevant departure place or arriving at brtimes.com-any train that has neither a diamond symbol nor an R symbol cannot be reserved.)
##### Barred Journey
The quota mechanism explained so far covers many unusual phenomena regarding the availability of early bird fares. However, even if there are theoretically quotas available, train companies will have more policies to reduce early availability.
These mechanisms are called Barred Journeys and involve blocking or reducing quotas for journeys that begin and/or end at specific stations. This is usually just to increase revenue, not to control the demand for services.
For example, East Coast competes with Virgin Trains West Coast from London to Edinburgh. Virgin usually has a lot of surplus capacity on their trains, and offers cheap advance tickets from London Euston to Edinburgh through the West Coast main line to try to fill the gap. The East Coast needs to compete with this, so it offers a full range of cheap and low-cost pre-sale tickets from London King’s Cross to Edinburgh.
On the other hand, the main competitor from York to Edinburgh’s east coast is CrossCountry. Their trains are often overcrowded, they do not provide so many cheap pre-sale tickets, so there is no need to compete so fiercely on the East Coast. To make the most of this situation, they may set a limit on the cheapest level for the journey from York to Edinburgh. As a result, passengers trying to book from York to Edinburgh may only face higher-level pre-sale tickets, even if there are still cheap early bird ticket quotas available on the train-or it may be bookings for passenger journeys from Edinburgh to London.
Unfortunately, although the ticket from Edinburgh to London may be cheaper than the ticket from Edinburgh to York, there is no easy way to bypass this competition-based pricing because early bird ticket fares do not allow for a break.
&CONNECTIONS Connection (&Connections Advance)
Most long-distance train companies provide prepaid fares for travel, and most of these trips are done on their services, but at one or both ends of the journey, the local train company's connection distance is relatively short. This is called &Connections Advance.
When the connection service also allows seat reservations, this type of ticket has complications. The booking engine usually does not know which is the "primary" service and which is the "connected" service. Therefore, if the connection service also provides seat reservations, the reservation engine must try to book on the train to ensure that the prepaid fare on the train is not subject to quota control (this is usually rare for the connection service, although the long-distance city International TOC may set a zero quota for each other's prepayments, for example, to avoid using "XC and CONNECTIONS" prepayments on Virgin Services.
Break of Journey
One advantage of rail travel is that you can usually stop somewhere on the journey (interrupt the trip), do things like go shopping, make friends or sightseeing, and then resume the trip at leisure. Sometimes it is convenient to start your journey at a station somewhere on the route instead of the starting point on the ticket (starting from a short position) or ending early (at the end).
However, some tickets restrict whether you can break your journey.
Definition of stroke interruption
The current National Railway Travel Conditions (NRCoT) does not define the concept of "trip interruption", but Section 16 of the former National Railway Transport Conditions (NRCoC) defines a trip interruption as: "If you leave the train company or the railway after you start the journey Service company station."
However, it also defines the following exception as not a break of journey (Break of Journey):
- Join a train at another station, or
- If you cannot reasonably complete the journey in one day, then stay overnight, or
- Follow any instructions from train company employees.
Therefore, if you have to go to another station to continue driving, you won’t get a permit from a staff member (for example, to smoke a cigarette) because there are no more trains to reach your destination.
If you just want to use the station facilities (such as shops, bars, ticket offices, etc.), you will not disrupt your journey. Sometimes this will require you to cross obstacles, but this does not mean that you are breaking your journey.
Types of trip interruption
Breaking and Resuming Later
Unless your train ticket restricts the interruption of the journey (see Restrictions), you can leave the train on the permitted route at any station during the validity period of the ticket. (Please note that if your ticket is allowed to be restricted because of a through train, you cannot do so).
There is no limit to the number of times your journey can be interrupted, except for how long the ticket is valid.
If you hold a ticket valid for more than one day, your trip interruption can also include one or more nights, provided that you continue the trip while the ticket is still valid.
Some tickets that are valid for only one day can also be allowed to stay overnight. For example, the restriction code on the external part of an off-peak ticket states "If the journey cannot be completed at this time, you can use the ticket to continue the next day's journey...". Other conditions may apply, detailed information about the restriction code.
End the trip early
If your ticket allows for a break, NRCoT specifically allows you to start and/or end your journey. Article 16.4 provides:
"In general, as long as the ticket you hold is valid for the train you want to use, you can start at any intermediate station, or rest and resume the journey (in either direction of returning the ticket). This may not be
Some situations where an indirect route is taken through services. You can also end your journey (in either direction of the return ticket) before the destination shown on the ticket. "
You must ensure that any platform you choose to start or end is on the allowed route from the origin of the ticket to the destination.
Because the fare is priced and depends on your journey and the route you want, some money may be saved at the beginning or end.
London Underground (DLR)
You can "break the transfer journey" and exit any intermediate subway station, for example: if you are traveling between Victoria and Euston, you can take the Oxford Circus exit. However, if you subsequently wish to continue to take the subway, you must purchase another ticket.
Constraint for Stroke Interruption
Some tickets restrict the right to interrupt the trip, while other tickets are free to allow a break. If you hold ANYTIME or season tickets, there are no restrictions. For other tickets, you will find any restrictions defined by the restriction code.
Early bird tickets (Advance) will never let you break your journey, or start or end it at the middle station.
Occasionally Off Peak and Super Off Peak tickets may limit the interruption of the trip on the departure journey, but it is allowed when returning, so it is important to study the restriction code carefully. It may also be prudent to print it out on your journey.
Trip interruption permission
If the staff of the train company instructs you (or allows you) to exit the station, it will not be treated as an interruption of the trip. For example, if you are waiting for a connecting train, you can leave the station while waiting. Although you do not have automatic rights, you will find that most staff will allow such reasonable requests.
Split Ticketing
Through tickets can be purchased from almost anywhere to any other place on the railway network. However, sometimes it may be more cost-effective to purchase more than one ticket to complete the journey. The reasons may include:
- Save money through fares
- Interrupt your journey, and direct door tickets are not allowed to interrupt the journey
- Circular journey
- Change plan when traveling
- Bypass restrictive non-peak conditions
- Take a route that is not an allowed route
- No suitable fare
Reasons for cutting tickets to save money
Most tickets are priced by specific train operating companies (TOC). Some TOC pricing policies keep ticket prices low, while other TOCs try to increase prices as much as possible each year.
If the pass is priced according to the price of the TOC ticket of the expensive train company, but you can buy two tickets for the same trip, and these fares are priced by the cheaper TOC, you can save money.
In addition, some regions have local fare policies to keep prices down and some tickets (especially day tickets are often cheaper than the period fare) may not be suitable for long-distance travel.
How to find the cut ticket
You need to do some research to find the best segmentation set. Using the source of fare information, try to check the fare of each station where the train stops. Then find the best combination.
A website approved by the National Railways will sell fare combinations, such as trainsplit.
Cut early bird ticket
Split Advance tickets are often cheaper. This may be because the quota for long-distance travel has been used up, but it can still be used for short-distance travel, or because booking fares to London are often cheaper (if booked in advance), the combination of round trips to London may be of great value.
Remember, you must take the booking service. However, if you encounter a delay on the route, you can use the later transfer service even on the ticket cut.
Rights of passengers who cut tickets
When using ticket cuts, you are entitled to the same rights as non-stop passengers, namely:
- If the last train goes home due to delays in the railway network, any related TOC must help you go home or arrange overnight accommodation for you, but you must ensure that the shortest connection time is observed. We recommend that you print the itinerary, as this will ensure that your connection is valid.
- If your train is delayed, you have the right to receive compensation for the delay of your operator's full journey. This usually uses a delayed repayment scheme, but some older TOCs have their own schemes.
- When using one or more early bird tickets, if you are delayed on the route, you can use the next available service. We recommend that you stamp at the booking office to confirm the delay, but this is not absolutely necessary
Ticket types and discount tickets
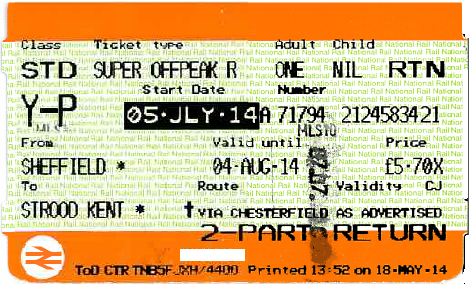
Paper ticket
Many train tickets are printed on orange cards the size of credit cards. The ticket may have multiple parts. For example, the return ticket will include the round-trip ticket and the return part. The Advance ticket will be accompanied by a ticket and one or more discount coupons.
smart card
Smart cards are contactless cards, a way to store tickets or credit cards. Some smart cards can be recharged with pay-as-you-go (PAYG), just like using PAYG phones. Alternatively, you can store products by purchasing products in advance, such as season tickets and travel cards.
London Oyster Card

The most commonly used smart card on the railway is the Oyster Card. With an Oyster card, you can store a Travelcard season pass or credit card to use Pay at any time. Oyster is a transportation card accepted on most public transport in London. It can be used for bus, tram, subway, DLR and national rail services. You can buy it at tube stations, London Overground stations, some national railway stations, Oyster Ticket Stops. A refundable deposit of GBP 5 is required. More and more operators are introducing smart cards into some of their services, mainly as part of new franchise requirements.
Although not every train operator along the route where a smart card can be used can equip the conductor with a smart card reader, the ticket is as valid as a paper ticket unless otherwise stated otherwise.
Oyster Card
Oyster is a cashless payment system accepted on most public transport in Greater London. Oyster cards can store up to £90 in cash payments, season cards for travel cards and national rail discount cards. It can be used for bus, tram, subway, DLR and national rail services. You can buy it at tube stations, London Overground stations, some national railway stations, Oyster Ticket Stops (shops). A refundable deposit of GBP 5 is required.
When the card is touched (laid flat) on the card reader, each Oyster card communicates with the Oyster card reader (verifier). The card does not require physical contact with the card reader, because it uses short-range wireless, so it can communicate with the ticket holder through the wallet.
On the bus, you must touch the bus while boarding, and on the tram, you must touch the station reader before boarding. You must not touch the bus or tram. On pipelines, DLRs and national railways, you must touch at the beginning of the journey and at the end in order to charge the correct fare. With the gate running, if valid, your card will open the gate. If the gates are not running, you must still be able to touch or make them, if they are locked open, or a yellow verifier that can be used to enter or exit. A valid card will change the orange light to green, while the adult card will emit a beep, or the child card will emit more than two beeps. If there is a problem, the light will turn red and you will beep twice.
Oyster system charges every time. One-way travel can include national railways, subways, mixed travel on the ground and DLR, or separate other modes, such as buses, as long as the gap between the parts is reasonable.
Oyster Card Out of Station Interchange (OSI)
Sometimes you can switch between track/pipe mode and punch in (for example, between National Rail and Greenwich DLR), but usually, punching is necessary. The system is programmed with many such exchanges, and these journeys are combined to form a single journey. The time allowed depends on the distance involved and the frequency of the next train.
Oyster control center can set and delete emergency OSI in real time to meet short-term site shutdown and some weekend engineering work. EOSI will be set up at multiple sites and allow exchanges between any site within 30 minutes, including re-entry to the same site.
Each zone combination allows the longest travel time. Sometimes, OSI combines multiple independent journeys into one journey, and then may exceed the maximum journey time, so the maximum fare is charged and not included in the daily limit. If you have made many journeys, the gap between them is very small, and this situation is more likely to happen. You can prevent OSI from happening by touching the bus between the track branches, but please note that for user payment, you will need to pay the bus fee.
Print @ Home Ticket
Some operators provide Print@Home tickets. This is when you buy a ticket online, under normal circumstances, you can print a PDF on an A4 paper instead of sending the ticket home or picking it up at the station ticket machine. When traveling on a Print@Home ticket, you need to specify the name of the main traveler and select the form of identification that you must show on the train to prove that they are traveling, such as a credit card.
Hand ticket (m-ticket)
Most train companies have their own mobile phone applications, such as iPhone, Windows Phone, Android and Blackberry. These applications are usually very similar because they are made by the same company Masabi. Using these apps, you can buy tickets. Normally, you will be asked to collect your ticket from the self-service ticket machine at the station, but sometimes you will be sold a mobile ticket.
M-ticket stands for mobile ticket. Hand ticket is divided into two parts: travel details and barcode. The travel details contain information about your journey, so you can be sure to take the correct train. The barcode can be scanned by the train or station staff to check if you have a valid ticket. You need to activate your m-ticket on the day of travel before the trip.
Although many applications are very similar, you usually need to book a ticket from the application of the train company you travel to take advantage of the mobile ticket. In addition, usually only early bird tickets can be used as mobile tickets.
Multi-Journey Ticket
If you travel regularly, multi-trip tickets can save you the cost of buying a daily one-way or return ticket. There are many multi-range travel products to meet different travel modes.
If you take a certain route regularly, the Season Ticket may be the best for your needs. In addition to the weekly season ticket (Weekly Season Ticket), you can have a season ticket at any time between one month and 12 months. In most cases, the price of an annual season pass is the same as 40 weekly season passes, which can save a lot of costs.
If you travel a lot outside the morning rush hour in a certain area, you may have a Day Ranger ticket or a Rover ticket, allowing you to make unlimited trips in your area. These tickets are cost-effective because most day rangers and wanderers offer a 75% discount, effectively providing discounts for off-peak fares.
If you need to travel multiple times in London, Travelcards and Oyster PAYG (Oyster Card Pay-As-You-Go) may be your best choice. The travel card provides unlimited travel on the National Rail, London Underground, Docklands Light Railway, Tramlink and London bus services in the London area. During different days of the year, there are A variety of different area combinations. If you need to travel in London but do not have enough journeys to guarantee a travel card, the Oyster PAYG card is the ideal choice. They save a lot of money than cash fares.
Day Ranger Ticket (Day Ranger)
A one-day day ranger ticket allows the holder to make an unlimited number of days of travel within the specified area. Some days ranger products have other names, such as West Yorkshire DayRover, Island Liner (Day Rover), East Yorkshire Round Robin, (Merseytravel) Saveaway, Ride Cornwall, etc.
Rover Ticket (Rover)
The Rover ticket allows the holder to make unlimited trips in the designated area for three days or more.
There are two different forms of Rover products: Consecutive Rovers and Flexi Rovers.
The continuous vagabond ticket is valid continuously from the first day to the last day of the validity period (for example, the 7-day northwest vagrant ticket). The flexible vagrant ticket is valid for the number of valid days on the first day of the validity period (for example, an optional four-day vagrant ticket for eight days in the northwest), not every day within its validity period.
The product with the widest coverage of the national railway network in the UK is All Line Rover, which has two versions: 7-day and 14-day wanderer.
The Scottish Free Travel Pass provides complete coverage of Scotland (8 days 4 days or 15 days 8 days), while Exploring Wales Flexipass gives you complete free travel on buses in Wales for 8 consecutive days, 4 of which include rail services.
London Travelcards
A day trip Travelcard (A Day Travelcard) provides unlimited travel within the London National Rail, London Underground, Docklands Light Railway (DLR), Tramlink and London transportation services. The Inboundary Day Travelcard is only valid in the zone, while the Outboundary Day Travelcard also includes a return trip from the departure station (which will be outside the zone) to the zone zone.
The Inboundary Travel Card can be used in Zone 1-2, Zone 1-4 or Zone 1-6.
Map of London zones
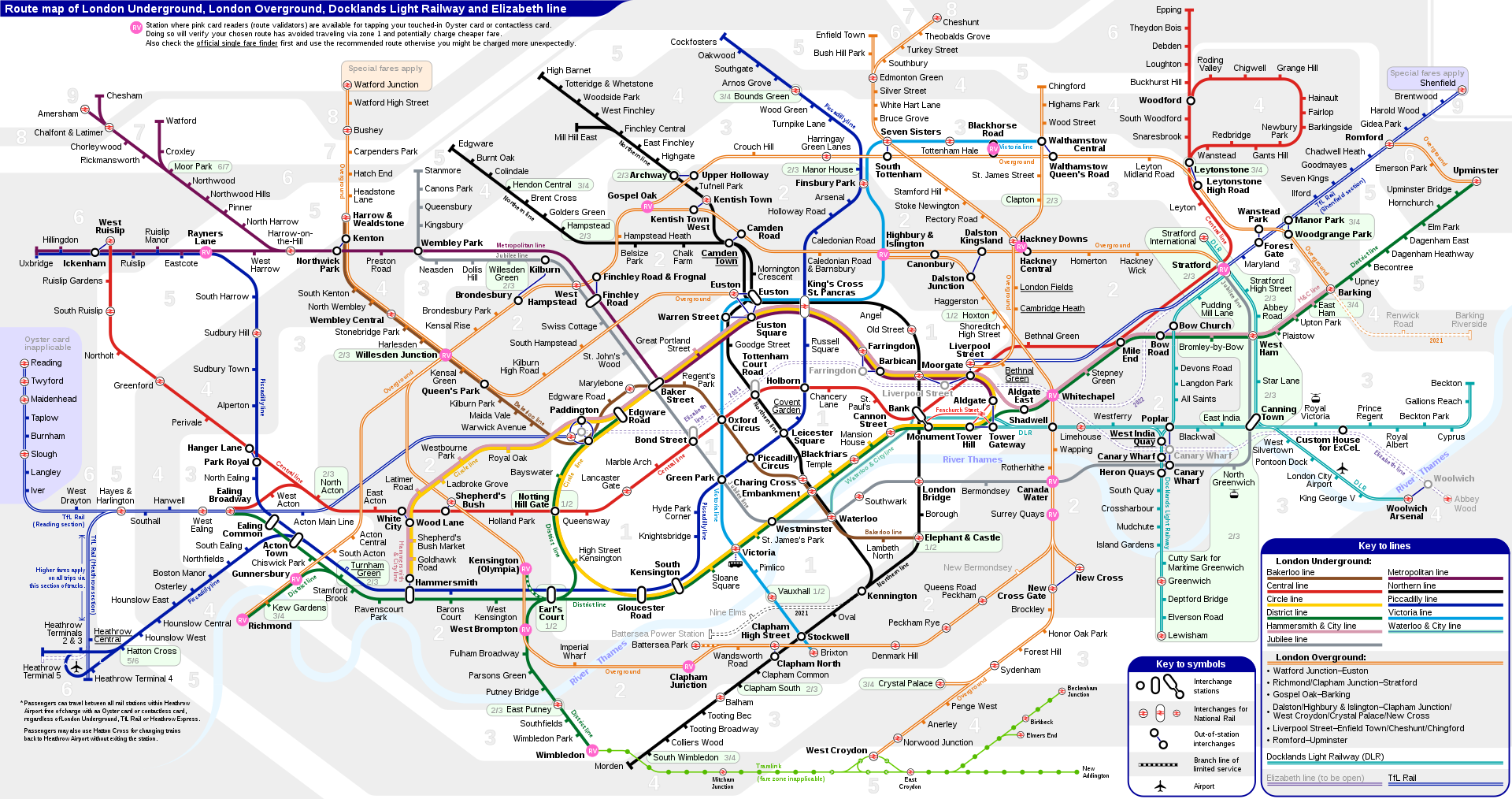
Outboundary day Travelcards are limited to unlimited travel within zones 1-6. When the origin is in area 7-9 or one of WATFORD JUNCTION, BROXBOURNE, BRENTWOOD or SHENFIELD, special arrangements apply.
The daily travel card is valid on all London Transport Bureau bus services, regardless of the area they cover. One day Travelcard is valid on the entire Tramlink network, if it is valid in any zone of zone 3, zone 4, zone 5 or zone 6.
Family Travelcards
The following train companies offer discounted (off-peak) family travel cards:
- c2c;
- Chiltern Railways;
- First Great Western (selected journeys only);
- Greater Anglia;
- London Midland;
- Southern.
The maximum group size is 2 adults and 4 children, and each group must include at least one adult and one child. Children take a one-way fare of £1, except in Greater Anglia, where they need to pay a one-way fare of £2, and at Chiltern Railway, they pay a one-way fare of £3. The group must always travel together.
Family travel cards no longer enjoy discounts on railway cards. For some routes, group tickets (such as GroupSave) may be more cost-effective.
Discount card
There are many Railcards offering discount travel. Each railway card has its own qualification criteria and conditions of use. In addition, the railway card in the local area can be used by residents of the selected area.
For travel within the London area, you can use certain types of rail cards to obtain off-peak Oyster Pay-As-You-Go and off-peak daily fares (off-peak daily) discount. The discount entitlement must be manually recharged to your Oyster card.
The discount cards are:
- 16-25 Railcard
- Senior Railcard
- Disabled Persons Railcard
- Family & Friends Railcard
- Armed Forces Railcard
- Network Railcard
- Local Railcards
- Cambrian Railcard
- Cotswold Line Railcard
- Dales Railcard
- Derbyshire B_Line
- Devon and Cornwall Railcard
- easitCRAWLEY, easitEAST SURREY, easitTHAMES VALLEY PARK
- ENCTS Trial in West of England
- Esk Valley Railcard
- Gatwick Express Partners' Card
- Gatwick Express Staff Discount Card
- Heart of Wales Line Railcard
- Highland Railcard
- Pembrokeshire Railcard
- Scottish Youth Railcard
- Student Connect
- Unizone
- Valleys Senior Railcard
- Valleys Student Railcard
Combination ticket
PlusBus
PlusBus is an add-on component of rail tickets (issued as separate coupons), allowing designated companies in one of hundreds of designated areas in the UK to ride the bus service without restrictions. PlusBus is managed by Journey Solutions. PlusBus is usually suitable for most (if not all) companies operating in designated areas, and can be used as a day ticket for all locations.
Compared with specific or all operator day or season tickets of the relevant operators, PlusBus day and season tickets are usually excellent value for money. However, if you only travel once, singles (sometimes returning) are usually more valuable than PlusBus day tickets. PlusBus is only applicable to the ticket origin and/or destination station, not the intermediate station.
Bus & Tram links
One-way or return combination tickets by train, bus or tram can travel to and from many non-railway service destinations. For some of these tickets, non-rail service locations are only available as destinations (such as Leeds Bradford Airport), while in other cases, non-rail service locations can also be used as starting points (such as Whitby (Whitby Bus).
London Underground, Docklands Light Railway (DLR)
One-way and round-trip train tickets for National Rail journeys that require customers to travel between two different train stations in London usually include the subway and/or DLR required to enable customers to make this transfer.
Depending on the itinerary, you can enter the following stations of the London Underground and DLR systems by ticket: Aldgate, Amersham, Baker Street, Balham, Bank, Barking, Blackfriars, Blackhorse Road, Brixton, Canada Water, Cannon Street, Charing Cross, Ealing Broadway, Edgware Road , Elephant & Castle, Embankment, Euston, Euston Square, Farringdon, Finsbury Park, Greenwich, Highbury & Islington, Kensington (Olympia), Kentish Town, King's Cross St. Pancras, Lancaster Gate, Lewisham, Limehouse, Liverpool Street, London Bridge, Marylebone, Moorgate, Old Street, Paddington, Queen's Park, Richmond, Seven Sisters, Shadwell, Shepherd's Bush, Southwark, Stratford, Stratford International, Tottenham Hale, Tower Hill, Upminster, Vauxhall, Victoria, Walthamstow Central, Waterloo, West Brompton, West Ham, West Hampstead, Whitechapel, Wimbledon, Woolwich Arsenal.
Allow short-distance transfers at any subway station in Zone 1 or any intermediate underground/DLR station on a reasonable route. If you choose to do so, the train ticket does not allow further subway/DLR travel; if you wish to continue using the subway/DLR, you will need to purchase additional tickets. If you do this, it is unlikely to exit the gate by ticket, and you need to ask the station staff for assistance.
† (Cross) symbol appears at the beginning of the "route" on the ticket, indicating that it has been coded to enter the underground/DLR ticket gate. The absence of this symbol does not necessarily mean that your train ticket is not suitable for subway travel.
When traveling through London, but if you plan your own journey, you may need to consider the shortest transfer time, as shown in the figure below. In many cases, the transfer can be completed in a much shorter time than the minimum transfer time.
Through single/return tickets
One-way or round-trip tickets can be purchased from many train stations to the subway or DLR station, although it is usually cheaper to purchase tickets for the national railway part separately and use Oyster Pay As You Go for the subway and DLR parts. These tickets need to cover all the areas that your journey will travel through Underground.


























